|
Retropharyngeal Space
The retropharyngeal space (abbreviated as "RPS") is a potential space and deep compartment of the head and neck situated posterior to the pharynx. The RPS is bounded anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia, posteriorly by the alar fascia, and laterally by the carotid sheath. It spans from the base of the skull superiorly to the mediastinum inferiorly. It contains the retropharyngeal lymph nodes. Sources consider the retropharyngeal space to be in principle subdivided into the so-called "true retropharyngeal space" or "retropharyngeal space proper" (part of the RSP situated anterior to the alar fascia), and the danger space (part of the RSP situated posterior to the alar fascia). The danger space is sometimes also lumped together with the true RPS and the whole referred to as the RPS because the alar fascia is an ineffective barrier. Infections from the head and neck can spread down through the danger space into the posterior mediastinum. Anatomy Superiorly, the retropharingeal sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebra
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, and inferio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
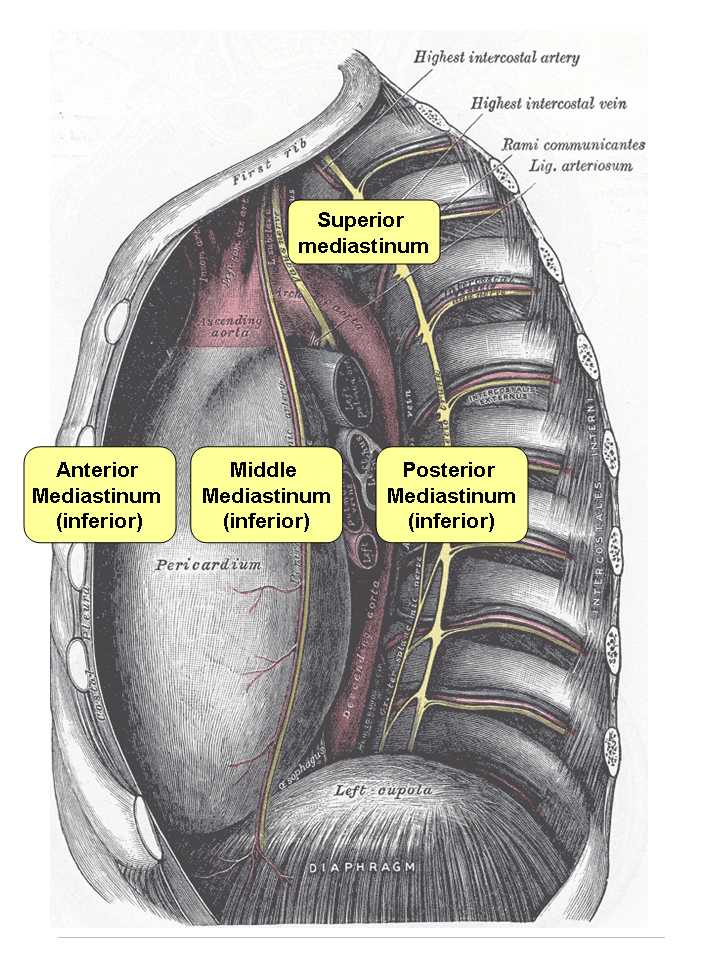
Posterior Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane. * The inferior mediastinum from this level to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retropharyngeal Abscess
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA) is an abscess located in the tissues in the back of the throat behind the posterior pharyngeal wall (the retropharyngeal space). Because RPAs typically occur in deep tissue, they are difficult to diagnose by physical examination alone. RPA is a relatively uncommon illness, and therefore may not receive early diagnosis in children presenting with stiff neck, malaise, difficulty swallowing, or other symptoms listed below. Early diagnosis is key, while a delay in diagnosis and treatment may lead to death. Parapharyngeal space communicates with retropharyngeal space and an infection of retropharyngeal space can pass down behind the esophagus into the mediastinum. RPAs can also occur in adults of any age. RPA can lead to airway obstruction or sepsis – both life-threatening emergencies. Fatalities normally occur from patients not receiving treatment immediately and suffocating prior to knowing that anything serious was wrong. Signs and symptoms Signs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retropharyngeal Abscess
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA) is an abscess located in the tissues in the back of the throat behind the posterior pharyngeal wall (the retropharyngeal space). Because RPAs typically occur in deep tissue, they are difficult to diagnose by physical examination alone. RPA is a relatively uncommon illness, and therefore may not receive early diagnosis in children presenting with stiff neck, malaise, difficulty swallowing, or other symptoms listed below. Early diagnosis is key, while a delay in diagnosis and treatment may lead to death. Parapharyngeal space communicates with retropharyngeal space and an infection of retropharyngeal space can pass down behind the esophagus into the mediastinum. RPAs can also occur in adults of any age. RPA can lead to airway obstruction or sepsis – both life-threatening emergencies. Fatalities normally occur from patients not receiving treatment immediately and suffocating prior to knowing that anything serious was wrong. Signs and symptoms Signs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevertebral Fascia
The prevertebral fascia (or prevertebral layer of cervical fascia) is a fascia in the neck. Variations In some literature, the prevertebral fascia also includes the other fascial layers extending around the vertebral column and enclosing all muscles laterally and posteriorly to it. However, in this article, it is assumed to be as marked in the corresponding picture. Location The prevertebral fascia extends medially behind the carotid vessels, where it assists in forming their sheath, and passes in front of the prevertebral muscles. The prevertebral fascia is fixed above to the base of the skull, and below it extends behind the esophagus into the posterior mediastinal cavity of the thorax. It descends in front of the longus colli muscles. The prevertebral fascia is prolonged downward and laterally behind the carotid vessels and in front of the scalene muscles. It forms a sheath for the brachial nerves, subclavian artery, and subclavian vein in the posterior triangle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccopharyngeal Fascia
The buccopharyngeal fascia is a fascia in the head and neck. Structure The buccopharyngeal runs parallel to the medial aspect of the carotid sheath. It is a thin lamina given off from the pretracheal fascia. It is attached to the prevertebral fascia by loose connective tissue, with the retropharyngeal space found between them. It may also be attached to the alar fascia posteriorly at C3 and C6 levels. The thyroid gland wraps around the trachea and oesophagus anterior to the buccopharyngeal fascia, so that the lateral parts of the thyroid gland border it. Function The buccopharyngeal fascia envelops the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It closely invests the constrictor muscles of the pharynx. It is continued forward from the constrictor pharyngis superior onto the buccinator The buccinator () is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Sheath
The carotid sheath is an anatomical term for the fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the vascular compartment of the neck. It is part of the deep cervical fascia of the neck, below the superficial cervical fascia meaning the subcutaneous adipose tissue immediately beneath the skin. The deep cervical fascia of the neck includes four parts: * The investing layer (encloses the SCM and Trapezius) * The carotid sheath (encloses the vascular region of the neck) * The pretracheal fascia (encloses the visceral region of the neck) * The prevertebral fascia (encloses the vertebral region of the neck) Structure The carotid sheath is located at the lateral boundary of the retropharyngeal space at the level of the oropharynx on each side of the neck and deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It extends from the base of the skull to the first rib and sternum, varying between C7 and T4. It merges with the axillary sheath when it reaches the subclavian vein. Contents The four major stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Mediastinal
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane. * The inferior mediastinum from this level to the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
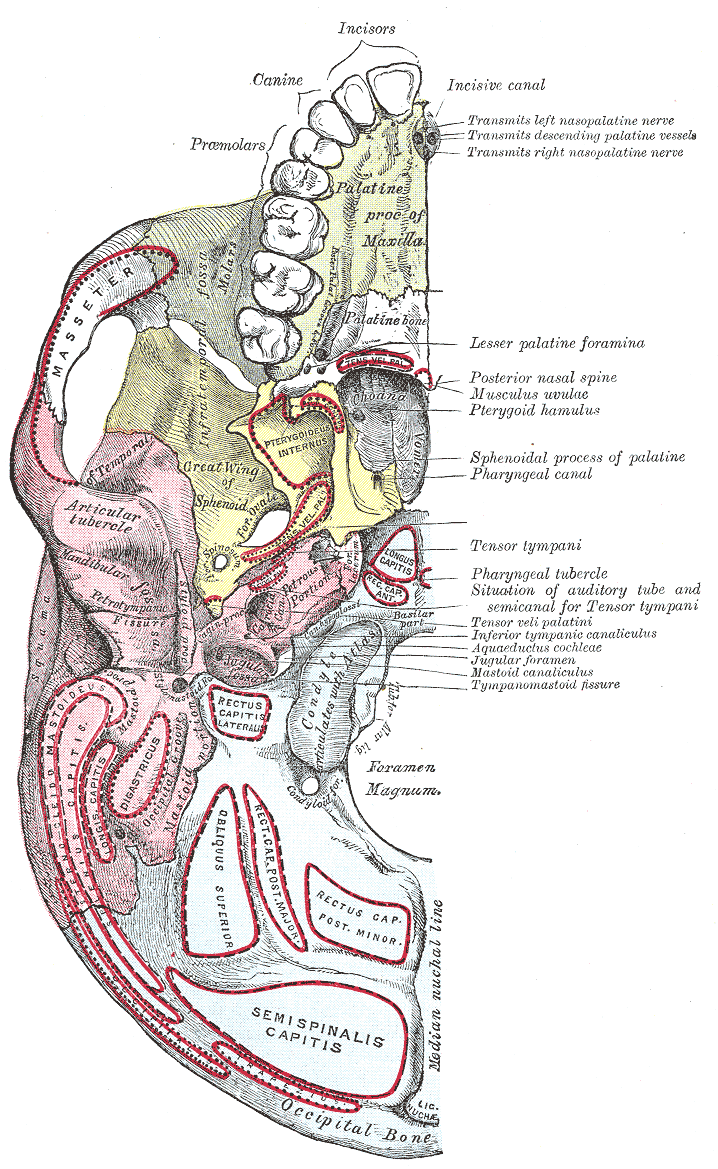
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone * Sphenoid bone * Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sphenoidal lingula *Subarcuate fossa *Dorsum sellae *Jugular process *Petro-occipital fissure *Condylar canal * Jugular tubercle * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clivus (anatomy)
The clivus (, Latin for "slope"), or Blumenbach clivus, is a bony part of the cranium The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ... at the base of the skull. It is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. It slopes gradually to the anterior part of the basilar occipital bone at its junction with the sphenoid bone. It extends to the foramen magnum. It is related to the pons and the abducens nerve (CN VI). Structure The clivus is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. It slopes gradually to the anterior part of the basilar occipital bone at its junction with the sphenoid bone. Synchondrosis of these two bones forms the clivus. The clivus extends inferiorly to the foramen magnum. On axial planes, it sits just posterior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danger Space
The danger space or alar space, is a region of the neck. The common name originates from the risk that an infection in this space can spread directly to the thorax, and, due to being a space continuous on the left and right, can furthermore allow infection to spread easily to either side. Structure It is bounded at the top by the skull base, at the front by the alar fascia and behind by the prevertebral fascia. It comes to an end at the level of the diaphragm. The retropharyngeal space is found anterior to the danger space, between the alar fascia and buccopharyngeal fascia. There exists a midline raphe in this space so some infections of this space appear unilateral. Clinical significance On CT or MRI it is only visible when distended by fluid or pus, below the level of T1-T6, as the retropharyngeal space ends at this level, allowing distinction between the two entities. Superior spread of infection can affect the contents of the carotid sheath, including the internal jugular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |