|
Roman Client Kingdoms In Britain
The Roman client kingdoms in Britain were native tribes which chose to align themselves with the Roman Empire because they saw it as the best option for self-preservation or for protection from other hostile tribes. Alternatively, the Romans created (or enlisted) some client kingdoms when they felt influence without direct rule was desirable. Client kingdoms were ruled by client kings. In Latin these kings were referred to as ''rex sociusque et amicus'', which translates to "king, ally, and friend". The type of relationships between client kingdoms and Rome was reliant on the individual circumstances in each kingdom. The beginnings of the system are to be found in Caesar's re-enthroning of Mandubracius as king of the Trinovantes, who had been dethroned by Cassivellaunus and then aided Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BC. The system further developed in the following hundred years, particularly under Augustus's influence, so that by the time of the Roman invasion in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britain
Britain most often refers to: * Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales * The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland. * The realm of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, comprising the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies, and British Overseas Territories. Britain may also refer to: Places * British Isles, an archipelago comprising Great Britain, Ireland and many other smaller islands * British Islands, the UK, Channel Islands and Isle of Man collectively * Roman Britain, a Roman province corresponding roughly to modern-day England and Wales * Historical predecessors to the present-day United Kingdom: ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707 to 1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801 to 1922) * Britain (place name) * Britain, Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States People * Calvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
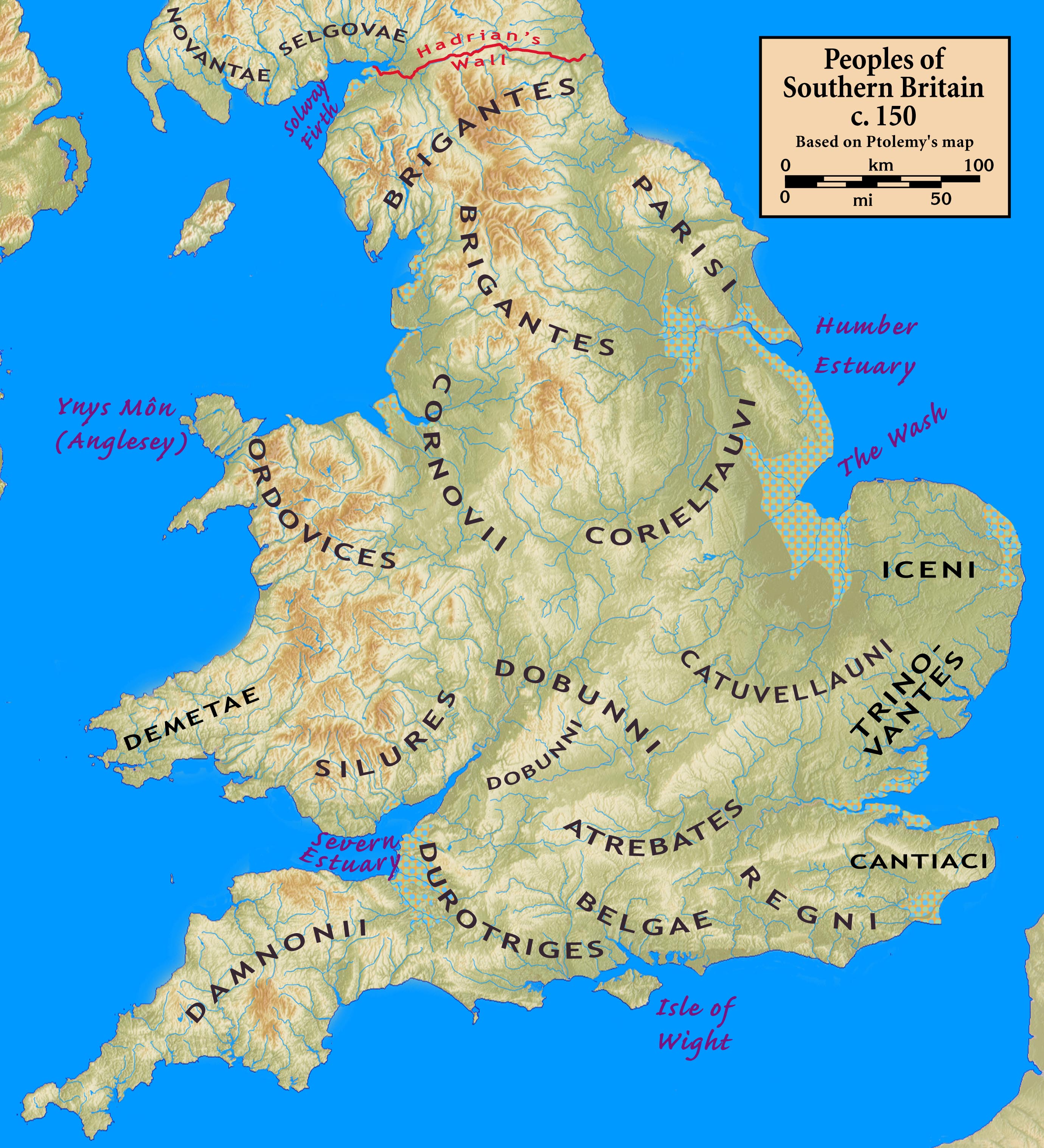
Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geographer Ptolemy named the Brigantes as a people in Ireland also, where they could be found around what is now counties Wexford, Kilkenny and Waterford, while another people named '' Brigantii'' is mentioned by Strabo as a sub-tribe of the Vindelici in the region of the Alps. Within Britain, the territory which the Brigantes inhabited was bordered by that of four other peoples: the Carvetii in the northwest, the Parisii to the east and, to the south, the Corieltauvi and the Cornovii. To the north was the territory of the Votadini, which straddled the present day border between England and Scotland. Etymology The name ( in Ancient Greek) shares the same Proto-Celtic root as the goddess Brigantia, meaning 'high, elevated', and it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Ostorius Scapula
Publius Ostorius Scapula, modern statue on the terrace of the Roman Baths (Bath) Publius Ostorius Scapula (died 52) was a Roman statesman and general who governed Britain from 47 until his death, and was responsible for the defeat and capture of Caratacus. Early life Publius Ostorius Scapula was the son of a Publius and likely the nephew of Quintus Ostorius Scapula, the first joint commander of the Praetorian Guard appointed by Augustus and later prefect of Egypt. The Quintus Ostorius Scapula who was consul in 41 AD was probably his brother or cousin. Career Nothing is known of his early career. He was suffect consul, probably in 46. In the winter of 47 he was appointed the second governor of Roman Britain by the emperor Claudius, succeeding Aulus Plautius. The south and east of the island was securely occupied and alliances had been made with tribes outside the Roman-controlled area, but other tribes continued to resist. Believing a new governor would be reluctant to ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caratacus
Caratacus was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the Catuvellauni tribe, who resisted the Roman conquest of Britain. Before the Roman invasion, Caratacus is associated with the expansion of his tribe's territory. His apparent success led to Roman invasion, nominally in support of his defeated enemies. He resisted the Romans for almost a decade, using guerrilla warfare, but when he offered a set-piece battle he was defeated by Roman forces. After defeat he fled to the territory of Queen Cartimandua, who captured him and handed him over to the Romans. He was sentenced to death but made a speech before his execution that persuaded the Emperor Claudius to spare him. Caratacus' speech to Claudius has been a popular subject in visual art. Name Caratacus' name appears as both ''Caratacus'' and ''Caractacus'' in manuscripts of Tacitus, and as ''Καράτακος'' and ''Καρτάκης'' in manuscripts of Dio. Older reference works tend to favour the spelling "Caractacus", coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunobeline
Cunobeline or Cunobelin (Common Brittonic: *''Cunobelinos'', "Dog-Strong"), also known by his name's Latin form , was a king in pre-Roman Britain from about to about Malcolm Todd (2004)"Cunobelinus [Cymbeline/nowiki> (d. ''c''. AD 40), king in southern Britain"">/nowiki>Cymbeline">"Cunobelinus [Cymbeline/nowiki> (d. ''c''. AD 40), king in southern Britain" ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography''. Retrieved 28 December 2017. He is mentioned in passing by the classical historians Suetonius and Dio Cassius, and many coins bearing his inscription have been found. He controlled a substantial portion of southeastern Britain, including the territories of the Catuvellauni and the [ rinovantes, and he was called " King of the Britons" (''Britannorum rex'') by Suetonius. Cunobeline may have been a client king of Rome, based on the images and legends appearing on his coins. Cunobeline appears in British legend as Cynfelyn ( Welsh), Kymbelinus (medieval Latin) or Cymbeline, as in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England Celtic Tribes - South
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Roman Italy, Italy. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to an illness he suffered when young, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's assassination, at which point he was the last adult male of his family. Despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age Tribes In Britain
The names of the Celtic Iron Age tribes in Britain were recorded by Roman and Greek historians and geographers, especially Ptolemy. Information from the distribution of Celtic coins has also shed light on the extents of the territories of the various groups that occupied the island. Historiography Available evidence seems to indicate that the tribes of the Middle Iron Age tended to group together into larger tribal kingdoms during the Late Iron Age. The Belgae and Atrebates share their names with tribes in France and Belgium, which, together with Caesar's note that Diviciacus of the Suessiones had ruled territory in Britain, suggests that this part of the country might have been conquered and ruled from abroad. The Parisii have also been suggested as having been an immigrant group. Some historians have suggested that it might be possible to distinguish the distributions of different tribes from their pottery assemblages for the Middle Iron Age. However, no names are avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar's Invasions Of Britain
In the course of his Gallic Wars, Julius Caesar invaded Britain twice: in 55 and 54 BC. On the first occasion, Caesar took with him only two legions, and achieved little beyond a landing on the coast of Kent. The second invasion was more substantial, consisting of 800 ships, five legions and 2,000 cavalry. The force was so imposing that the Celtic Britons did not contest Caesar's landing, waiting instead until he began to move inland. Caesar eventually penetrated into Middlesex and crossed the Thames, forcing the British warlord Cassivellaunus to pay tribute to Rome and setting up Mandubracius of the Trinovantes as a client king. The Romans then returned to Gaul without conquering any territory. Caesar included accounts of both invasions in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', which contains the earliest surviving significant eyewitness descriptions of the island's people, culture and geography. This is effectively the start of the written history, or at least the protohistor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumberland
Northumberland ( ) is a ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North East England, on the Anglo-Scottish border, border with Scotland. It is bordered by the North Sea to the east, Tyne and Wear and County Durham to the south, Cumbria to the west, and the Scottish Borders council area to the north. The town of Blyth, Northumberland, Blyth is the largest settlement. Northumberland is the northernmost county in England. The county has an area of and a population of 320,274, making it the least-densely populated county in England. The south-east contains the largest towns: Blyth, Northumberland, Blyth, Cramlington, Ashington, Bedlington, and Morpeth, Northumberland, Morpeth, the last of which is the administrative centre. The remainder of the county is rural, the largest towns being Berwick-upon-Tweed in the far north and Hexham in the south-west. For local government purposes Northumberland is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area. The county Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Celtic Britons, Brittonic people of the British Iron Age, Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and north-east England, extending from the Firth of Forth and around modern Stirling to the River Tyne, including at its peak what are now the Falkirk, Lothian and Scottish Borders, Borders regions and Northumberland. This area was briefly part of the Roman province of ''Roman Britain, Britannia''. The earliest known capital of the Votadini appears to have been the Traprain Law hill fort in East Lothian, until that was abandoned in the early 5th century. They afterwards moved to Din Eidyn (Edinburgh). The name is recorded as ''Votadini'' in classical sources, and as ''Otodini'' on old maps of ancient Roman Britain. Their descendants were the early medieval kingdom known in Old Welsh as ''Gododdin, Guotodin'', and in later Welsh as ''Gododdin'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer State
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between two greater powers, which is demilitarised in the sense of not hosting the armed forces of either power (though it will usually have its own military forces). The invasion of a buffer state by one of the powers surrounding it will often result in war between the powers. Buffer states, when authentically independent, typically pursue a neutralist foreign policy, which distinguishes them from satellite states. The concept of buffer states is part of a theory of the balance of power that entered European strategic and diplomatic thinking in the 18th century. After the First World War, notable examples of buffer states were Poland and Czechoslovakia, situated between major powers such as Germany and the Soviet Union. Lebanon is another si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |