|
Robert Metzenberg
Robert Lee Metzenberg (June 11, 1930 – July 15, 2007) was an American geneticist known for his work on genetic regulation and metabolism with Neurospora crassa. Education and early life Robert Lee Metzenberg was born in Chicago, Illinois, USA. In 1951 Metzenberg graduated from Pomona College in California where he had specialised in chemistry with physics and biology as minor subjects. He then studied at the California Institute of Technology and was awarded a Ph.D. in 1955. 1951 and 1955, he earned a PhD at California Institute of Technology in the Division of Biological Sciences supervised by Herschel K. Mitchell. During this time he met and was influenced by several geneticists including George Beadle, Alfred Sturtevant, Herschel K. Mitchell and Max Delbrück. Career In 1955 Metzenberg was appointed as a professor at the University of Wisconsin where he remained until he retired in 1996. In 1977 he was appointed the John Bascom Professor by the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück (; September 4, 1906 – March 9, 1981) was a German–American biophysicist who participated in launching the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s. He stimulated physical science, physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time. Formed in 1945 and led by Delbrück along with Salvador Luria and Alfred Hershey, the Phage Group made substantial headway unraveling important aspects of genetics. The three shared the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the replication mechanism and the genetic structure of viruses"."The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1969" Nobel Media AB 2013, ''Nobelprize.org'', Web access November 6, 2013. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1930 Births
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 1 – Year of the Five Emperors: The Roman Senate chooses Publius Helvius Pertinax, against his will, to succeed the late Commodus as Emperor. Pertinax is forced to reorganize the handling of finances, which were wrecked under Commodus, to reestablish discipline in the Roman army, and to suspend the food programs established by Trajan, provoking the ire of the Praetorian Guard. * March 28 – Pertinax is assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard, who storm the imperial palace. The Empire is auctioned o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics Society Of America
The Genetics Society of America (GSA) is a scholarly membership society of more than 5,500 genetics researchers and educators, established in 1931. The Society was formed from the reorganization of the Joint Genetics Sections of the American Society of Zoologists and the Botanical Society of America. An Abridged History of the Genetics Society of America GSA members conduct fundamental and applied research using a wide variety of s to enhance understanding of living systems. Some of the systems of study include '''' (fruit flies), '' |
Caltech
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasionally referred to as "CIT", most notably in its alma mater, but this is uncommon. is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California. Caltech is ranked among the best and most selective academic institutions in the world, and with an enrollment of approximately 2400 students (acceptance rate of only 5.7%), it is one of the world's most selective universities. The university is known for its strength in science and engineering, and is among a small group of Institute of Technology (United States), institutes of technology in the United States which is primarily devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. The institution was founded as a preparatory and vocational school by Amos G. Throop in 1891 and began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including ''co-suppression'', ''post-transcriptional gene silencing'' (PTGS), and ''quelling''. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics (journal)
''Genetics'' is a monthly scientific journal publishing investigations bearing on heredity, genetics, biochemistry and molecular biology. Genetics is published by the Genetics Society of America. It has a delayed open access policy, and makes articles available online without a subscription after 12 months have elapsed since first publication. Since 2010, it is published online-only.http://www.councilscienceeditors.org/wp-content/uploads/v36n1p14-15_17.pdf George Harrison Shull George Harrison Shull (April 15, 1874 – September 28, 1954) was an eminent American plant geneticist and the younger brother of botanical illustrator and plant breeder J. Marion Shull. He was born on a farm in Clark County, Ohio, graduated fr ... was the founding editor of ''Genetics'' in 1916. Editors-in-Chief References External linksOfficial website Genetics journals Delayed open access journals English-language journals Publications established in 1916 Online-only journals {{ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
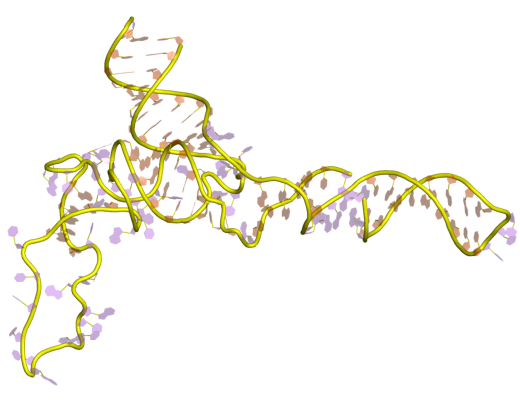
5S RRNA
The 5S ribosomal RNA (5S rRNA) is an approximately 120 nucleotide-long ribosomal RNA molecule with a mass of 40 kDa. It is a structural and functional component of the large subunit of the ribosome in all domains of life (bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes), with the exception of mitochondrial ribosomes of fungi and animals. The designation 5S refers to the molecule's sedimentation velocity in an ultracentrifuge, which is measured in Svedberg units (S). Biosynthesis In prokaryotes, the 5S rRNA gene is typically located in the rRNA operons downstream of the small and the large subunit rRNA, and co-transcribed into a polycistronic precursor. A particularity of eukaryotic nuclear genomes is the occurrence of multiple 5S rRNA gene copies (5S rDNA) clustered in tandem repeats, with copy number varying from species to species. Eukaryotic 5S rRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase III, whereas other eukaryotic rRNAs are cleaved from a 45S precursor transcribed by RNA polymerase I. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assimilation (biology)
Assimilation is the process of absorption of vitamins, minerals, and other chemicals from food as part of the nutrition of an organism. In humans, this is always done with a chemical breakdown (enzymes and acids) and physical breakdown (oral mastication and stomach churning). The second process of bio assimilation is the chemical alteration of substances in the bloodstream by the liver or cellular secretions. Although a few similar compounds can be absorbed in digestion bio assimilation, the bioavailability of many compounds is dictated by this second process since both the liver and cellular secretions can be very specific in their metabolic action (see chirality). This second process is where the absorbed food reaches the cells via the liver. Most foods are composed of largely indigestible components depending on the enzymes and effectiveness of an animal's digestive tract. The most well-known of these indigestible compounds is cellulose; the basic chemical polymer in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)