|
Richard Worsam Meade II
Richard Worsam Meade II (May 21, 1807 – April 16, 1870) (also called Richard Worsam Meade, Sr., in relation to his son, Rear Admiral Richard Worsam Meade III) was an officer in the United States Navy. Life and career Meade was born in Cádiz, Spain on May 21, 1807 to American parents, Richard Worsam Meade I and his wife Margaret Coats Butler Meade; his younger brother was Major General George Gordon Meade, the victor of Gettysburg. Meade entered the Navy as a midshipman in April 1826, appointed from the state of Pennsylvania. During the next decade he served in a number of ships, among them the frigate ''Brandywine'' (during the later 1820s and early 1830s) and sloop-of-war ''Saint Louis'' (in the mid-1830s). He was promoted to lieutenant in December 1837 and was subsequently assigned to the U.S. Coast Survey, the New York Navy Yard, the steamer ''Fulton'' and storeship ''Erie''. Beginning in the mid-1840s his Navy service became intermittent, with a long period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia. Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, was founded by the Phoenicians.Strabo, '' Geographica'' 3.5.5 In the 18th century, the Port in the Bay of Cádiz consolidated as the main harbor of mainland Spain, enjoying the virtual monopoly of trade with the Americas until 1778. It is also the site of the University of Cádiz. Situated on a narrow slice of land surrounded by the sea‚ Cádiz is, in most respects, a typically Andalusian city with well-preserved historical landmarks. The older part of Cádiz, within the remnants of the city walls, is commonly referred to as the Old Town (Spanish: ''Casco Antiguo''). It is characterized by the antiquity of its various quarters (''barrios''), among them ''El Pópulo'', ''La Viña'', and ''Santa María'', which present a marked contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Order Of The Loyal Legion Of The United States
The Military Order of the Loyal Legion of the United States (MOLLUS), or simply the Loyal Legion is a United States patriotic order, organized April 15, 1865, by three veteran officers of the Army. The original membership was composed of members of the Army, Navy, or Marine Corps of the United States, who had served during the American Civil War as commissioned officers in Federal service, or who had served and thereafter been commissioned, and who thereby "had aided in maintaining the honor, integrity, and supremacy of the national movement" during the Civil War. The Loyal Legion was formed by in response to rumors from Washington of a conspiracy to destroy the Federal government by assassination of its leaders, in the immediate aftermath of the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln. The founding members stated their purpose as the cherishing of the memories and associations of the war waged in defense of the unity and indivisibility of the Republic; the strengthening of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau, Bahamas, Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama Islands were inhabited by the Lucayan people, Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-Taino language, speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receiving Ship
A hulk is a ship that is afloat, but incapable of going to sea. Hulk may be used to describe a ship that has been launched but not completed, an abandoned wreck or shell, or to refer to an old ship that has had its rigging or internal equipment removed, retaining only its buoyant qualities. The word hulk also may be used as a verb: a ship is "hulked" to convert it to a hulk. The verb was also applied to crews of Royal Navy ships in dock, who were sent to the receiving ship for accommodation, or "hulked". Hulks have a variety of uses such as housing, prisons, salvage pontoons, gambling sites, naval training, or cargo storage. In the days of sail, many hulls served longer as hulks than they did as functional ships. Wooden ships were often hulked when the hull structure became too old and weak to withstand the stresses of sailing. More recently, ships have been hulked when they become obsolete or when they become uneconomical to operate. Sheer hulk A sheer hulk (or shear hulk) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Squadron
The Pacific Squadron was part of the United States Navy squadron stationed in the Pacific Ocean in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially with no United States ports in the Pacific, they operated out of storeships which provided naval supplies and purchased food and obtained water from local ports of call in the Hawaiian Islands and towns on the Pacific Coast. Throughout the history of the Pacific Squadron, American ships fought against several enemies. Over one-half of the United States Navy would be sent to join the Pacific Squadron during the Mexican–American War. During the American Civil War, the squadron was reduced in size when its vessels were reassigned to Atlantic duty. When the Civil War was over, the squadron was reinforced again until being disbanded just after the turn of the 20th century. History Formation The "United States Naval Forces on Pacific Station" was established in 1818, with the HMS Macedonian#As USS Macedonian, USS ''Macedonian'' under Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Scourge (1846)
USS ''Scourge'' was a steamer warship in service during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). She was the third United States Navy ship of that name. Acquisition The ship was launched on 29 May 1845 by Betts, Harlan, and Hollingsworth of Wilmington, Delaware as merchant steamer ''Bangor''. She was powered by twin screws and was the first iron-hulled, sea-going merchant vessel in the United States. She ran between Bangor and Boston in 1845 and 1846. On 1 September 1846 ''Bangor'' caught on fire and was run aground. She was rebuilt and continued the Bangor-Boston route and she was bought by the U.S. Government on 30 December 1846 for the Mexican War. Once equipped, she was renamed ''Scourge.'' Service USS ''Scourge'' joined the forces of Commodore Matthew C. Perry in the Gulf of Mexico on March 29, 1847. She was part of the " Mosquito Flotilla" and was immediately assigned to take part in a concerted sea-land attack upon the port of Alvarado. *On 7 March 1847, commanded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
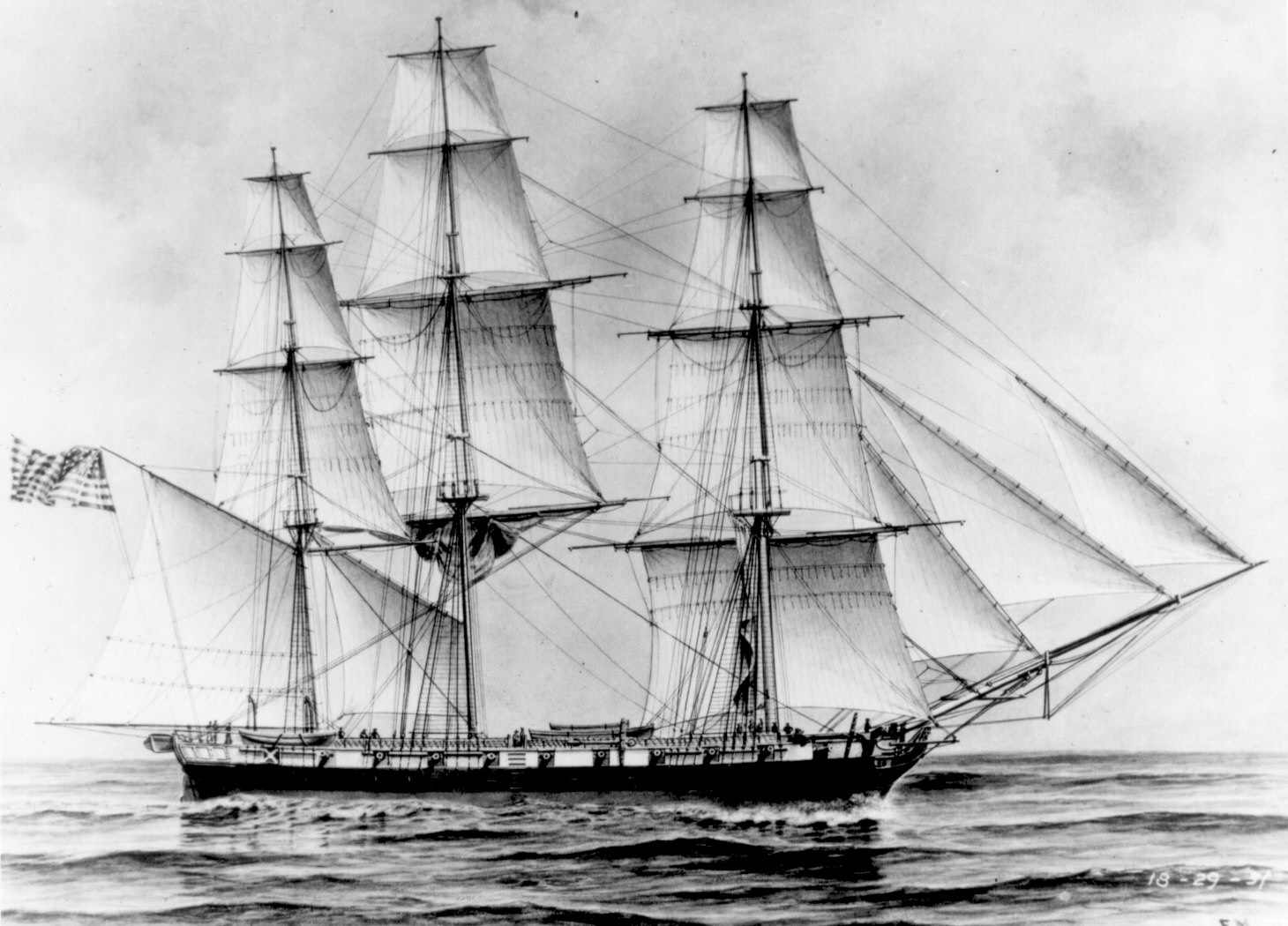
USS Erie (1813)
USS ''Erie'' was a three-masted, wooden-hulled sloop-of-war of the United States Navy in the early 19th century. Launch ''Erie'' was launched 3 November 1813 by Thomas Kemp, Baltimore, Maryland; and first put to sea 20 March 1814, Commander Charles G. Ridgeley in command. Service in the Mediterranean Unable to reach the open sea because of the British blockade at Hampton Roads, Erie was forced to return to Baltimore 7 April 1814 where she remained berthed at Baltimore without a crew until early in 1815. On 8 May she sailed to Boston, Massachusetts to join Commodore William Bainbridge's squadron sailing for the Mediterranean 2 July. With peace concluded with Algiers before the squadron reached the area, the squadron returned to the United States, leaving ''Erie'' to cruise with the naval force assigned to protect commerce and guard against any further disturbance of peace by the Barbary States. She remained on station for 4 years, sailing from Gibraltar for home 27 No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Fulton (1837)
USS ''Fulton'' was a steamer that served the U.S. Navy prior to the American Civil War, and was recommissioned in time to see service in that war. However, her participation was limited to being captured by Confederate forces in the port of Pensacola, Florida, at the outbreak of war. The second ship to be named ''Fulton'' by the Navy, a side wheel steamer, her build commenced in 1835, and she was launched 18 May 1837 by Brooklyn Navy Yard; and commissioned 13 December 1837, Captain M. C. Perry in command. She was often called ''Fulton II''. ''Fulton I'' was the renamed floating battery ''Demologos''. Service in the North Atlantic ''Fulton'' cruised the Atlantic coast, aiding ships in distress, conducting ordnance experiments, and training officers in gunnery. A major event of her early service came on 23 November 1838, when she bested the British steamer in a speed contest off New York. In 1841, Captain John T. Newton was in command of ''Fulton''. Experiments in gunne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships came into practical usage during the early 1800s; however, there were exceptions that came before. Steamships usually use the prefix designations of "PS" for ''paddle steamer'' or "SS" for ''screw steamer'' (using a propeller or screw). As paddle steamers became less common, "SS" is assumed by many to stand for "steamship". Ships powered by internal combustion engines use a prefix such as "MV" for ''motor vessel'', so it is not correct to use "SS" for most modern vessels. As steamships were less dependent on wind patterns, new trade routes opened up. The steamship has been described as a "major driver of the first wave of trade globalization (1870–1913)" and contributor to "an increase in international trade that was unprecedented in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Navy Yard
The Brooklyn Navy Yard (originally known as the New York Navy Yard) is a shipyard and industrial complex located in northwest Brooklyn in New York City, New York (state), New York. The Navy Yard is located on the East River in Wallabout Bay, a semicircular bend of the river across from Lower East Side#Corlears Hook, Corlears Hook in Manhattan. It is bounded by Navy Street to the west, Flushing Avenue to the south, Kent Avenue to the east, and the East River on the north. The site, which covers , is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The Brooklyn Navy Yard was established in 1801. From the early 1810s through the 1960s, it was an active shipyard for the United States Navy, and was also known as the United States Naval Shipyard, Brooklyn and New York Naval Shipyard at various points in its history. The Brooklyn Navy Yard produced wooden ships for the U.S. Navy through the 1870s, and steel ships after the American Civil War in the 1860s. The Brooklyn Navy Yard has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast Survey
United may refer to: Places * United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Films * ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film * ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two film Literature * ''United!'' (novel), a 1973 children's novel by Michael Hardcastle Music * United (band), Japanese thrash metal band formed in 1981 Albums * ''United'' (Commodores album), 1986 * ''United'' (Dream Evil album), 2006 * ''United'' (Marvin Gaye and Tammi Terrell album), 1967 * ''United'' (Marian Gold album), 1996 * ''United'' (Phoenix album), 2000 * ''United'' (Woody Shaw album), 1981 Songs * "United" (Judas Priest song), 1980 * "United" (Prince Ital Joe and Marky Mark song), 1994 * "United" (Robbie Williams song), 2000 * "United", a song by Danish duo Nik & Jay featuring Lisa Rowe Television * ''United'' (TV series), a 1990 BBC Two documentary series * ''United!'', a soap opera that aired on BBC One from 1965-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)




.jpg)