|
Roman Republic (1849)
) , capital = Rome , national_anthem = , common_languages = Italian , government_type = Directorial parliamentary republic , official_languages = Italian French Italian , regional_languages = German , religion = Roman Catholicism , title_leader = Triumvirate , leader1 = , year_leader1 = 1849 , today = , image_coat = Emblem of Roman Republic 1849.svg The Roman Republic ( it, Repubblica Romana) was a short-lived state declared on 9 February 1849, when the government of the Papal States was temporarily replaced by a republican government due to Pope Pius IX's departure to Gaeta. The republic was led by Carlo Armellini, Giuseppe Mazzini, and Aurelio Saffi. Together they formed a triumvirate, a reflection of a form of government during the first century BC crisis of the Roman Republic. One of the major innovations the Republic hoped to achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Scudo
The Roman scudo (plural: ''scudi romani'') was the currency of the Papal States until 1866. It was subdivided into 100 baiocchi (singular: ''baiocco''), each of 5 quattrini (singular: ''quattrino''). Other denominations included the ''grosso'' of 5 baiocchi, the ''carlino'' of baiocchi, the ''giulio'' and ''paoli'' both of 10 baiocchi, the ''testone'' of 30 baiocchi and the ''doppia'' of 3 scudi. History In addition to issues for the Papal States as a whole, the currency was also issued by many of the individual municipalities. In the late 18th century, this included issues from Ancona, Ascoli, Bologna, Civitavecchia, Fano, Fermo, Foligno, Gubbio, Macerata, Matelica, Montalto, Pergola, Perugia, Ronciglione, San Severino, Spoleto, Terni, Tivoli and Viterbo. Uniquely in Bologna the baiocco, also known as the ''bolognino'', was subdivided into 6 quattrini. Between 1798 and 1799, the revolutionary French forces established the Roman Republic, which issued coins denominated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It has had different definitions and interpretations which vary significantly based on historical context and methodological approach. Republicanism may also refer to the non-ideological scientific approach to politics and governance. As the republican thinker and second president of the United States John Adams stated in the introduction to his famous '' A Defense of the Constitutions of Government of the United States of America,'' the "science of politics is the science of social happiness" and a republic is the form of government arrived at when the science of politics is appropriately applied to the creation of a rationally designed government. Rather than being ideological, this approach focuses on applying a scientific methodology to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of The Vatican City
The politics of Vatican City take place in a framework of a theocratic absolute elective monarchy, in which the Pope, religiously speaking, the leader of the Catholic Church and Bishop of Rome, exercises ex officio supreme legislative, executive, and judicial power over the Vatican City (an entity distinct from the Holy See), a rare case of non-hereditary monarchy. The pope is elected in the Conclave, composed of all the cardinal electors which are bishops and archbishops appointed by the pope (now limited to all the cardinals below the age of 80), after the death or resignation of the previous Pope. The Conclave is held in the Sistine Chapel, where all the electors are locked in (Latin: ''cum clave'') until the election for which a two-thirds majority is required. The faithful can follow the results of the polls (usually two in the morning and two in the evening, until election) by a chimney-top, visible from St. Peter's Square: in a stove attached to the chimney are burnt the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellegrino Rossi
Pellegrino Luigi Odoardo Rossi (13 July 1787 – 15 November 1848) was an Italian economist, politician and jurist. He was an important figure of the July Monarchy in France, and the minister of justice in the government of the Papal States, under Pope Pius IX. Biography Rossi was born in Carrara, then under the Duchy of Massa and Carrara. Educated at the University of Pisa and the University of Bologna, he became professor of law at the latter in 1812. In 1815 he gave his support to Joachim Murat and his Neapolitan anti-Austrian expedition: after the latter's fall, he escaped to France, and then proceeded to Geneva, where he began teaching a course of jurisprudence applied to Roman law, the success of which gained him the unusual honour of naturalization as a citizen of Geneva. In 1820 he was elected as a deputy to the cantonal council, and was a member of the diet of 1832; Rossi was entrusted with the task of drawing up a revised constitution, which was known as the ''Pacte Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Law
Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a State (polity), state, namely, the executive (government), executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as the basic rights of citizens and, in federal countries History of the United States Constitution, such as the United States and Provinces of Canada, Canada, the relationship between the central government and state, provincial, or territorial governments. Not all nation states have codified constitutions, though all such states have a ''jus commune'', or law of the land, that may consist of a variety of imperative and consensual rules. These may include custom (law), customary law, Convention (norm), conventions, statutory law, precedent, judge-made law, or international law, international rules and norms. Constitutional law deals with the fundamental principles by which the government exercises its authority. In some instances, these princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against the person, such as murder, mass murder, aggravated cases of rape (often including child sexual abuse), terrorism, aircraft hijacking, war crimes, crimes against h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions. Judaism is considered by religious Jews to be the expression of the covenant that God established with the Israelites, their ancestors. It encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. The Torah, as it is commonly understood by Jews, is part of the larger text known as the ''Tanakh''. The ''Tanakh'' is also known to secular scholars of religion as the Hebrew Bible, and to Christians as the " Old Testament". The Torah's supplemental oral tradition is represented by later texts s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Of Religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedom to change one's religion or beliefs, "the right not to profess any religion or belief", or "not to practise a religion". Freedom of religion is considered by many people and most nations to be a fundamental rights, fundamental human right. In a country with a state religion, freedom of religion is generally considered to mean that the government permits religious practices of other sects besides the state religion, and does not religious persecution, persecute believers in other faiths (or those who have no faith). Freedom of belief is different. It allows the right to believe what a person, group, or religion wishes, but it does not necessarily allow the right to practice the religion or belief openly and outwardly in a public manner, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
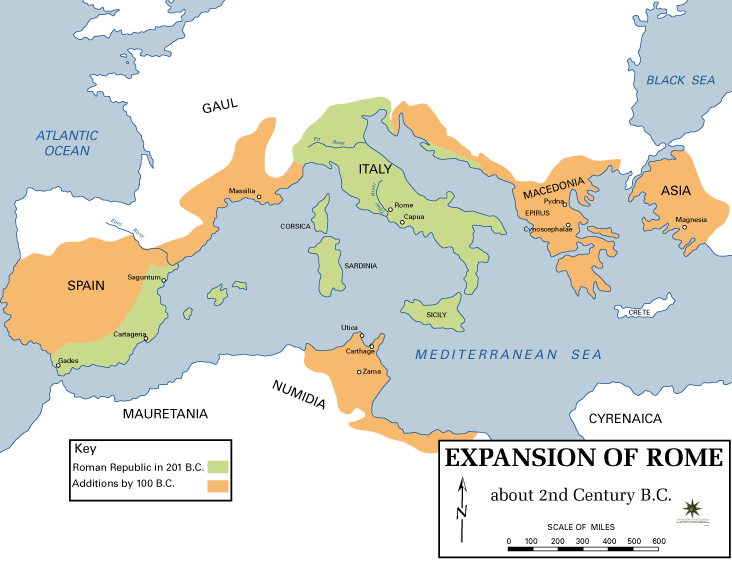
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Roman Republic
The crisis of the Roman Republic refers to an extended period of political instability and social unrest from about 134 BC to 44 BC that culminated in the demise of the Roman Republic and the advent of the Roman Empire. The causes and attributes of the crisis changed throughout the decades, including the forms of slavery, brigandage, wars internal and external, overwhelming corruption, land reform, the invention of excruciating new punishments, the expansion of Roman citizenship, and even the changing composition of the Roman army. Modern scholars also disagree about the nature of the crisis. Traditionally, the expansion of citizenship (with all its rights, privileges, and duties) was looked upon negatively by Sallust, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Gibbon, and others of their schools, because it caused internal dissension, disputes with Rome's Italian allies, slave revolts, and riots.Fields, p. 41, citing Sallust, ''Iugurthinum'' 86.2. However, other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)