|
Rhapsody No. 1 (Bartók)
Rhapsody No. 1, Sz. 86, 87, and 88, BB 94 is the first of two virtuoso works for violin and piano, written by Béla Bartók in 1928 and subsequently arranged in 1929 for violin and orchestra, as well as for cello and piano. It is dedicated to Hungarian virtuoso violinist Joseph Szigeti, a close friend of Bartók, who gave the first performance of the orchestra version in Königsberg on 1 November 1929, with Hermann Scherchen conducting the orchestra. Bartók evidently composed both rhapsodies purely as a personal gesture, rather than on commission, and did so without telling anyone until they were both completed. According to the violinist Zoltán Székely, he and the composer met one day in 1928 and, after chatting for a time, Bartók suddenly announced that he had a surprise for him, and produced the manuscripts of the two rhapsodies, which no one else had previously seen. "One is for you; one is for Szigeti," Bartók told him. "You may choose which one you like for the dedica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
András Szőllősy
András Szőllősy (; 27 February 1921 in Orăştie – 6 December 2007 in Budapest) was the creator of the Szőllősy index (abbreviated "Sz."), a frequently used index of the works of Hungarian composer Béla Bartók. Szőllősy studied composition under Zoltán Kodály at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music where he was a professor of music history and theory from 1950 until his death. He was awarded a Ph.D. from the University of Budapest. He won numerous prizes and awards for his own compositions, including Distinguished Composition of the Year 1970 at UNESCO's International Rostrum of Composers in Paris for ''Concerto No. 3 for sixteen strings'', and the 1971 Erkel Prize. In 1985 he won the Kossuth Prize – the highest official recognition of the Hungarian state – and in 1987 he was proclaimed Commandeur of the Ordre des Arts et des Lettres by the French government. He became a member of the Széchenyi Academy of Literature and Arts in 1993 and was awarded the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coda (music)
In music, a coda () ( Italian for "tail", plural ''code'') is a passage that brings a piece (or a movement) to an end. It may be as simple as a few measures, or as complex as an entire section. In classical music The presence of a coda as a structural element in a movement is especially clear in works written in particular musical forms. Codas were commonly used in both sonata form and variation movements during the Classical era. In a sonata form movement, the recapitulation section will, in general, follow the exposition in its thematic content, while adhering to the home key. The recapitulation often ends with a passage that sounds like a termination, paralleling the music that ended the exposition; thus, any music coming after this termination will be perceived as extra material, i.e., as a coda. In works in variation form, the coda occurs following the last variation and will be very noticeable as the first music not based on the theme. One of the ways that Beeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositions For Violin And Orchestra
Composition or Compositions may refer to: Arts and literature * Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography * Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include visuals and digital space * Composition (music), an original piece of music and its creation *Composition (visual arts), the plan, placement or arrangement of the elements of art in a work * ''Composition'' (Peeters), a 1921 painting by Jozef Peeters *Composition studies, the professional field of writing instruction * ''Compositions'' (album), an album by Anita Baker *Digital compositing, the practice of digitally piecing together a video Computer science *Function composition (computer science), an act or mechanism to combine simple functions to build more complicated ones * Object composition, combining simpler data types into more complex data types, or function calls into calling functions History * Composition of 1867, Austro-Hunga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1928 Compositions
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album '' 63/19'' by Kool A.D. * '' Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositions By Béla Bartók
Composition or Compositions may refer to: Arts and literature * Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography *Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include visuals and digital space *Composition (music), an original piece of music and its creation *Composition (visual arts), the plan, placement or arrangement of the elements of art in a work * ''Composition'' (Peeters), a 1921 painting by Jozef Peeters *Composition studies, the professional field of writing instruction * ''Compositions'' (album), an album by Anita Baker *Digital compositing, the practice of digitally piecing together a video Computer science *Function composition (computer science), an act or mechanism to combine simple functions to build more complicated ones *Object composition, combining simpler data types into more complex data types, or function calls into calling functions History *Composition of 1867, Austro-Hungarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Companions To Music
The Cambridge Companions to Music form a book series published by Cambridge University Press Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambr .... Each book is a collection of essays on the topic commissioned by the publisher. on Cambridge University Press website, accessed 21 September 2015. Volumes (sortable table) References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, such as "the arrangement of musical units of rhythm, melody, and/or harmony that show repetition or variation, the arrangement of the instruments (as in the order of solos in a jazz or bluegrass performance), or the way a symphonic piece is orchestrated", among other factors. It is, "the ways in which a composition is shaped to create a meaningful musical experience for the listener."Kostka, Stefan and Payne, Dorothy (1995). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.152. McGraw-Hill. . These organizational elements may be broken into smaller units called phrases, which express a musical idea but lack sufficient weight to stand alone. Musical form unfolds over time through the expansion and development of these ideas. In tonal harmony, form is articulated pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Transylvania
Transylvania, a historical province in present-day Romania, has been historically and culturally more closely linked to Central Europe than Southeastern Europe, and its music reflects those influences. Inhabited by Romanians, Székelys and other Hungarians, Germans, Serbs, Slovaks, Gypsies, and others, Transylvania has long been a center for folk music from all of these different cultures. Bartók and Kodály collected many folk songs from Transylvania early in the 20th century. Kodály's '' Székelyfonó'' (The Spinning Room) uses folk tunes from the area. In our days, Deep Forest included folk songs from Transylvania on their albums. Violin, kontra and double bass, sometimes with a cimbalom, are the most integral ensemble unit. They are used to play a wide variety of songs, including numerous kinds of specific wedding songs. Hungarians from Transylvania, which make up around 20% of the population of the region, are known for their vibrant musical cultures, famous examples bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydian Mode
The modern Lydian mode is a seven-tone musical scale formed from a rising pattern of pitches comprising three whole tones, a semitone, two more whole tones, and a final semitone. : Because of the importance of the major scale in modern music, the Lydian mode is often described as the scale that begins on the fourth scale degree of the major scale, or alternatively, as the major scale with the fourth scale degree raised half a step. This sequence of pitches roughly describes the scale underlying the fifth of the eight Gregorian (church) modes, known as Mode V or the authentic mode on F, theoretically using B but in practice more commonly featuring B. The use of the B as opposed to B would have made such piece in the modern day F major scale. Ancient Greek Lydian The name Lydian refers to the ancient kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, there was a Lydian scale or " octave species" extending from ''parhypate hypaton'' to ''trite diezeugmenon'', equivalent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mureș County
Mureș County (, ro, Județul Mures, hu, Maros megye) is a county ('' județ'') of Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania, with the administrative centre in Târgu Mureș. The county was established in 1968, after the administrative reorganization that re-introduced the historical ''judeţ'' (county) system, still used today. This reform eliminated the previous Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region, which had been created in 1952 within the People's Republic of Romania. Mureș County has a vibrant multicultural fabric that includes Hungarian-speaking Székelys and Transylvanian Saxons, with a rich heritage of fortified churches and towns. Name In Hungarian, it is known as ''Maros megye'' (), and in German as ''Kreis Mieresch''. Under Kingdom of Hungary, a county with an similar name ( Maros-Torda County, ro, Comitatul Mureş-Turda) was created in 1876. There was a county with the same name under the Kingdom of Romania, and a Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region (1960– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
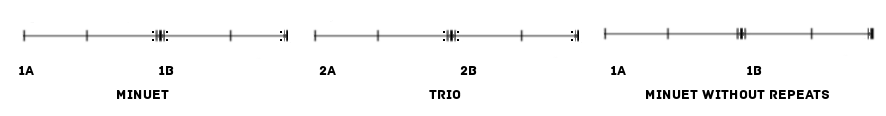
Ternary Form
Ternary form, sometimes called song form, is a three-part musical form consisting of an opening section (A), a following section (B) and then a repetition of the first section (A). It is usually schematized as A–B–A. Prominent examples include the da capo aria "The trumpet shall sound" from Handel's ''Messiah'', Chopin's Prelude in D-Flat Major "Raindrop", ( Op. 28) and the opening chorus of Bach's ''St John Passion''. Simple ternary form In ternary form each section is self-contained both thematically as well as tonally (that is, each section contains distinct and complete themes), and ends with an authentic cadence. The B section is generally in a contrasting but closely related key, usually a perfect fifth above or the parallel minor of the home key of the A section (V or i); however, in many works of the Classical period, the B section stays in tonic but has contrasting thematic material. It usually also has a contrasting character; for example section A might be stif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
László Somfai
László Somfai (born 15 August 1934) is a Hungarian musicologist. He was born in 1934 in Jászladány. He first studied History of Music, graduating in 1959 with a dissertation on the classical string quartet idiom of Joseph Haydn. He went on to earn a PhD in musicology. He is a professor at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music, where he specializes in classical style, Haydn, and Béla Bartók. He has also taught at the City University of New York and the University of California, Berkeley The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u .... Among his work is the BB catalogue of Bartók's compositions. External links Biography at bartokfestival.hu 1934 births Living people Hungarian musicologists International Musicological Society presidents Bartók scholars {{Hungary-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |