|
Rolling-mill
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is similar to the rolling of dough. Rolling is classified according to the temperature of the metal rolled. If the temperature of the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, then the process is known as hot rolling. If the temperature of the metal is below its recrystallization temperature, the process is known as cold rolling. In terms of usage, hot rolling processes more tonnage than any other manufacturing process, and cold rolling processes the most tonnage out of all cold working processes... Roll stands holding pairs of rolls are grouped together into rolling mills that can quickly process metal, typically steel, into products such as structural steel (I-beams, angle stock, channel stock), bar stock, and rails. Most steel mills ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
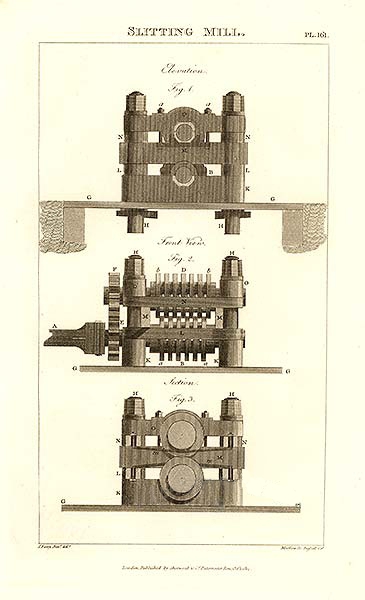
Slitting Mill
The slitting mill was a watermill for slitting bars of iron into rods. The rods then were passed to nailers who made the rods into nails, by giving them a point and head. The slitting mill was probably invented near Liège in what is now Belgium. The first slitting mill in England was built at Dartford, Kent in 1590. This was followed by one near Rugeley at the once separate village which was called Stonehouse, but now called Slitting Mill, by about 1611, and then Hyde Mill in Kinver in 1627. Others followed in various parts of England where iron was made. However, there was a particular concentration of them on the River Stour between Stourbridge and Stourport, where they were conveniently placed to slit iron that was brought up (or down) the River Severn before it reached nailers in the Black Country. The slitting mill consisted of two pairs of rollers turned by water wheels. Mill bars were flat bars of iron about three inches (75 mm) wide and half an inch (13&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fareham
Fareham ( ) is a market town at the north-west tip of Portsmouth Harbour, between the cities of Portsmouth and Southampton in south east Hampshire, England. It gives its name to the Borough of Fareham. It was historically an important manufacturer of bricks, used to build the Royal Albert Hall, and grower of strawberries and other seasonal fruits. Current employers include Fareham Shopping Centre, small-scale manufacturers, and the Defence Science and Technology Laboratory. History Archaeological excavations around the old High Street area and the church of St Peter & Paul on high ground over the Wallington Estuary have yielded evidence of settlement on the site contemporary with the Roman occupation. No extensive programme of investigation has been possible owing to the historic nature of the buildings in this area. The town has a documented history dating back to the Norman era, when a part of William's army marched up from Fareham Creek before continuing to the Saxon c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Cort
Henry Cort (c. 1740 – 23 May 1800) was an English ironware producer although formerly a Navy pay agent. During the Industrial Revolution in England, Cort began refining iron from pig iron to wrought iron (or bar iron) using innovative production systems. In 1784, he patented an improved version of the Puddling (metallurgy), puddling process for refining cast iron although its commercial viability was only accomplished by innovations introduced by the Merthyr Tydfil ironmasters Crawshay and Homfray. Biography Little is known of Cort's early life other than that he was possibly born into a family coming from Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster, England although his parents are unknown. Although his date of birth is traditionally given as 1740, this can not be confirmed and his early life remains an enigma. By 1765, Cort had become a Royal Navy pay agent, acting on commission collecting half pay and widows' pensions from an office in Crutched Friars near Aldgate in London. At th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motors
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be powered by AC or DC, be brushed or brushless, single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase, axial or radial flux, and may be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. Standardized motors provide c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Wheels
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets arranged on the outside rim forming the driving car. Water wheels were still in commercial use well into the 20th century but they are no longer in common use. Uses included milling flour in gristmills, grinding wood into pulp for papermaking, hammering wrought iron, machining, ore crushing and pounding fibre for use in the manufacture of cloth. Some water wheels are fed by water from a mill pond, which is formed when a flowing stream is dammed. A channel for the water flowing to or from a water wheel is called a mill race. The race bringing water from the mill pond to the water wheel is a headrace; the one carrying water after it has left the wheel is commonly referred to as a tailrace. Waterwheels were used for various purposes from ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Polhem
Christopher Polhammar (18 December 1661 – 30 August 1751) better known as Christopher Polhem (), which he took after his ennoblement in 1716, was a Swedish scientist, inventor and industrialist. He made significant contributions to the economic and industrial development of Sweden, particularly mining. He was ennobled by King Charles XII of Sweden for his contributions to Swedish technological development. Christopher Polhem Svenskt biografiskt lexicon Biography Polhem (Polhammar) was born on the island of in the small village of , situated northeast of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinplate
Tinplate consists of sheets of steel coated with a thin layer of tin to impede rusting. Before the advent of cheap milled steel, the backing metal was wrought iron. While once more widely used, the primary use of tinplate now is the manufacture of tin cans. Tinplate is made by rolling the steel (or formerly iron) in a rolling mill, removing any mill scale by pickling it in acid and then coating it with a thin layer of tin. Plates were once produced individually (or in small groups) in what became known as a ''pack mill''. In the late 1920s pack mills began to be replaced by ''strip mills'' which produced larger quantities more economically. Formerly, tinplate was used for cheap pots, pans and other holloware. This kind of holloware was also known as tinware and the people who made it were tinplate workers. For many purposes, tinplate has been replaced by galvanised (zinc-coated or tinned) vessels, though not for cooking as zinc is poisonous. The zinc layer prevents the iron f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackplate
Blackplate is hot rolled or cold rolled,DIN 55405:2006-11 ''Verpackung - Terminologie - Begriffe'', Berlin: Beuth Verlag. non-descaled sheet steel or sheet iron.''Blackplate'' at www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 30 Apr 2017. Manufacture and properties Blackplate is made of non- iron or and is annealed on open flames or in an annealing box. Its dark appearance is caused by its reaction with the surrounding air. ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontypool
Pontypool ( cy, Pont-y-pŵl ) is a town and the administrative centre of the county borough of Torfaen, within the historic boundaries of Monmouthshire in South Wales. It has a population of 28,970. Location It is situated on the Afon Lwyd river in the county borough of Torfaen. Located at the eastern edge of the South Wales coalfields, Pontypool grew around industries including iron and steel production, coal mining and the growth of the railways. A rather artistic manufacturing industry which also flourished here alongside heavy industry was Japanning, a type of lacquer ware. Pontypool itself consists of several smaller districts, these include Abersychan, Cwmffrwdoer, Pontnewynydd, Trevethin, Penygarn, Wainfelin, Tranch, Brynwern, Pontymoile, Blaendare, Cwmynyscoy, New Inn, Griffithstown and Sebastopol. History The name of the town in Welsh – ''Pont-y-pŵl'' – originates from a bridge ('pont') associated with a pool in the Afon Lwyd. The Welsh word ''pŵl'' is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |