|
Robotic Sensors
Robotic sensors are used to estimate a robot's condition and environment. These signals are passed to a controller to enable appropriate behavior. Sensors in robots are based on the functions of human sensory organs. Robots require extensive information about their environment in order to function effectively. Classification Sensors provide analogs to human senses and can monitor other phenomena for which humans lack explicit sensors. * Simple Touch: Sensing an object's presence or absence. * Complex Touch: Sensing an object's size, shape and/or hardness. * Simple Force: Measuring force along a single axis. * Complex Force: Measuring force along multiple axes. * Simple Vision: Detecting edges, holes and corners. * Complex Vision: Recognizing objects. * Proximity: Non-contact detection of an object. Sensors can measure physical properties, such as the distance between objects, the presence of light and the frequency of sound. They can measure: * Object Proximity: The presence/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity Sensor
A velocity receiver (velocity sensor) is a sensor that responds to velocity rather than absolute position. For example, dynamic microphones are velocity receivers. Likewise, many electronic keyboards used for music are velocity sensitive, and may be said to possess a velocity receiver in each key. Most of these function by measuring the time difference between switch closures at two different positions along the travel of each key. There are two types of velocity receivers, moving coil and piezoelectric. The former contains a coil supported by springs and a permanently fixed magnet and require no output signal amplifiers. Movement causes the coil to move relative to the magnet, which in turn generates a voltage that is proportional to the velocity of that movement. Piezoelectric sensor velocity receivers are similar to a piezoelectric accelerometer An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechatronics
Mechatronics engineering also called mechatronics, is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that focuses on the integration of mechanical, electrical and electronic engineering systems, and also includes a combination of robotics, electronics, computer science, telecommunications, systems, control, and product engineering. As technology advances over time, various subfields of engineering have succeeded in both adapting and multiplying. The intention of mechatronics is to produce a design solution that unifies each of these various subfields. Originally, the field of mechatronics was intended to be nothing more than a combination of mechanics, electrical and electronics, hence the name being a portmanteau of the words "mechanics" and "electronics"; however, as the complexity of technical systems continued to evolve, the definition had been broadened to include more technical areas. The word ''mechatronics'' originated in Japanese-English and was created by Tetsuro Mori, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Robotics Articles
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots. Robotics is related to the sciences of electronics, engineering, mechanics, and software. The word "robot" was introduced to the public by Czech writer Karel Čapek in his play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots), published in 1920. The term "robotics" was coined by Isaac Asimov in his 1941 science fiction short-story " Liar!"According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' the term "robotics" was first used in the short story "Liar!" published in the May, 1941 issue of ''Astounding Science Fiction.'' Articles related to robotics include: 0–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z References External links {{Robotics Robotics Robotics Robotics is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots. Robotics is related to the sciences of electronics, engineering, mechanics, and software. The following is a list of common definitions related to the Robotics field. __NOTOC__ A *Actuator, a motor that translates control signals into mechanical movement. The control signals are usually electrical but may, more rarely, be pneumatic or hydraulic. The power supply may likewise be any of these. It is common for electrical control to be used to modulate a high-power pneumatic or hydraulic motor. *Aerobot a robot capable of independent flight on other planets. A type of aerial robot. *Arduino The current platform of choice for small-scale robotic experimentation and physical computing. *Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. *Aura (satellite) a robotic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
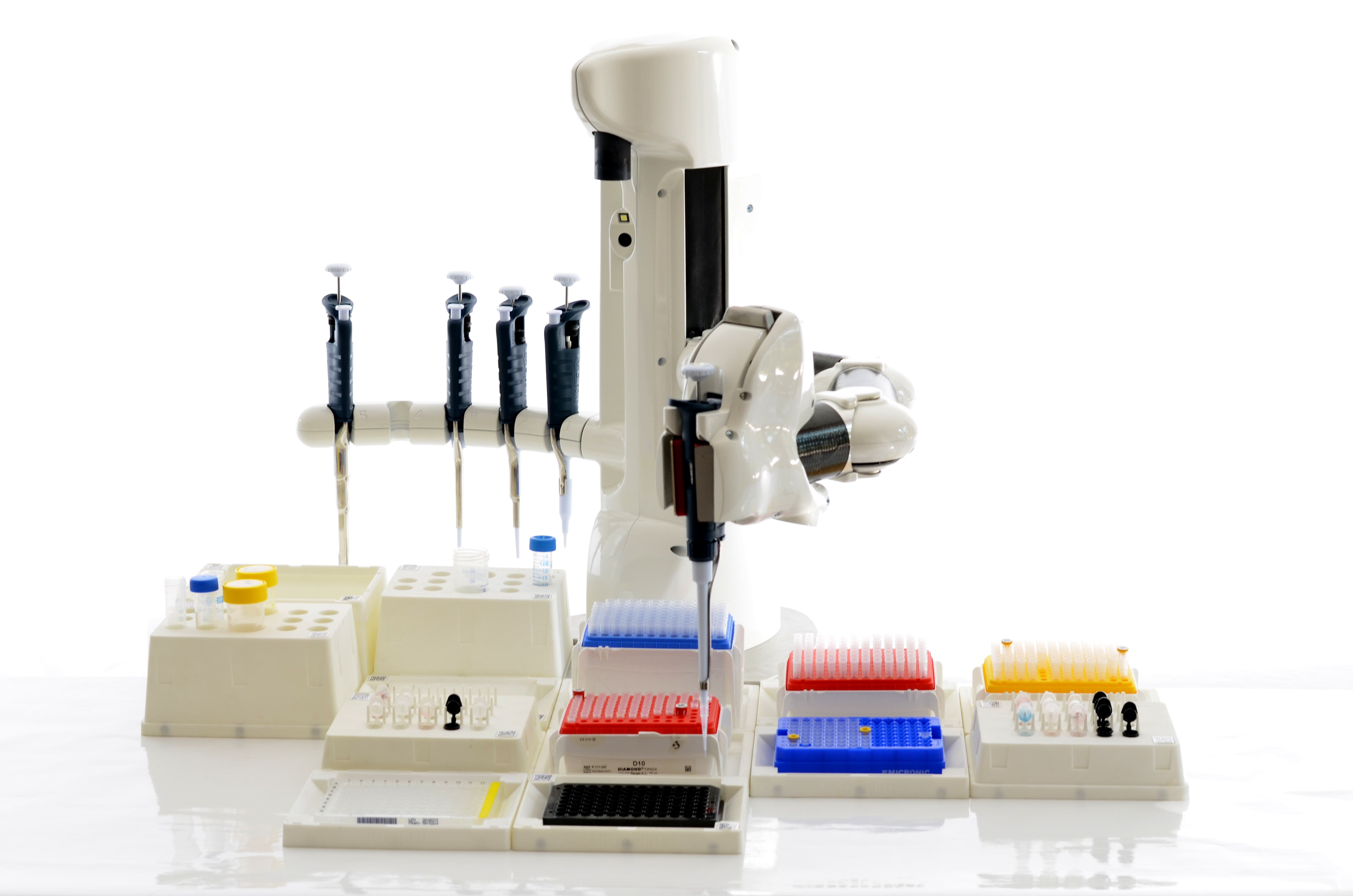
Liquid Handling Robot
A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a robot that dispenses a selected quantity of reagent, samples or other liquid to a designated container. Introduction Liquid handling plays a pivotal role in life science laboratories. The sample volumes are usually small, at the micro- or nanoliter level, and the number of transferred samples can be huge. Under these conditions, liquid handling by hand is tedious, time-consuming, and impractical. Consequently, there is a strong demand for automated liquid handling robots. Types of liquid handling robots The simplest version simply dispenses an allotted volume of liquid from a motorized pipette or syringe; more complicated machines can also manipulate the position of the dispensers and containers (often a Cartesian coordinate robot, such as thXYZ Triton Robotfrom TriContinent Scientific) and/or integrate additional laboratory devices, such as centrifuges, microplate readers, hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot App Store
The Robot App Store is a digital application distribution platform for applications for robots opened to the public on late 2011. The service allows users to browse and download applications that were developed for robots, and published through the RobotAppStore.com website. Depending on the developer, applications are available either for free or at a cost. The applications can be downloaded directly to a robot, (like NAO) or downloaded onto a personal computer (PC) or a smartphone. 70% of the sale price goes to the developer of the app. History The Robot App Store opened on Aug. 28, 2011. for developers. In early 2012, the website was opened for consumers. The Robot App Store is available for developers and robot-owners from around the world. The portal offers a centralized encyclopedia for robotics topics called Robopedia. A comprehensive knowledge-base for developers covering development lessons for popular robotics platforms such as Roomba, AR.Drone, LEGO NXT and eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Robotics
following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics: Robotics is a branch of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots, as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing. These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans in dangerous environments or manufacturing processes, or resemble humans in appearance, behaviour, and or cognition. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics. The word "robot" was introduced to the public by Czech writer Karel Čapek in his play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots), published in 1920. The term "robotics" was coined by Isaac Asimov in his 1941 science fiction short-story " Liar!" Nature of robotics Robotics can be described as: * An applied science – scientific knowledge trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot Locomotion
Robot locomotion is the collective name for the various methods that robots use to transport themselves from place to place. Wheeled robots are typically quite energy efficient and simple to control. However, other forms of locomotion may be more appropriate for a number of reasons, for example traversing rough terrain, as well as moving and interacting in human environments. Furthermore, studying bipedal and insect-like robots may beneficially impact on biomechanics. A major goal in this field is in developing capabilities for robots to autonomously decide how, when, and where to move. However, coordinating numerous robot joints for even simple matters, like negotiating stairs, is difficult. Autonomous robot locomotion is a major technological obstacle for many areas of robotics, such as humanoids (like Honda's Asimo). Types of locomotion Walking * ''See'' Passive dynamics * ''See'' Zero Moment Point * ''See'' Leg mechanism * ''See'' Hexapod (robotics) Walking robots si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tactile Sensor
A tactile sensor is a device that measures information arising from physical interaction with its environment. Tactile sensors are generally modeled after the biological sense of cutaneous touch which is capable of detecting stimuli resulting from mechanical stimulation, temperature, and pain (although pain sensing is not common in artificial tactile sensors). Tactile sensors are used in robotics, computer hardware and security systems. A common application of tactile sensors is in touchscreen devices on mobile phones and computing. Tactile sensors may be of different types including piezoresistive, piezoelectric, optical, capacitive and elastoresistive sensors.. Tactile sensors also come in the form of pressure indicating films that reveal pressure distribution and magnitude between contacting surfaces by virtue of an immediate and permanent color change. These pressure indicating films are one-time use sensor that capture the maximum pressure they were exposed to. Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Sensing
Robotic sensing is a subarea of robotics science intended to give robots sensing capabilities. Robotic sensing mainly gives robots the ability to see,Roh SG, Choi HR (Jan 2009).3-D Tag-Based RFID System for Recognition of Object" IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 6 (1): 55–65.Arivazhagan S, Ganesan L, Kumar TGS (Jun 2009).A modified statistical approach for image fusion using wavelet transform" Signal Image and Video Processing 3 (2): 137-144.Jafar FA, et al (Mar 2011).An Environmental Visual Features Based Navigation Method for Autonomous Mobile Robots" International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control 7 (3): 1341-1355. touch,Anderson S, et al (Dec 2010).Adaptive Cancelation of Self-Generated Sensory Signals in a Whisking Robot" IEEE Transactions on Robotics 26 (6): 1065-1076.Kim YM, et al (Aug 2010)A Robust Online Touch Pattern Recognition for Dynamic Human-robot Interaction" IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 56 (3): 1979-1987. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
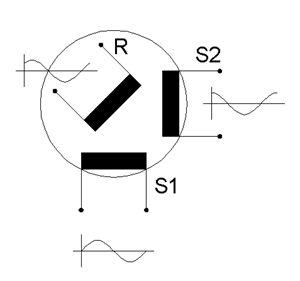
Resolver (electrical)
A resolver is a type of rotary electrical transformer used for measuring degrees of rotation. It is considered an analog device, and has digital counterparts such as the digital resolver, rotary (or pulse) encoder. Description The most common type of resolver is the brushless transmitter resolver (other types are described at the end). On the outside, this type of resolver may look like a small electrical motor having a stator and rotor. On the inside, the configuration of the wire windings makes it different. The stator portion of the resolver houses three windings: an exciter winding and two two-phase windings (usually labeled "x" and "y") (case of a brushless resolver). The exciter winding is located on the top; it is a coil of a turning (rotary) transformer. This rotary transformer induces current in the rotor without wires or brushes to provide a direct electrical connection. The two other windings are on the bottom, wound on a lamination. They are configured at 90 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |