|
Rhinesuchus
''Rhinesuchus'' (meaning "rasp crocodile" for the ridged surface texture on its skull bones) is a large temnospondyl amphibian. Remains of the genus are known from the Permian of the South African Karoo Basin's ''Tapinocephalus'' and ''Cistecephalus'' assemblage zones, both belonging to the Beaufort Group. The skull of ''Rhinesuchus'' had a flat triangular shape with blunt snout similar to some of the other large amphibians, and had a palate filled with small sharp teeth, suggesting that it hunted fish. Also, the small eyes were on top of the head suggesting that it approached its prey from below. The name ''Rhinesuchus'' comes from Greek ρίνη (''rhine'') "file, rasp" plus σούχος (''soukhos'') "crocodile" for the skull surface texture: "The upper cranial bones are ornamented by a rather fine reticulation of sharp ridges". (The name does not mean "nose crocodile" (as if from Greek ''rhis, rhinos'' "nose") or refer to the Rhine River in Germany.) The type species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinesuchus
''Rhinesuchus'' (meaning "rasp crocodile" for the ridged surface texture on its skull bones) is a large temnospondyl amphibian. Remains of the genus are known from the Permian of the South African Karoo Basin's ''Tapinocephalus'' and ''Cistecephalus'' assemblage zones, both belonging to the Beaufort Group. The skull of ''Rhinesuchus'' had a flat triangular shape with blunt snout similar to some of the other large amphibians, and had a palate filled with small sharp teeth, suggesting that it hunted fish. Also, the small eyes were on top of the head suggesting that it approached its prey from below. The name ''Rhinesuchus'' comes from Greek ρίνη (''rhine'') "file, rasp" plus σούχος (''soukhos'') "crocodile" for the skull surface texture: "The upper cranial bones are ornamented by a rather fine reticulation of sharp ridges". (The name does not mean "nose crocodile" (as if from Greek ''rhis, rhinos'' "nose") or refer to the Rhine River in Germany.) The type species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
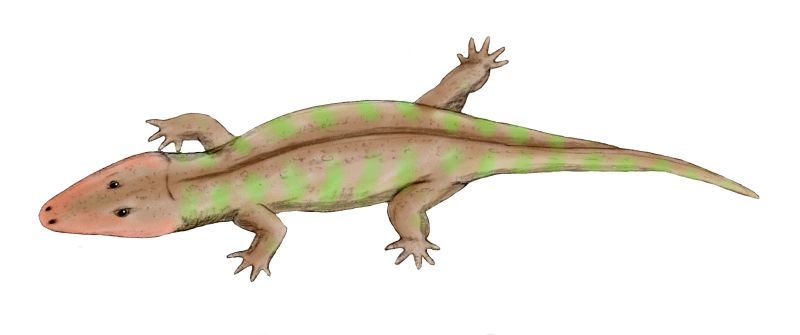
Rhinesuchus BW
''Rhinesuchus'' (meaning "rasp crocodile" for the ridged surface texture on its skull bones) is a large temnospondyl amphibian. Remains of the genus are known from the Permian of the South African Karoo Basin's ''Tapinocephalus'' and ''Cistecephalus'' assemblage zones, both belonging to the Beaufort Group. The skull of ''Rhinesuchus'' had a flat triangular shape with blunt snout similar to some of the other large amphibians, and had a palate filled with small sharp teeth, suggesting that it hunted fish. Also, the small eyes were on top of the head suggesting that it approached its prey from below. The name ''Rhinesuchus'' comes from Greek ρίνη (''rhine'') "file, rasp" plus σούχος (''soukhos'') "crocodile" for the skull surface texture: "The upper cranial bones are ornamented by a rather fine reticulation of sharp ridges". (The name does not mean "nose crocodile" (as if from Greek ''rhis, rhinos'' "nose") or refer to the Rhine River in Germany.) The type species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinesuchoides
''Rhinesuchoides'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric temnospondyl in the family Rhinesuchidae. It contains two species, ''R. tenuiceps'' and ''R. capensis'', both from the Karoo Supergroup of South Africa. The latter was formerly a species of ''Rhinesuchus''. See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accep ... References Stereospondyls {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone
The ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the middle Abrahamskraal Formation, Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The thickest outcrops, reaching approximately , occur from Merweville and Leeu-Gamka in its southernmost exposures, from Sutherland through to Beaufort West where outcrops start to only be found in the south-east, north of Oudshoorn and Willowmore, reaching up to areas south of Graaff-Reinet. Its northernmost exposures occur around the towns Fraserburg and Victoria West. The ''Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone'' is the second biozone of the Beaufort Group. The name of the biozone refers to '' Tapinocephalus atherstonei'', a large herbivorous tapinocephalid dinocephalian therapsid. It is characterised by the presence of this dinocephalian species along with the appearance of other advanced tapinocephalid dinoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone
The ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone found in the Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a majorly fossiliferous and geologically important geological group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops located in the Teekloof Formation north-west of Beaufort West in the Western Cape, in the upper Middleton and lower Balfour Formations respectively from Colesberg of the Northern Cape to east of Graaff-Reinet in the Eastern Cape. The ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be Late Permian in age. The name of the biozone refers to ''Cistecephalus'', a small, burrowing dicynodont therapsid. It is characterized by the presence of this species, known especially from the upper sections of this biozone, and the first appearance of the dicynodont ''Aulacephalodon''. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyli
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had characteristics, such as scales and armour-like bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial animal, terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 80% of the population are Black South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is also not precisely defined. The Karoo is partly defined by its topography, geology and climate, and above all, its low rainfall, arid air, cloudless skies, and extremes of heat and cold.Potgieter, D.J. & du Plessis, T.C. (1972) ''Standard Encyclopaedia of Southern Africa''. Vol. 6. pp. 306–307. Nasou, Cape Town.''Reader’s Digest Illustrated Guide to Southern Africa''. (5th Ed. 1993). pp. 78–89. Reader’s Digest Association of South Africa Pty. Ltd., Cape Town. The Karoo also hosted a well-preserved ecosystem hundreds of million years ago which is now represented by many fossils. The ǃ’Aukarob formed an almost impenetrable barrier to the interior from Cape Town, and the early adventurers, explorers, hunters, and travelers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Group
The Beaufort Group is the third of the main subdivisions of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. It is composed of a lower Adelaide Subgroup and an upper Tarkastad Subgroup. It follows conformably after the Ecca Group and unconformably underlies the Stormberg Group. Based on stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic and biostratigraphic correlations, palynological analyses, and other means of geological dating, the Beaufort Group rocks are considered to range between Middle Permian (Wordian) to Early Triassic (Anisian) in age. Background During the period when sedimentation of the Beaufort Group rocks took place, the Ecca sea had retreated to the northeastern Karoo Basin. All sediment deposition at this time took place in a terrestrial, although in a predominantly fluvial or alluvial environment that was seasonally arid. This environment covered a vast area and deposition was influenced by a retroarc foreland basin. This foreland system was caused by crustal uplift (oro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)


