|
Richard Rede
Richard Rede (died after 1416) was a leading Irish statesman and judge of the late fourteenth and early fifteenth centuries. He held office as Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer, Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, Deputy Lord Chancellor of Ireland and Deputy Treasurer of Ireland.Ball, F. Elrington ''The Judges in Ireland 1221-1921'' John Murray London 1926 Vol. 1 pp.171-2 He was born in County Meath. Rede (also spelt Reid) had been a common Irish name, especially in Ulster, since the thirteenth century. Little seems to be known about his parents. His wife was Elizabeth Netterville, daughter and heiress of Richard Netterville of Dowth. One branch of the Netterville family would later become one of the most prominent landowning families in Meath, and acquired the title Viscount Netterville. Rede is best remembered for being kidnapped and held for ransom by the Fleming family, Barons of Slane. They extracted a large sum of money from him, and despite his outraged protests, escaped punish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Baron Of The Irish Exchequer
The Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer was the Baron (judge) who presided over the Court of Exchequer (Ireland). The Irish Court of Exchequer was a mirror of the equivalent court in England and was one of the four courts which sat in the building which is still called The Four Courts in Dublin. The title Chief Baron was first used in 1309 by Walter de Islip. In the early centuries of its existence, it was a political as well as a judicial office, and as late as 1442 the Lord Treasurer of Ireland thought it necessary to recommend that the Chief Baron should always be a properly trained lawyer (which Michael Gryffin, the Chief Baron at the time, was not). There is a cryptic reference in the Patent Roll for 1390 to the Liberty of Ulster having its own Chief Baron. The last Chief Baron, The Rt Hon. Christopher Palles, continued to hold the title after the Court was merged into a new High Court of Justice in Ireland in 1878, until his retirement in 1916, when the office lapsed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, historic county in South East England, southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London, with small sections in neighbouring ceremonial counties. Three rivers provide most of the county's boundaries; the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Lea to the east and the River Colne, Hertfordshire, Colne to the west. A line of hills forms the northern boundary with Hertfordshire. Middlesex county's name derives from its origin as the Middle Saxons, Middle Saxon Province of the Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex, with the county of Middlesex subsequently formed from part of that territory in either the ninth or tenth century, and remaining an administrative unit until 1965. The county is the List of counties of England by area in 1831, second smallest, after Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Privy Council
The Privy Council of England, also known as His (or Her) Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council (), was a body of advisers to the sovereign of the Kingdom of England. Its members were often senior members of the House of Lords and the House of Commons, together with leading churchmen, judges, diplomats and military leaders. The Privy Council of England was a powerful institution, advising the sovereign on the exercise of the royal prerogative and on the granting of royal charters. It issued executive orders known as Orders in Council and also had judicial functions. History During the reigns of the Norman monarchs, the English Crown was advised by a (Latin for "royal court"), which consisted of magnates, clergy and officers of the Crown. This body originally concerned itself with advising the sovereign on legislation, administration and justice. Later, different bodies assuming distinct functions evolved from the court. The courts of law took over the business of dispensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV Of England
Henry IV ( April 1367 – 20 March 1413), also known as Henry Bolingbroke, was King of England from 1399 to 1413. He asserted the claim of his grandfather King Edward III, a maternal grandson of Philip IV of France, to the Kingdom of France. Henry was the first English ruler since the Norman Conquest, over three hundred years prior, whose mother tongue was English rather than French. Henry was the son of John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster, himself the son of Edward III. John of Gaunt was a power in England during the reign of Henry's cousin Richard II. Henry was involved in the revolt of the Lords Appellant against Richard in 1388, resulting in his exile. After John died in 1399, Richard blocked Henry's inheritance of his father's duchy. That year, Henry rallied a group of supporters, overthrew and imprisoned Richard II, and usurped the throne, actions that later would lead to what is termed the Wars of the Roses and a more stabilized monarchy. As king, Henry faced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cornwalsh
James Cornwalsh (died 1441) was an Irish judge who held the office of Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer. He was a political figure of considerable importance in fifteenth-century Ireland, and a supporter of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, James Butler, 4th Earl of Ormond.Beresford, David "Cornwalsh, James ''Cambridge Dictionary of Irish Biography'' 2009 He was murdered as a result of a feud over the possession of Baggotrath Castle, near Dublin.Smith, J. Huband "The Castle and Manor of Baggotrath" (1856) ''Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy (1836-1869)'' Vol.6 p.306 Family He was born in Ireland, the son of William Cornwalsh: as their name suggests, the Cornwalsh family had come to Ireland from Cornwall in the fourteenth century.Otway-Ruthven, A.J. ''History of Mediaeval Ireland'' Barnes and Noble 1993 p.115 The name has several alternative spellings, such as Cornwalysch and Cornwallis. He was probably descended from Sir John de Cornwall or Cornwaille, Constable of Carlow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ransom
Ransom is the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release, or the sum of money involved in such a practice. When ransom means "payment", the word comes via Old French ''rançon'' from Latin ''redemptio'' = "buying back": compare " redemption". Ransom cases Julius Caesar was captured by pirates near the island of Pharmacusa, and held until someone paid 50 talents to free him. In Europe during the Middle Ages, ransom became an important custom of chivalric warfare. An important knight, especially nobility or royalty, was worth a significant sum of money if captured, but nothing if he was killed. For this reason, the practice of ransom contributed to the development of heraldry, which allowed knights to advertise their identities, and by implication their ransom value, and made them less likely to be killed out of hand. Examples include Richard the Lion Heart and Bertrand du Guesclin. In 1532, Francisco Pizarro was paid a rans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized, such as a relative, employer, law enforcement or government to act, or refrain from acting, in a certain way, often under threat of serious physical harm or death to the hostage(s) after expiration of an ultimatum. The ''Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition'' (1910-1911) defines a hostage as "a person who is handed over by one of two belligerent parties to the other or seized as security for the carrying out of an agreement, or as a preventive measure against certain acts of war." A party who seizes one or more hostages is known as a hostage-taker; if the hostages are present voluntarily, then the receiver is known as a host. In civil society, along with kidnapping for ransom and human trafficking (often willing to ransom its captives when lucrative or to trade on influence), hostage taking is a cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Fleming, 2nd Baron Slane
Thomas Fleming (1358-1435), 2nd Baron Slane, was a member of the Parliament of Ireland from 1394-1395, and again from 1401-12. He is mainly remembered for kidnapping the senior judge Richard Rede, from whom he extorted a large ransom. He managed to escape punishment for the crime. Background Thomas was the son of Simon Fleming, 1st Baron Slane, and his wife Cecily Champernowne, daughter of Sir Thomas Champernowne of Modbury, Devon and Eleanor de Rohart. He was the Commander of the Guardians of the Peace in County Meath in about 1385, and again in 1400. He was knighted in 1396. In 1412 he was licensed to hold a market and fair at Drumconrath in County Meath. Abduction of Richard Rede From what is known of his character, Thomas seems to have been ruthless, determined and unscrupulous. The marriage of the wealthy heiress Elizabeth Netterville of Dowth to Richard Rede, Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer, had given grave offence to other landowning families in Meath, who had hoped to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skryne
Skryne or Skreen (), is a village situated on and around a hill between the N2 and N3 national primary roads in County Meath, Ireland. It is situated on the far side of the Gabhra valley from the Hill of Tara. This valley is sometimes referred to as the Tara-Skryne Valley. The Hill of Skryne is higher than the neighbouring Hill of Tara. About 1170 Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath granted Skryne to Adam de Feypo, whose descendants used the customary title Baron Skryne Baron Skryne was the title of the holder of an Irish feudal barony: the title derived from the parish of Skryne, or Skreen, in County Meath. It was not recognised as a barony in the Peerage of Ireland, but was habitually used firstly by the de Feyp ..., which was not a peerage in the strict sense. A 15th-century church, known locally as Skryne Church, Skryne tower or The Steeple, remains in good condition at the top of the hill and is visible from a large area of Meath. At the foot of the tower is a pub and stables tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim, County Meath
Trim () is a town in County Meath, Ireland. It is situated on the River Boyne and has a population of 9,194. The town is noted for Trim Castle – the largest Norman castle in Ireland. One of the two cathedrals of the United Dioceses of Meath and Kildare — St Patrick's cathedral — is located north of the river. Trim won the Irish Tidy Towns Competition in 1972, 1984, 2014 and 2022, and was the "joint" winner with Ballyconnell in 1974. Trim was historically the county town of Meath, but this title was passed on in 1898 to the larger, neighbouring town of Navan. History Early history At an early date, a monastery was founded at Trim, which lay within the petty kingdom ('' tuath'') of the Cenél Lóegairi. It is traditionally thought to have been founded by St. Patrick and left in the care of its patron saint Lommán, also locally known as Loman, who flourished sometime between the 5th and early 6th centuries.Stalmans and Charles-Edwards, "Meath, saints of (act. ''c''.4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
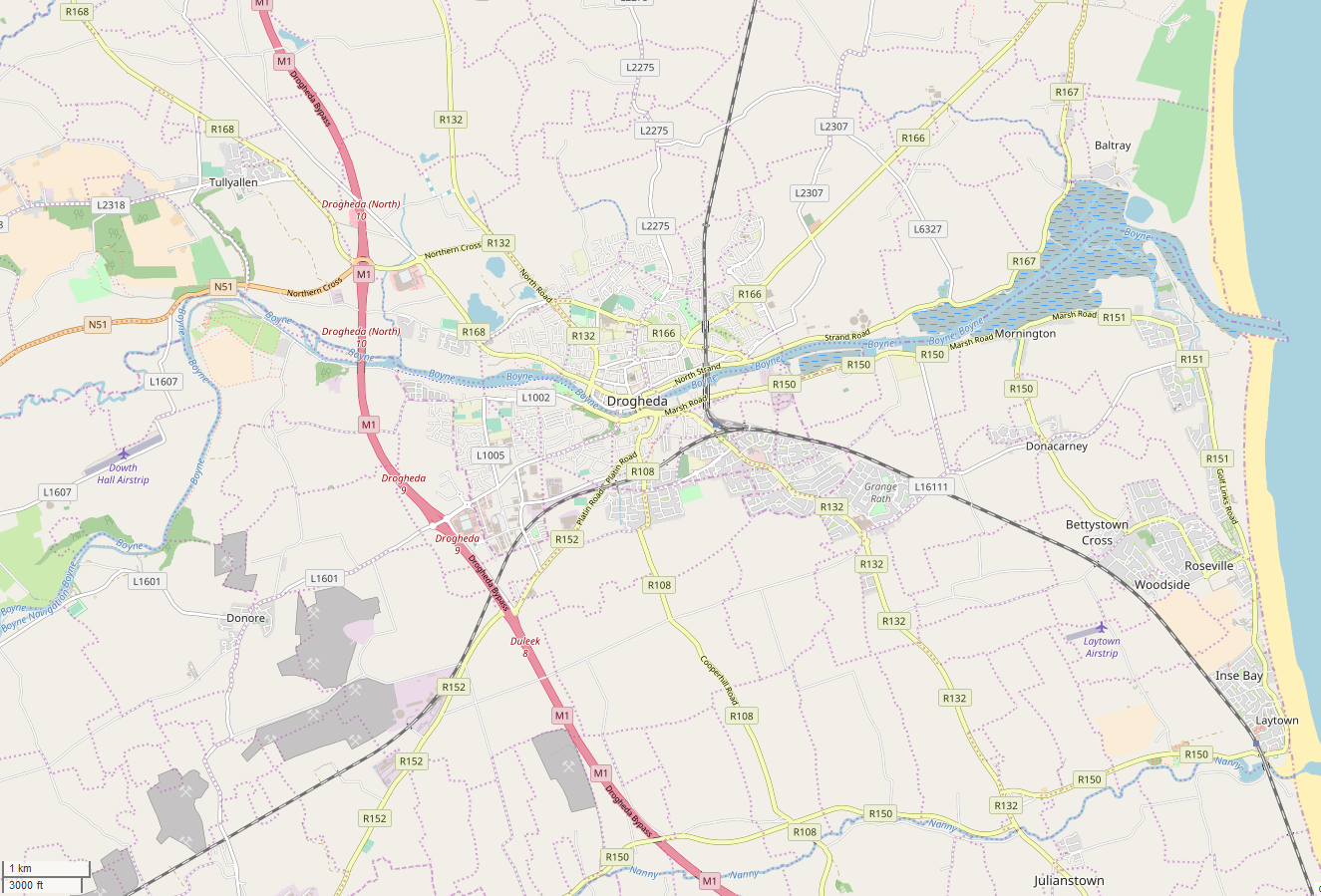
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin. Drogheda has a population of approximately 41,000 inhabitants (2016), making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in the Republic of Ireland by both population and area. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Meath, Lordship and Liberty of Meath, from which a charter was granted in 1194) and Drogheda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cranley
Thomas Cranley DD a.k.a. Thomas Craule ( c.1340–1417) was a leading statesman, judge and cleric in early fifteenth-century Ireland, who held the offices of Chancellor of Oxford University, Archbishop of Dublin and Lord Chancellor of Ireland. Early career He was born in England about 1340; little seems to be known about his family. He entered the Carmelite order. He is recorded as a Fellow of Merton College, Oxford, in 1366. He became Warden of New College in 1389 and Chancellor of the University of Oxford in 1390. He was a Doctor of Divinity and a judge. Irish career In 1397, on the death of Richard Northalis, he was made Archbishop of Dublin and arrived in Ireland the following year. After the accession of King Henry IV, Cranley undertook a diplomatic mission to Rome, and was made Lord Chancellor of Ireland in 1401. When Henry's son Thomas, Duke of Clarence, was made Lord Deputy of Ireland, Cranley was appointed to his council. A letter which he sent to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)