|
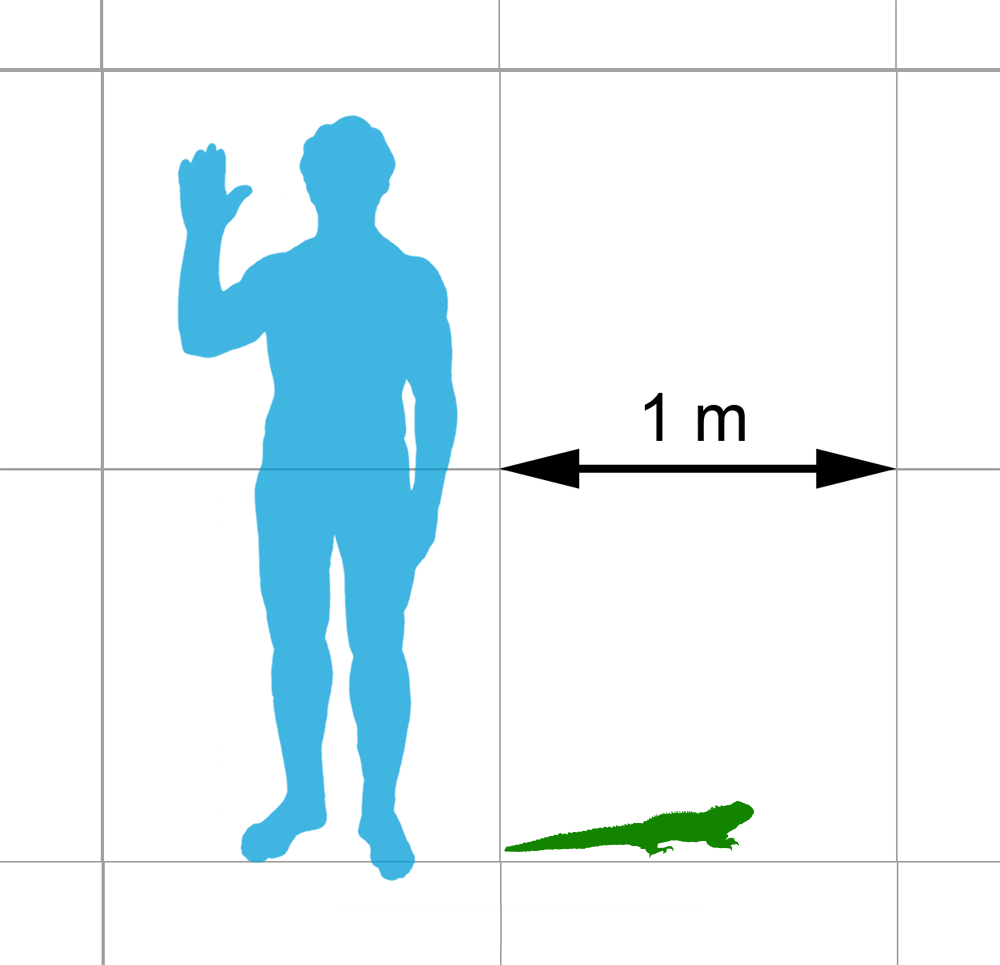
Rhynchocephalian
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse group including a wide array of morphologically distinct forms. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Many of the niches occupied by lizards today were held by sphenodontians during the Triassic and Jurassic, although lizard diversity began to overtake sphenodontian diversity in the Cretaceous, and they had disappeared almost entirely by the beginning of the Cenozoic. While the modern tuatara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godavarisaurus
''Godavarisaurus'' was a sphenodontid reptile from the Early Jurassic (Hettangian to Pliensbachian) Kota Formation of Andhra Pradesh, India. See also * Rhynchocephalia Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse g ... References Sphenodontia Jurassic lepidosaurs Extinct animals of India Prehistoric reptile genera {{paleo-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenodon Punctatus
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthodontia (reptiles)
Opisthodontia is a proposed clade of sphenodontian reptiles, uniting ''Opisthias'' from the Late Jurassic-earliest Cretaceous of Europe and North America with the Elienodontinae, a group of herbivorous sphenodontians known from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Description Teeth and diet Like other sphenodonts, opisthodonts had acrodont teeth which grew directly from the bone. They had one row of teeth on the lower jaw and two rows on the roof of the mouth. When processing food, their mandibular teeth would have slid between the outer (maxillary) teeth and inner (palatine) teeth. Some opisthodonts, such as '' Sphenotitan'', also had clusters of small teeth on the pterygoid at the center of the mouth roof. Opisthodont teeth were wide, numerous, and tightly-packed for grinding and shredding tough plant matter. Although wide shredding teeth are also known in a few other sphenodontians, such as ''Clevosaurus'' and ''Pelecymala'', the most diverse and long-lasting group of he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planocephalosaurus
''Planocephalosaurus'' is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian. Fossils of the genus were found in the Tecovas Formation of Texas and the Magnesian Conglomerate of England. ''Planocephalosaurus'' was one of the first sphenodonts and bore a strong resemblance to the extant tuatara, albeit much smaller, at only in length. The creature is presumed to have fed on large invertebrates and small vertebrates. Dentition ''Planocephalosaurus'' exhibits very interesting dentition. Initially, it was believed to have been attached to the bone via acrodont tooth implantation, however, after this specimen was exposed to X-radiography it was determined that this animal has a combination of different tooth implantation types. Similar to another rhynchocephalian, ''Diphydontosaurus'', it possesses acrodont teeth in the posterior portion of the jaw, and pleurodont dentition in the anterior portion. ''Planocephalosauruss teeth were also fused with the cartilage, unlike its only extant Extant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanceirosphenodon
''Lanceirosphenodon'' is an extinct genus of sphenodontian from the Late Triassic Candelária Formation of Brazil Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area .... It contains a single species, ''Lanceirosphenodon ferigoloi.'' References {{Sphenodontia Sphenodontia Prehistoric reptile genera Fossil taxa described in 2021 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebbanasaurus
''Rebbanasaurus'' is a small sphenodontian reptile found in the Kota Formation of India. The type specimen is a partial jawbone which has acrodont Acrodonty (from Greek ''akros'' 'highest' + ''dont'' 'tooth') is an anatomical placement of the teeth at the summit of the alveolar ridge of the jaw, without sockets, characteristic of bony fish. Functionally, acrodont tooth implantation may be rela ... teeth. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q28432033 Sphenodontia Jurassic reptiles of Asia Fossil taxa described in 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate groups like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoeosaurus
''Homoeosaurus'' is an extinct genus of sphenodont reptile. It was found in limestone in Bavaria, Germany, as well as in France and the United Kingdom. It was related to the modern tuatara, though it was a considerably more gracile. There were several species varying greatly in size and morphology.G. A. Boulenger, (1891) On British Remains of ''Homœosaurus'', with Remarks on the Classification of the Rhynchocephalia Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse g .... Article in ''Journal of Zoology'' 59(1):167 - 172. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1891.tb06820.x References Jurassic lepidosaurs Sphenodontia Solnhofen fauna Late Jurassic reptiles of Europe Prehistoric reptile genera {{jurassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamarquesaurus
''Lamarquesaurus'' is an extinct genus of sphenodontian from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) of Patagonia. It is known from a single species, ''Lamarquesaurus cabazai''. This genus and species is represented by MML-PV-42, a well-preserved right maxillary bone (including 10 teeth of varying completeness). This bone was found at the Cerro Tortuga site near Lamarque, Argentina, which preserves fossils from the Cretaceous Allen Formation. The discoverer of the Cerro Tortuga locality, Tito Cabaza, is the namesake of the species. Description The maxilla is in length; including missing portions it would have been about long if complete. The inner surface of the maxilla is deeply concave but the outer surface has several scattered pits as well as deep facets above the third and fifth teeth. These facets are reminiscent of those which sphenodonts possess on the lower jaw due to abrasion from teeth of the upper jaw, but this cannot be the case in ''Lamarquesaurus'''s maxilla. This is be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamizinsaurus
''Pamizinisaurus'' is a genus of sphenodontian reptile known from Lower Cretaceous (Albian) Tlayúa Formation of Mexico. A crushed skeleton of a juvenile reptile was found in Tlayua Quarry, in central Mexico. It was named ''Pamizinsaurus tlayuaensis'' by Reynoso in 1997, after the name of the quarry of which it was found. Its skull length is . The fossil was covered in small round osteoderms that could have protected it from predators. Relatives Reynoso (1997) argued that ''Pamizinsaurus'' was a genus of the subfamily Sphenodontinae; grouping it with the modern ''Sphenodon'' (better known as the ''Tuatara''), '' Zapatadon'', '' Cynosphenodon'', ''Homoeosaurus'', ''Sapheosaurus'', and ''Ankylosphenodon ''Ankylosphenodon'' is an extinct species of sphenodontian known from Tepexi de Rodriguez, Mexico. It is known from Early Cretaceous sedimentary deposits from the Tlayua formation. Lifestyle ''Ankylosphenodon'' is thought to have been an aqu ...''. References External ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingitana Anoualae
Mauretania Tingitana (Latin for "Tangerine Mauretania") was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia (or Chellah) and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Mulucha (or Malva) river. Its capital city was Tingis, which is the modern Tangier. Other major cities of the province were Iulia Valentia Banasa, Septem, Rusadir, Lixus and Tamuda. History After the death in 40 AD of Ptolemy of Mauretania, the last Ptolemaic ruler of the Kingdom of Mauretania, in about 44 AD Roman Emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom to the Roman Empire and partitioned it into two Roman provinces: Mauretania Tingitana and Mauretania Caesariensis. The Mulucha (Moulouya River), located around 60 km west of modern Oran, Algeria, became the border separating them. The Roman occupation did not extend very far into the continent. In the far west, the southern limit o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmala
''Sigmala'' was a reptile from the Late Triassic. Distribution ''Sigmala'' lived in the . Classification ''Sigmala'' was named a sphenodont by R.L. Carroll in 1988. See also *Lepidosauromorpha *Lepidosauria The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a subclass or superorder of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata includes snakes, lizards, and amphisbaenians. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, m ... References Fossils of Great Britain Sphenodontia Triassic lepidosaurs Fossil taxa described in 1986 {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_601758.jpg)