|
Revolutions Of Tunis
The Revolutions of Tunis or the Muradid War of Succession was a period of troubles and civil wars in Ottoman Tunisia. It ran from the death of the Muradid sovereign Murad II Bey in 1675 until the seizure of power by the Husainid sovereign Al-Husayn I ibn Ali at-Turki in 1705. The belligerents were Ali Bey al-Muradi and Muhammad Bey al-Muradi (sons of Murad II Bey), their uncle Muhammad al-Hafsi al-Muradi (Pasha of Tunis), several Deys of Tunis, the Turkish militia in Tunis and the Dey of Algiers. Historians agree that the revolutions originated from the constant power conflict between the Muradid dynasty, which attempted to detach itself from Ottoman control and the Turkish militia in Tunis (headed by the divan), which challenged the primacy of the Beys and refused to submit to their increasingly monarchical rule.André Raymond, ''Tunis sous les Mouradites : la ville et ses habitants au XVIIe siècle'', éd. Cérès, Tunis, 2006 The Deys of Tunis found themselves in the middle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
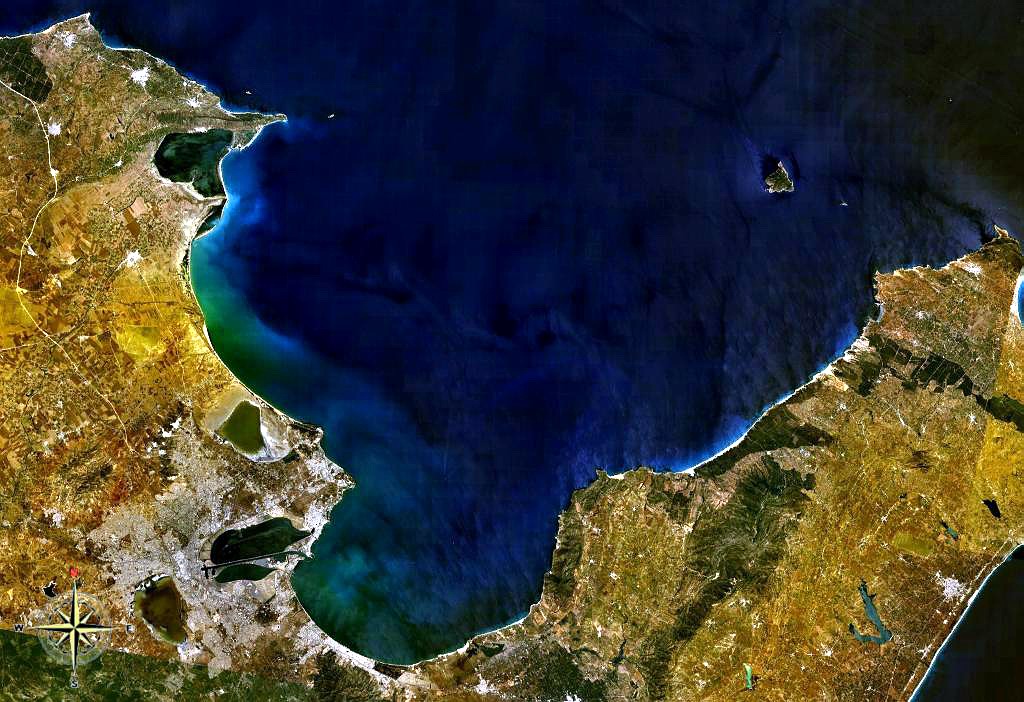
Gulf And Island Of Djerba By Piri Reis
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ..., Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden. See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djebel Ousselat, Tunísia
: ''For mountains or other uses, see: Jabal.'' Djebel (1937–1958) was a French Thoroughbred racehorse, who won 15 of 22 races during 1939–1942 including the Prix d'Essai, 2000 Guineas and Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe. He was later a leading sire in France and is responsible for the survival of the Byerley Turk sire line into the 21st century. Breeding Djebel was a bay stallion owned and bred by renowned horseman Marcel Boussac. He was sired by Tourbillon, who had won the French Derby and the Prix Lupin, and went on to become a notable sire. Djebel's dam, Loika, was a minor winner by Gay Crusader and out of Coeur a Coeur. Gay Crusader was the 1917 U.K. Triple Crown winner, and by the influential Bayardo. Coeur a Coeur was by Teddy, whose grandsire was the 1899 English Triple Crown champion Flying Fox. Therefore, Djebel traced back to Bay Ronald twice through his dam (both Bayardo and Teddy's dam-sire were by Bay Ronald). Loika was originally not a success as a broodmare, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
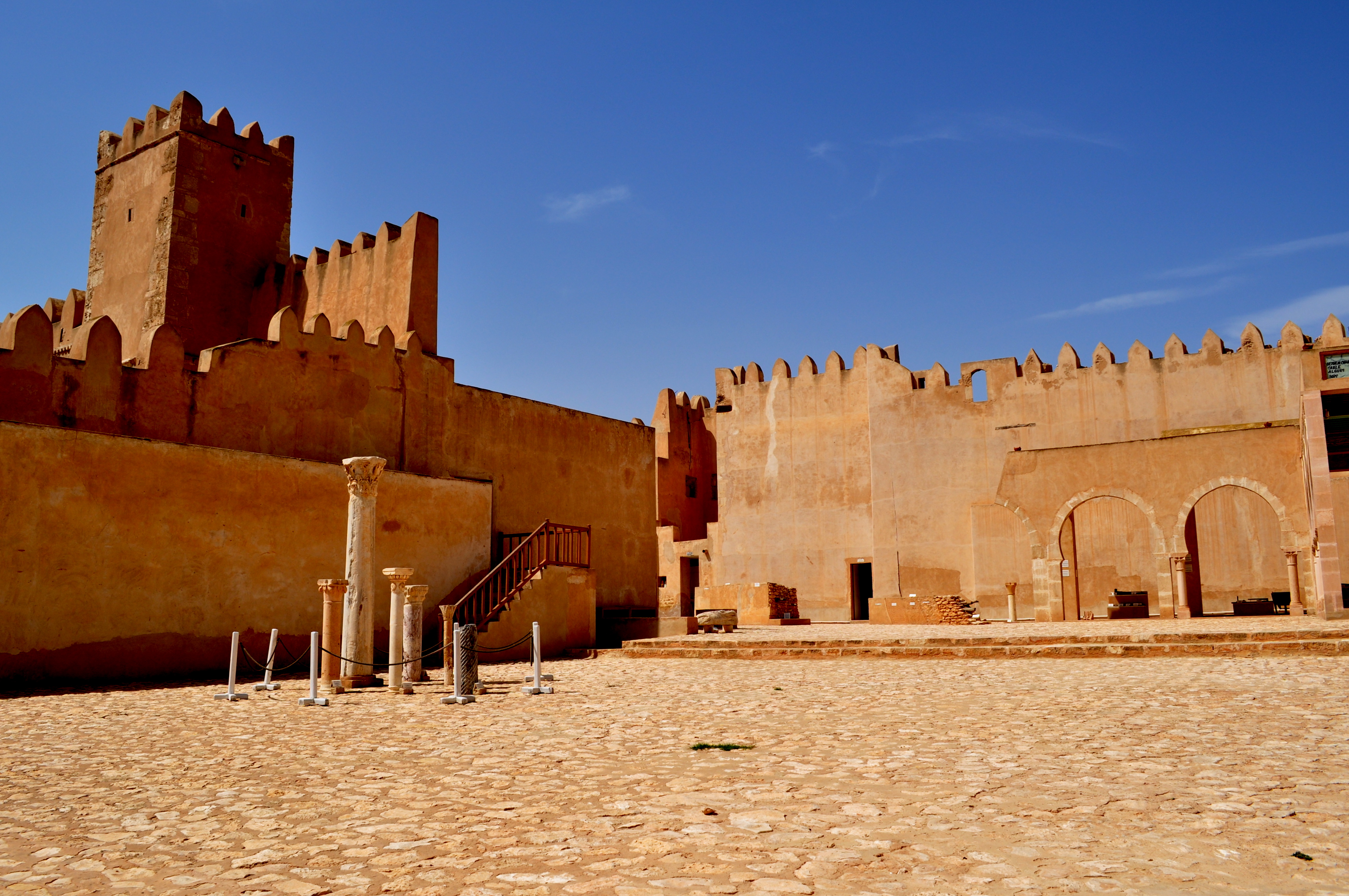
Kasbah
A kasbah (, also ; ar, قَـصَـبَـة, qaṣaba, lit=fortress, , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress, most commonly the citadel or fortified quarter of a city. It is also equivalent to the term ''alcazaba'' in Spanish (), which derives from the same Arabic word. By extension, the term can also refer to a medina quarter, particularly in Algeria. In various languages, the Arabic word, or local words borrowed from the Arabic word, can also refer to a settlement, a fort, a watchtower, or a blockhouse. Citadel or fortress The term ''qasaba'' was historically flexible but it essentially denotes a fortress, commonly a citadel that protects a city or settlement area, or that serves as the administrative center. A kasbah citadel typically housed the military garrison and other privileged buildings such as a palace, along with other amenities such as a mosque and a hammam (bathhouse). Some kasbahs are built in a strategic elevated position o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramadan
, type = islam , longtype = Religious , image = Ramadan montage.jpg , caption=From top, left to right: A crescent moon over Sarıçam, Turkey, marking the beginning of the Islamic month of Ramadan. Ramadan Quran reading in Bandar Torkaman, Iran. Community Iftar meal in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, Tarawah prayers in a mosque in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Foods served at a traditional Iftar meal. Ramadan decorations in Jerusalem. Zakat donation boxes in Taipei, Taiwan. , official_name = , observedby = Muslims , begins = At the last night of the month of Sha'ban , ends = At the last night of the month of Ramadan , date = Variable (follows the Islamic lunar calendar) , date2022 = 2 April – 2 May , celebrations = Community iftars and Community prayers , observances = * Sawm (fasting) * Zakat and sadaqah (alms giving) * Commemorating Qadr Night * Reading the Quran * Abstaining from all bad deeds and staying humble * Taraweeh prayer (Sunni Muslims) , relatedto = Eid al-F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismail Ibn Sharif
Moulay Ismail Ibn Sharif ( ar, مولاي إسماعيل بن الشريف), born around 1645 in Sijilmassa and died on 22 March 1727 at Meknes, was a Sultan of Morocco from 1672–1727, as the second ruler of the Alaouite dynasty. He was the seventh son of Moulay Sharif and was governor of the province of Fez and the north of Morocco from 1667 until the death of his half-brother, Sultan Moulay Rashid in 1672. He was proclaimed sultan at Fez, but spent several years in conflict with his nephew Moulay Ahmed ben Mehrez, who also claimed the throne, until the latter's death in 1687. Moulay Ismail's 55-year reign is the longest of any sultan of Morocco. The reign of Moulay Ismail marked a high watermark for Moroccan power. His military successes are explained by the creation of a strong army, originally relying on the 'Guichs' (especially the Udaya) and on the Black Guard (or Abid al-Bukhari), black slaves who were totally devoted to him. As a result, the central power could be le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mameluke
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') is a term most commonly referring to non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Southern Russian, Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) slave-soldiers and freed slaves who were assigned military and administrative duties, serving the ruling Arab dynasties in the Muslim world. The most enduring Mamluk realm was the knightly military class in Egypt in the Middle Ages, which developed from the ranks of slave-soldiers. Originally the Mamluks were slaves Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ... of Turkic peoples, Turkic orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, cultural and historic hub. The city straddles the Bosporus strait, lying in both Europe and Asia, and has a population of over 15 million residents, comprising 19% of the population of Turkey. Istanbul is the list of European cities by population within city limits, most populous European city, and the world's List of largest cities, 15th-largest city. The city was founded as Byzantium ( grc-gre, Βυζάντιον, ) in the 7th century BCE by Ancient Greece, Greek settlers from Megara. In 330 CE, the Roman emperor Constantine the Great made it his imperial capital, renaming it first as New Rome ( grc-gre, Νέα Ῥώμη, ; la, Nova Roma) and then as Constantinople () after himself. The city grew in size and influence, eventually becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ) * Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province") * Bulgarian: окръг ('' okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region") * el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province") or επαρχία (''eparchia'', meaning "eparchy") * lad, sancak , group=note (; ota, ; Modern Turkish: ''Sancak'', ) were administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire. ''Sanjak'', and the variant spellings ''sandjak'', ''sanjaq'' and ''sinjaq'', are English or French transliterations of the Turkish word ''sancak'', meaning "district", "banner" or "flag". Sanjaks were also called by the Arabic word for ''banner'' or ''flag'': '' liwa (Liwā or Liwā’)''. Ottoman provinces (eyalets, later vilayets) were divided into sanjaks (also called ''livas'') governed by sanjakbeys (also called ''Mutesarriff'') and were further subdivided into ''timars'' (fiefs held by ''timariots''), kadiluks (the area of responsibility of a judge, or K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qaid
Qaid ( ar , قائد ', "commander"; pl. '), also spelled kaid or caïd, is a word meaning "commander" or "leader." It was a title in the Norman kingdom of Sicily, applied to palatine officials and members of the ''curia'', usually to those who were Muslims or converts to Islam. The word entered the Latin language as lat, gaitus or lat, gaytus. Later the word was used in North Africa for the governor of a fortress or the warden of a prison, also in Spain and Portugal in the form with the definite article "alcayde" (Spanish) "alcaide" (Portuguese). It is also used as a male Arabic given name. Notable qaids * Al Qaid Johar (active 950–992), A Slavic general who conquered Maghreb for the Fatimid Imam-Caliph, Al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah; and later served as the Viceroy of the Fatimid State. *Thomas Brun (active 1137–1154), Englishman who served Roger II of Sicily *Ahmed es-Sikeli, known as Caid Peter (active 1160s), eunuch in the court of Sicily, confidant of Margaret of Nava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(14595532860).jpg)