|
Rieske Protein
Rieske proteins are iron–sulfur protein (ISP) components of cytochrome ''bc''1 complexes and cytochrome b6f complexes and are responsible for electron transfer in some biological systems. John S. Rieske and co-workers first discovered the protein and in 1964 isolated an acetylated form of the bovine mitochondrial protein. In 1979 Trumpower's lab isolated the "oxidation factor" from bovine mitochondria and showed it was a reconstitutively-active form of the Rieske iron-sulfur protein It is a unique Fe-2Scluster in that one of the two Fe atoms is coordinated by two histidine residues rather than two cysteine residues. They have since been found in plants, animals, and bacteria with widely ranging electron reduction potentials from -150 to +400 mV. Biological function Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase (also known as bc1 complex or complex III) is an enzyme complex of bacterial and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation systems. It catalyses the oxidation-reduction reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B6f Complex
The cytochrome ''b''6''f'' complex (plastoquinol—plastocyanin reductase; ) is an enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts of plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae, that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin. The reaction is analogous to the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome bc1 (Complex III) of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. During photosynthesis, the cytochrome b6f complex is one step along the chain that transfers electrons from Photosystem II to Photosystem I, and at the same time pumps protons into the thylakoid space, contributing to the generation of an electrochemical (energy) gradient that is later used to synthesize ATP from ADP. Enzyme structure The cytochrome b6f complex is a dimer, with each monomer composed of eight subunits. These consist of four large subunits: a 32 kDa cytochrome f with a c-type cytochrome, a 25 kDa cytochrome b6 with a low- and high-potential heme group, a 19 kDa Rieske iron- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B
Cytochrome b within both molecular and cell biology, is a protein found in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It functions as part of the electron transport chain and is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes. Function In the mitochondrion of eukaryotes and in aerobic prokaryotes, cytochrome b is a component of respiratory chain complex III () — also known as the bc1 complex or ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase. In plant chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, there is an analogous protein, cytochrome b6, a component of the plastoquinone-plastocyanin reductase (), also known as the b6f complex. These complexes are involved in electron transport, the pumping of protons to create a proton-motive force ( PMF). This proton gradient is used for the generation of ATP. These complexes play a vital role in cells. Structure Cytochrome b/b6 is an integral membrane protein of approximately 400 amino acid residues that probably has 8 transmembrane segments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
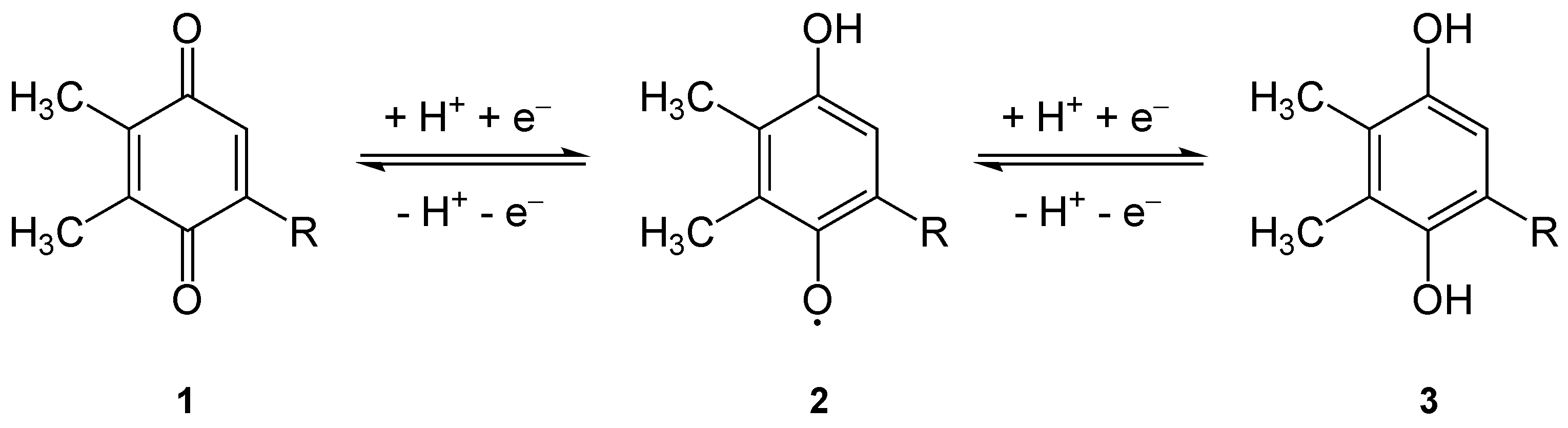
Semiquinone
Semiquinone (or ubisemiquinone) is a free radical resulting from the removal of one hydrogen atom with its electron during the process of dehydrogenation of a hydroquinone, such as hydroquinone itself or catechol, to a quinone or alternatively the addition of a single H atom to a quinone. It is highly unstable. It is the first of two stages in reducing the supplementary form of CoQ10 ubiquinone to the active form ubiquinol A ubiquinol is an electron-rich (reduced) form of coenzyme Q (ubiquinone). The term most often refers to ubiquinol-10, with a 10-unit tail most commonly found in humans. The natural ubiquinol form of coenzyme Q is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-poly p .... References Light reactions {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a porphyrin acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands." The definition is loose, and many depictions omit the axial ligands. Among the metalloporphyrins deployed by metalloproteins as prosthetic groups, heme is one of the most widely used and defines a family of proteins known as hemoproteins. Hemes are most commonly recognized as components of hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood, but are also found in a number of other biologically important hemoproteins such as myoglobin, cytochromes, catalases, heme peroxidase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The word ''haem'' is derived from Greek ''haima'' meaning "blood". Function Hemoproteins have diverse biological functions incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastoquinol
Plastoquinone (PQ) is an isoprenoid quinone molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. The most common form of plastoquinone, known as PQ-A or PQ-9, is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units. There are other forms of plastoquinone, such as ones with shorter side chains like PQ-3 (which has 3 isoprenyl side units instead of 9) as well as analogs such as PQ-B, PQ-C, and PQ-D, which differ in their side chains. The benzoquinone and isoprenyl units are both nonpolar, anchoring the molecule within the inner section of a lipid bilayer, where the hydrophobic tails are usually found. Plastoquinones are very structurally similar to ubiquinone, or coenzyme Q10, differing by the length of the isoprenyl side chain, replacement of the methoxy groups with methyl groups, and removal of the methyl group in the 2 position on the quinone. Like ubiquinone, it can come in several oxidation states: p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
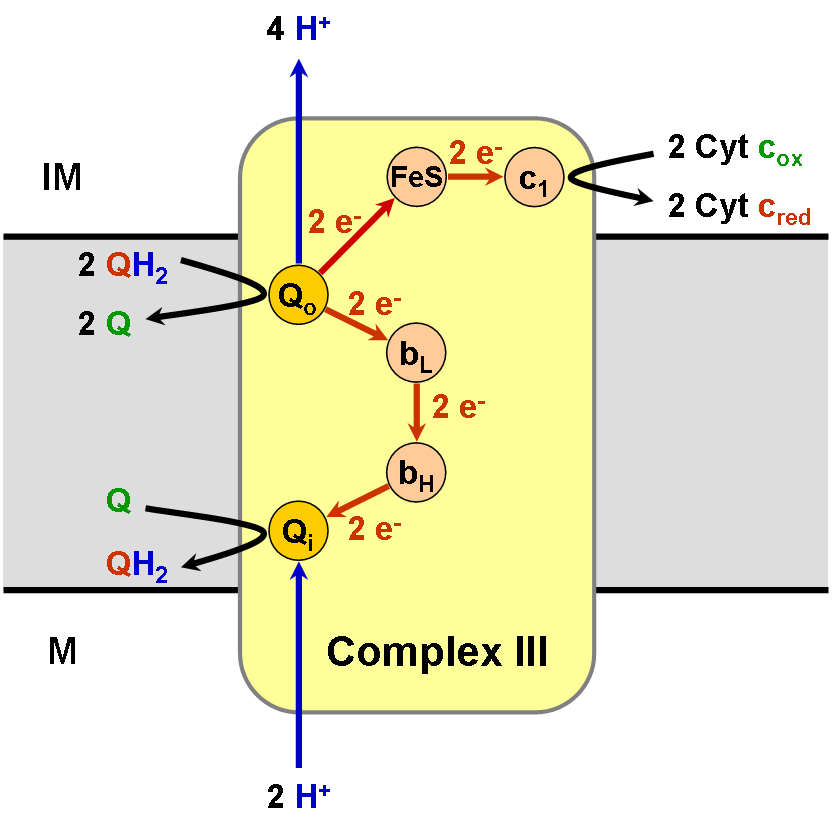
Coenzyme Q – Cytochrome C Reductase
The coenzyme Q : cytochrome ''c'' – oxidoreductase, sometimes called the cytochrome ''bc''1 complex, and at other times complex III, is the third complex in the electron transport chain (), playing a critical role in biochemical generation of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation). Complex III is a multisubunit transmembrane protein encoded by both the mitochondrial (cytochrome b) and the nuclear genomes (all other subunits). Complex III is present in the mitochondria of all animals and all aerobic eukaryotes and the inner membranes of most eubacteria. Mutations in Complex III cause exercise intolerance as well as multisystem disorders. The bc1 complex contains 11 subunits, 3 respiratory subunits (cytochrome B, cytochrome C1, Rieske protein), 2 core proteins and 6 low-molecular weight proteins. Ubiquinol—cytochrome-c reductase catalyzes the chemical reaction :QH2 + 2 ferricytochrome c \rightleftharpoons Q + 2 ferrocytochrome c + 2 H+ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome F
Cytochrome ''f'' is the largest subunit of cytochrome ''b''6''f'' complex (plastoquinol—plastocyanin reductase; ). In its structure and functions, the cytochrome b6f complex bears extensive analogy to the cytochrome bc1 complex of mitochondria and photosynthetic purple bacteria. Cytochrome f (cyt f) plays a role analogous to that of cytochrome c1, in spite of their different structures. The 3D structure of ''Brassica rapa'' (Turnip) cyt f has been determined. The lumen-side segment of cyt f includes two structural domains: a small one above a larger one that, in turn, is on top of the attachment to the membrane domain. The large domain consists of an anti-parallel beta-sandwich and a short haem-binding peptide, which form a three-layer structure. The small domain is inserted between beta-strands F and G of the large domain and is an all-beta domain. The haem nestles between two short helices at the N terminus of cyt f. Within the second helix is the sequence motif for the c-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in plast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductase
A reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes a reduction reaction. Examples * 5α-Reductase * 5β-Reductase * Dihydrofolate reductase * HMG-CoA reductase * Methemoglobin reductase * Ribonucleotide reductase * Thioredoxin reductase * ''E. coli'' nitroreductase * Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase See also * Oxidase * Oxidoreductase In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually u ... References Oxidoreductases {{Enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_cyt6bf_mutant.jpg)