|
Richard Smith (mining Engineer)
Richard Smith (January 30, 1783 – July 21, 1868) was an English-born mining engineer, industrialist and politician. He represented Cape Breton County in the Nova Scotia House of Assembly from 1833 to 1834. Between 1836 and 1864, Smith was the mineral agent for the estate of the Lords of Dudley. Life Richard Smith was born in Tipton, Staffordshire, the son of Thomas Smith and Mary Morris, and was educated at the Royal School of Mines. In 1811, he married Elizabeth Fereday. Smith and his father-in-law suffered financial losses when the coal and iron market collapsed at the end of the Napoleonic Wars. He subsequently set himself up in business again in London and also managed coal operations in Wales and Portugal. In 1824 he was engaged by Baron Rothschild to manage his estates in North and South Wales. In 1827, Smith was hired to establish coal mining operations in Nova Scotia for the General Mining Association. He established sites at Albion Mines (later Stellarton), Sydney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Bras D'Or, Nova Scotia
Little Bras d'Or is a community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality on Cape Breton County on Cape Breton Island. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, which is sli ... conducted by Statistics Canada, Little Bras D'Or had a population of 148 living in 64 of its 68 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of 135. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. References Little Bras d'Or on Destination Nova Scotia Communities in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality Designated places in Nova Scotia {{CapeBretonNS-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia Pre-Confederation MLAs
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. They are likely created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. When the orbital period falls in the range of several days to one day, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to start drawing accreted matter onto the surface of the white dwarf, which creates a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Tipton
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 Deaths
Events January–March * January 2 – British Expedition to Abyssinia: Robert Napier leads an expedition to free captive British officials and missionaries. * January 3 – The 15-year-old Mutsuhito, Emperor Meiji of Japan, declares the ''Meiji Restoration'', his own restoration to full power, under the influence of supporters from the Chōshū and Satsuma Domains, and against the supporters of the Tokugawa shogunate, triggering the Boshin War. * January 5 – Paraguayan War: Brazilian Army commander Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, Duke of Caxias enters Asunción, Paraguay's capital. Some days later he declares the war is over. Nevertheless, Francisco Solano López, Paraguay's president, prepares guerrillas to fight in the countryside. * January 7 – The Arkansas constitutional convention meets in Little Rock. * January 9 – Penal transportation from Britain to Australia ends, with arrival of the convict ship ''Hougoumont'' in Western Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1783 Births
Events January–March * January 20 – At Versailles, Great Britain signs preliminary peace treaties with the Kingdom of France and the Kingdom of Spain. * January 23 – The Confederation Congress ratifies two October 8, 1782, treaties signed by the United States with the United Netherlands. * February 3 – American Revolutionary War: Great Britain acknowledges the independence of the United States of America. At this time, the Spanish government does not grant diplomatic recognition. * February 4 – American Revolutionary War: Great Britain formally declares that it will cease hostilities with the United States. * February 5 – 1783 Calabrian earthquakes: The first of a sequence of five earthquakes strikes Calabria, Italy (February 5–7, March 1 & 28), leaving 50,000 dead. * February 7 – The Great Siege of Gibraltar is abandoned. * February 26 – The United States Continental Army's Corps of Engineers is disbanded. * March 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
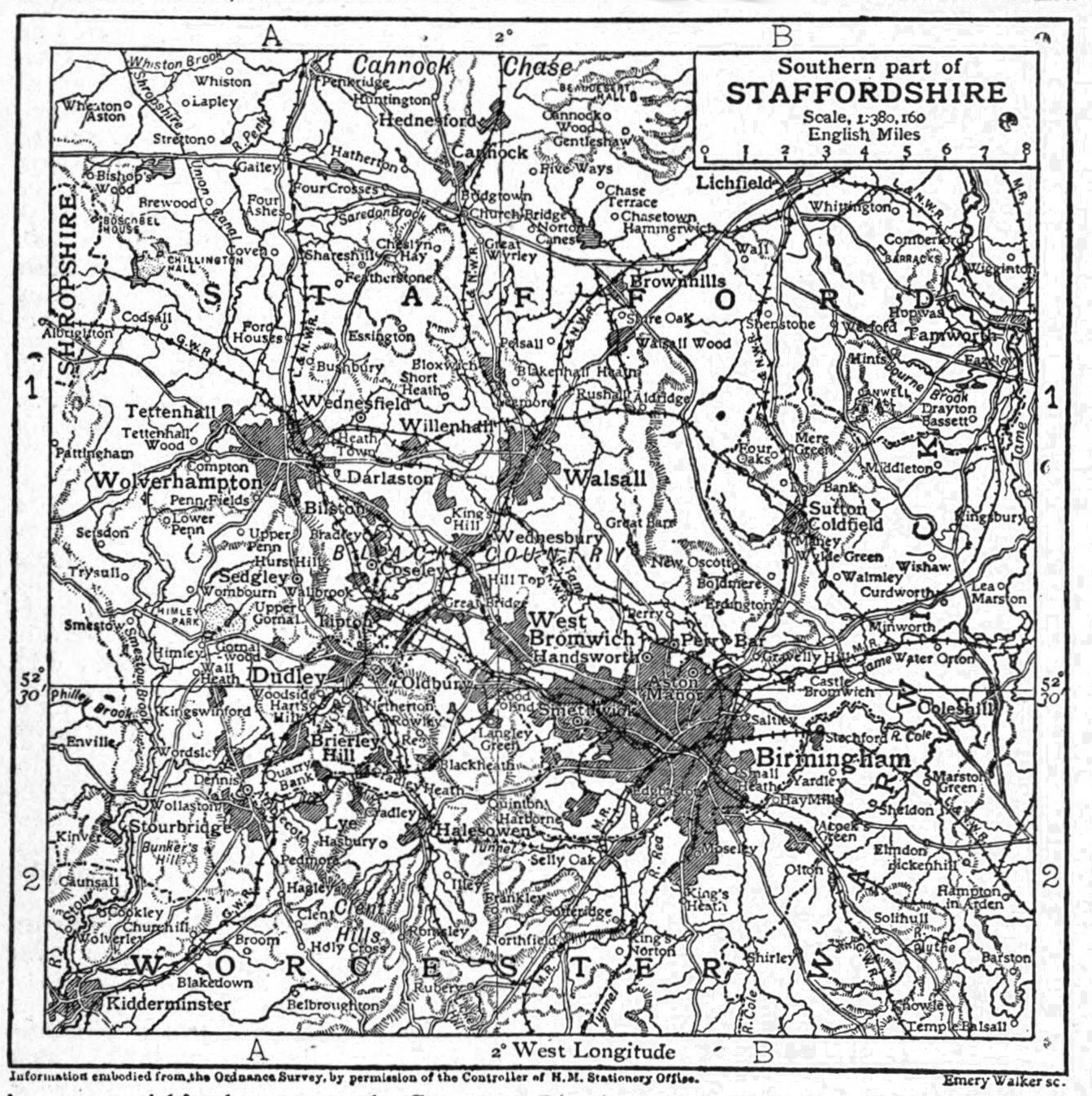
Lichfield
Lichfield () is a cathedral city and civil parish in Staffordshire, England. Lichfield is situated roughly south-east of the county town of Stafford, south-east of Rugeley, north-east of Walsall, north-west of Tamworth and south-west of Burton Upon Trent. At the time of the 2011 Census, the population was estimated at 32,219 and the wider Lichfield District at 100,700. Notable for its three-spired medieval cathedral, Lichfield was the birthplace of Samuel Johnson, the writer of the first authoritative ''Dictionary of the English Language''. The city's recorded history began when Chad of Mercia arrived to establish his Bishopric in 669 AD and the settlement grew as the ecclesiastical centre of Mercia. In 2009, the Staffordshire Hoard, the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver metalwork, was found south-west of Lichfield. The development of the city was consolidated in the 12th century under Roger de Clinton, who fortified the Cathedral Close and also laid ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Oak Steelworks
The Round Oak Steelworks was a steel production plant in Brierley Hill, West Midlands (formerly Staffordshire), England. It was founded in 1857 by Lord Ward, who later became, in 1860, The 1st Earl of Dudley, as an outlet for pig iron made in the nearby blast furnaces. During the Industrial Revolution, the majority of iron-making in the world was carried out within 32 kilometres of Round Oak. For the first decades of operation, the works produced wrought iron. However, in the 1890s, steelmaking was introduced. At its peak, thousands of people were employed at the works. The steelworks was the first in the United Kingdom to be converted to natural gas, which was supplied from the North Sea. The works were nationalized in 1951, privatized in 1953 and nationalized again in 1967 although the private firm Tube Investments continued to part manage the operations at the site. The steelworks closed in December 1982. History The Round Oak Iron Works The Ward family, Lords of Dudley Castle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Dudley’s Railway
The Earl of Dudley’s Railway or Pensnett Railway, was a railway that developed from a single line opened in 1829 to, at its maximum extent, a long network around the Earl of Dudley’s Iron Works at Round Oak near Brierley Hill. History Origins In the 19th century, the Ward family, owners of Dudley Castle, had large holdings of land in the Black Country region of England. They had added to their possessions in the 18th century by the enclosure of Pensnett Chase which had formerly been common land and, much further back in time, a hunting ground for the Barons of Dudley. Much of this land covered coal seams and deposits of industrial material including iron ore and fire-clay. Canals had been cut into the Black Country region in the second half of the 18th century but not all were conveniently close to the mines of the Dudley Estate. It was therefore decided to construct a railway linking coal mines near Shut End to a purpose-built canal basin at Ashwood on the Staffo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Country
The Black Country is an area of the West Midlands county, England covering most of the Metropolitan Boroughs of Dudley, Sandwell and Walsall. Dudley and Tipton are generally considered to be the centre. It became industrialised during its role as one of the birth places of the Industrial Revolution across the English Midlands with coal mines, coking, iron foundries, glass factories, brickworks and steel mills, producing a high level of air pollution. The name dates from the 1840s, and is believed to come from the soot that the heavy industries covered the area in, although the 30-foot-thick coal seam close to the surface is another possible origin. The road between Wolverhampton and Birmingham was described as "one continuous town" in 1785. Extent The Black Country has no single set of defined boundaries. Some traditionalists define it as "the area where the coal seam comes to the surface – so West Bromwich, Coseley, Oldbury, Blackheath, Cradley Heath, Old Hill, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Young (Nova Scotia Politician)
Sir William Young, (8 September 1799 – 8 May 1887) was a Nova Scotia politician and jurist. Born in Falkirk, the son of John Young and Agnes Renny, Young was first elected to the Nova Scotia House of Assembly in 1836 as a Reformer (or Liberal) and, as a lawyer, defended Reform journalists accused of libel. When responsible government was instituted in 1848, Young hoped to become the first Premier but was passed over in favour of fellow reformer James Boyle Uniacke and Young became Speaker. However, Young succeeded Uniacke in 1854. His government was accused of overlooking Catholics and tensions with Catholics were exacerbated by Joseph Howe's rupture with Nova Scotia's Irish Catholic community over his recruitment of Americans to fight on the British side in the Crimean War. In February 1857, ten Catholic and two Protestant Liberals voted with the Tories to bring down Young's government. Young returned to power in January 1860 when the Tory government was unable to comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgeport, Nova Scotia
Bridgeport is a neighbourhood that is part of the former town of Glace Bay, Nova Scotia in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality Cape Breton Regional Municipality (often referred to as simply "CBRM") is the Canadian province of Nova Scotia's second largest municipality and the economic heart of Cape Breton Island. As of 2016 the municipality has a population of 94,285. The ... on Cape Breton Island. References Bridgeport on Destination Nova Scotia Communities in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality General Service Areas in Nova Scotia {{CapeBretonNS-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)



.jpg)