|
Rishu
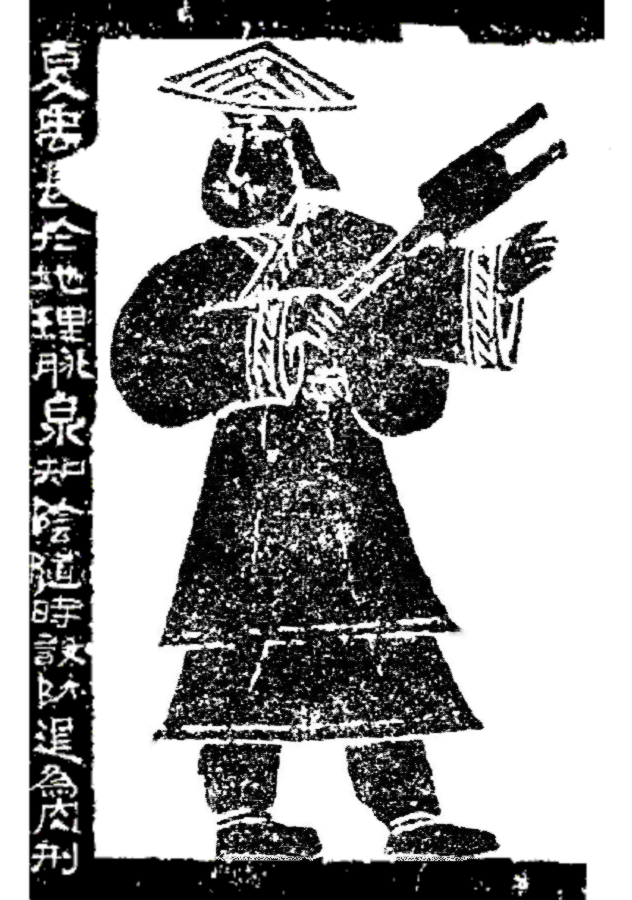
Rishu ('')'', lit. "Day Book," is a genre of divinatory texts that circulated widely in China from the late Warring States Period to the Western Han dynasty. Rishu is also the name of one of the primary literatures for the schools of orthodox Shingon Buddhism of Japan. This term finds its first evident presence dated back to 217 BCE in China. Historical Significance China In Mainland China, the ''Rishu'' () "Day Book" is one of the divinatory books discovered in late Warring States period tomb libraries which has confirmed the ''Baopuzi'' description of Yubu as a series of three steps. It has great cultural significance in ancient and medieval China. It is an almanac or hemerology which is one of the Shuihudi Qin bamboo texts recovered in 1975 in Shuihudi, Hubei, from a tomb dated 217 BCE. Donald Harper (1999:843) believes that for describing texts like the ''Rishu'' , which determine lucky and unlucky days on sexagenary cycle numerology without reference to astrology, " hemer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yubu
''Yubu'', translated as Pace(s) of Yu or Step(s) of Yu, is the basic mystic dance step of religious Daoism. This ancient walking or dancing technique typically involves dragging one foot after another, and is explained in reference to the legendary Yu the Great, who became lame on one side of his body from exerting himself while establishing order in the world after the Chinese mythology#Gun, Yu, and the Great Flood, Great Flood. Daoist religions, especially during the Six Dynasties period (220–589), incorporated ''Yubu'' into rituals, such as the ''Bugang'' "pace the Big Dipper", in which a Taoist priest would symbolically walk the nine stars of the ''Beidou'' "Big Dipper" in order to acquire that constellation's supernatural energy. Terminology The term Yubu , defined as ''boxing'' "limp; walk lame" (''Hanyu Da Cidian'' 1993 1.664), compound (linguistics), compounds two Chinese words. Yu was the legendary founder of the Xia dynasty (c. 2070 BCE-c. 1600 BCE), and worke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renge-in Tanjō-ji
Renge-in Tanjō-ji (蓮華院誕生寺) is a Buddhist temple of the Shingon Risshu, or Shingon-Vinaya Buddhism, in Tamana, Kumamoto, Tamana, Kumamoto Prefecture. It is the head temple of the Shingon Ritsu school in Kyūshū and a branch temple of Saidai-ji (西大寺) in Nara, Nara, Nara (奈良). It venerates Mahābodhisattva Kōen (皇円大菩薩, ''Kōen Daibosatsu'') as its patron deity. The temple stands on the site of Jōkō-ji Renge-in which was founded either at the end of the Heian period or the beginning of the Kamakura period and burnt down during the wars of the Sengoku period. The first abbot Zeshin Kawahara (1896 - 1977) was instructed through a spiritual communication by Kōen to restore Jōkō-ji Renge-in, which he accomplished in 1930 and renamed it Renge-in Tanjō-ji ("Birth Temple") in honor of the fact that it stands on the birthplace of Kōen. Addresses Main Temple: 2288 Tsuiji, Tamana, Kumamoto 865-0065 Oku-no-in: 1512-77 Tsuiji, Tamana, Kumamoto 86 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
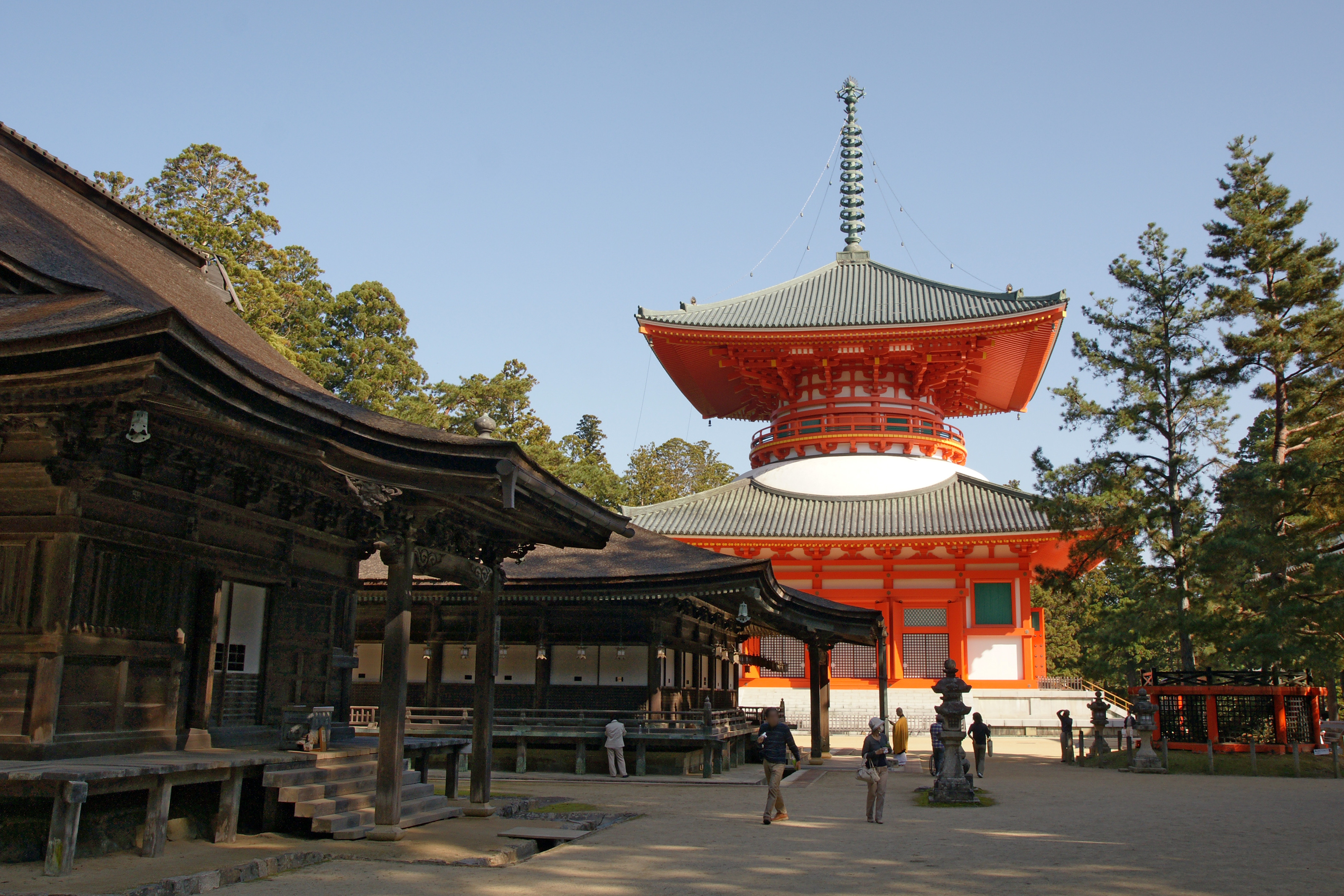
Shingon Buddhism
Shingon monks at Mount Koya is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asia, originally spread from India to China through traveling monks such as Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. Known in Chinese as the Tangmi (; the Esoteric School in Tang Dynasty of China), these esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named Kūkai (), who traveled to Tang China to acquire and request transmission of the esoteric teachings. For that reason, it is often called Japanese Esoteric Buddhism, or Orthodox Esoteric Buddhism. The word ''shingon'' is the Japanese reading of the Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word ("mantra"). History Shingon Buddhist doctrine and teachings arose during the Heian period (794-1185) after a Buddhist monk named Kūkai traveled to China in 804 to study Esoteric Buddhist practices in the city of Xi'an (), then called Chang-an, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yu The Great
Yu the Great (大禹) was a legendary king in ancient China who was famed for his introduction of flood control, his establishment of the Xia dynasty which inaugurated dynastic rule in China, and his upright moral character. He figures prominently in the Chinese legend of "Great Yu Who Controlled the Waters" (). The dates which have been proposed for Yu's reign predate the oldest-known written records in China, the oracle bones of the late Shang dynasty, by nearly a millennium. Yu's name was not inscribed on any artifacts which were produced during the proposed era in which he lived, nor was it inscribed on the later oracle bones; his name was first inscribed on vessels which date back to the Western Zhou period (c. 1045–771 BC). The lack of substantial contemporary documentary evidence has caused some controversy over Yu's historicity. Thus, proponents of his existence theorize that stories about his life and reign were orally transmitted in various areas of China until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolic Stars
In Chinese astrology, the symbolic stars, also translated as star spirits or calendar spirits, () represent beneficial and baleful influences believed to be present during particular times (including the year, month, and hour), typically in relation to the specific positions and interactions of the heavenly stems and earthly branches used in traditional Chinese timekeeping and the sexagenary cycle. Although they do not correspond to any particular observable stars visible in the night sky, they are described in similar terms to observable astronomical objects with the actual influence of any particular symbolic star at a given moment involving multiple cosmic factors, including its relationship to other such "stars" (whether in harmony or in opposition), its phase (ascendant or descendant), its aspect, and the time of its apogee, in addition its relationship to the Five Phases and Yin and Yang which are also used to characterise the influence of observable celestial objects such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin's wars of unification, Qin wars of conquest that saw the annexation of all other contender states, which ultimately led to the Qin (state), Qin state's victory in 221 BC as the first unified History of China#Imperial China, Chinese empire, known as the Qin dynasty. Although different scholars point toward different dates ranging from 481 BC to 403 BC as the true beginning of the Warring States, Sima Qian's choice of 475 BC is the most often cited. The Warring States era also overlaps with the second half of the Eastern Zhou Period, Eastern Zhou dynasty, though the Chinese sovereign, known as the king of Zhou, ruled merely as a figurehead and served as a backdrop against the machinations of the warring states. The "Warring St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
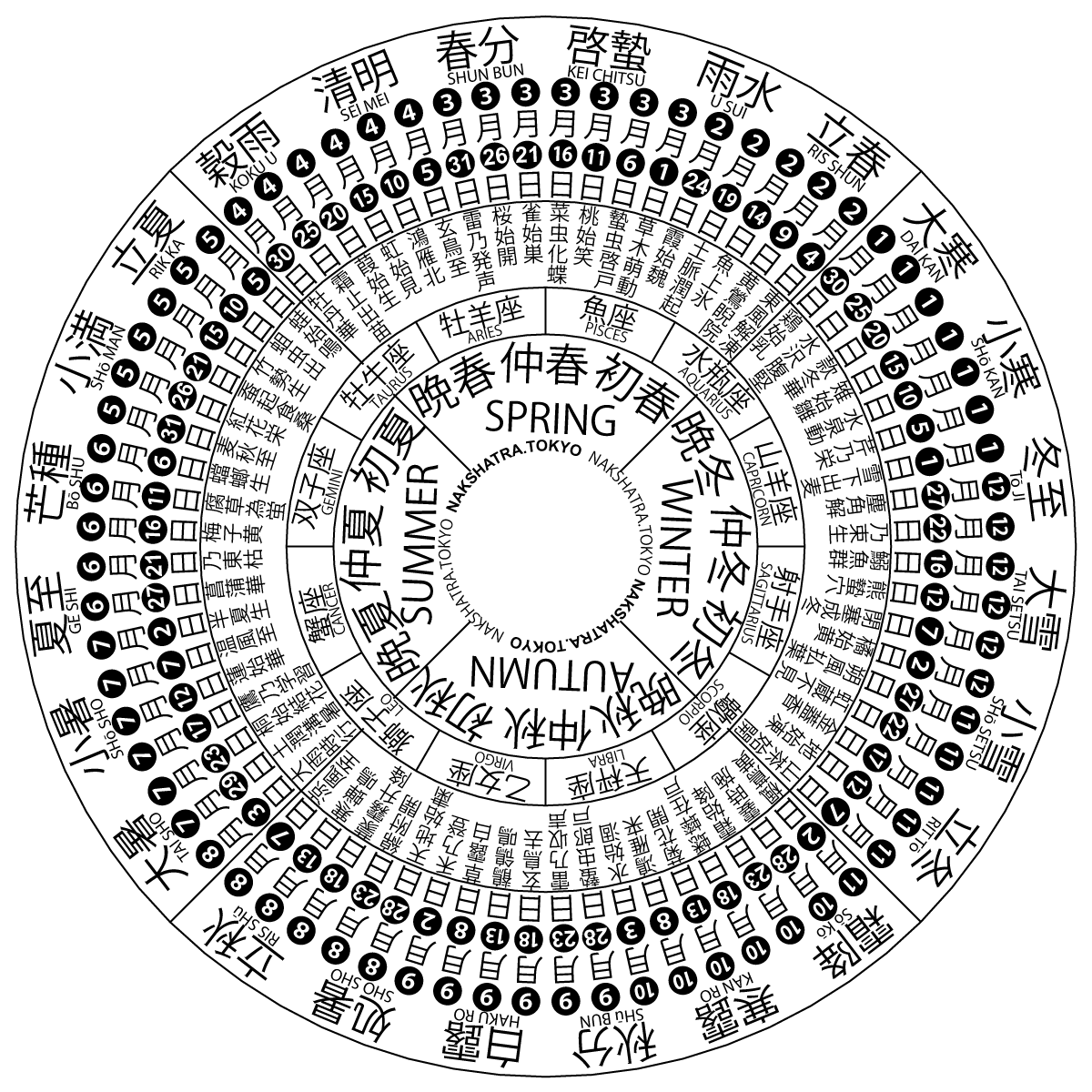
Jieqi
A solar term is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese calendar, Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate Intercalation (timekeeping), intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the ''Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (solar term), Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Duke of Zhou, Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient timekeeper instrument named Tu Gui (土圭). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; until 104 BC in the book Taichu Calendar, the entire twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liqiu
The traditional Chinese calendar divides a year into 24 solar terms. ''Lìqiū'', ''Risshū'', ''Ipchu'', or ''Lập thu'' () is the 13th solar term. It begins when the Sun reaches the celestial longitude of 135° and ends when it reaches the longitude of 150°. It more often refers in particular to the day when the Sun is exactly at the celestial longitude of 135°. In the Gregorian calendar The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ..., it usually begins around August 7 and ends around August 23. Liqiu signifies the beginning of autumn in East Asian cultures. Date and time References {{s-end Autumn 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognised by at least one other East Asian state due to severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under Chinese sovereignty. Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau are among the world's largest and most prosperous economies. East Asia borders Siberia and the Russian Far East to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia (a Pacific Ocean island group, classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantras
Tantras ("''doctrine''" or "''framework''" or "''system''" ) refers to numerous and varied scriptures pertaining to any of several esoteric traditions rooted in Hindu and Buddhist philosophy. The religious culture of the Tantras is essentially Hindu, and Buddhist Tantric material can be shown to have been derived from Hindu sources. And although Hindu and Buddhist Tantra have many similarities from the outside, they do have some clear distinctions. The rest of this article deals with Hindu Tantra. Buddhist Tantras are described in the article on Buddhist Tantras. Classes of Hindu Tantra The word ''tantra'' is made up by the joining (''sandhi'' in Sanskrit) of two Sanskrit words: ''tanoti'' (expansion) and ''rayati'' (liberation). Tantra means liberation of energy and expansion of consciousness from its gross form. It is a method to expand the mind and liberate the dormant potential energy, and its principles form the basis of all yogic practices. Hence, the Hindu Tantra scriptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |