|
Retinaculum
A retinaculum (plural ''retinacula'') is a band of thickened deep fascia around tendons that holds them in place. It is not part of any muscle. Its function is mostly to stabilize a tendon. The term retinaculum is New Latin, derived from the Latin verb ''retinere'' (to retain). Specific retinacula include: * In the wrist: ** Flexor retinaculum of the hand ** Extensor retinaculum of the hand * In the ankle: ** Flexor retinaculum of foot ** Superior extensor retinaculum of foot ** Inferior extensor retinaculum of foot ** Superior fibular retinaculum ** Inferior fibular retinaculum * In the knee: ** Lateral retinaculum The lateral retinaculum is the fibrous tissue on the lateral (outer) side of the kneecap (patella). The kneecap has both a medial (on the inner aspect) and a lateral (on the outer side) retinaculum, and these help to support the kneecap in its posi ... ** Medial patellar retinaculum References {{reflist Tendons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
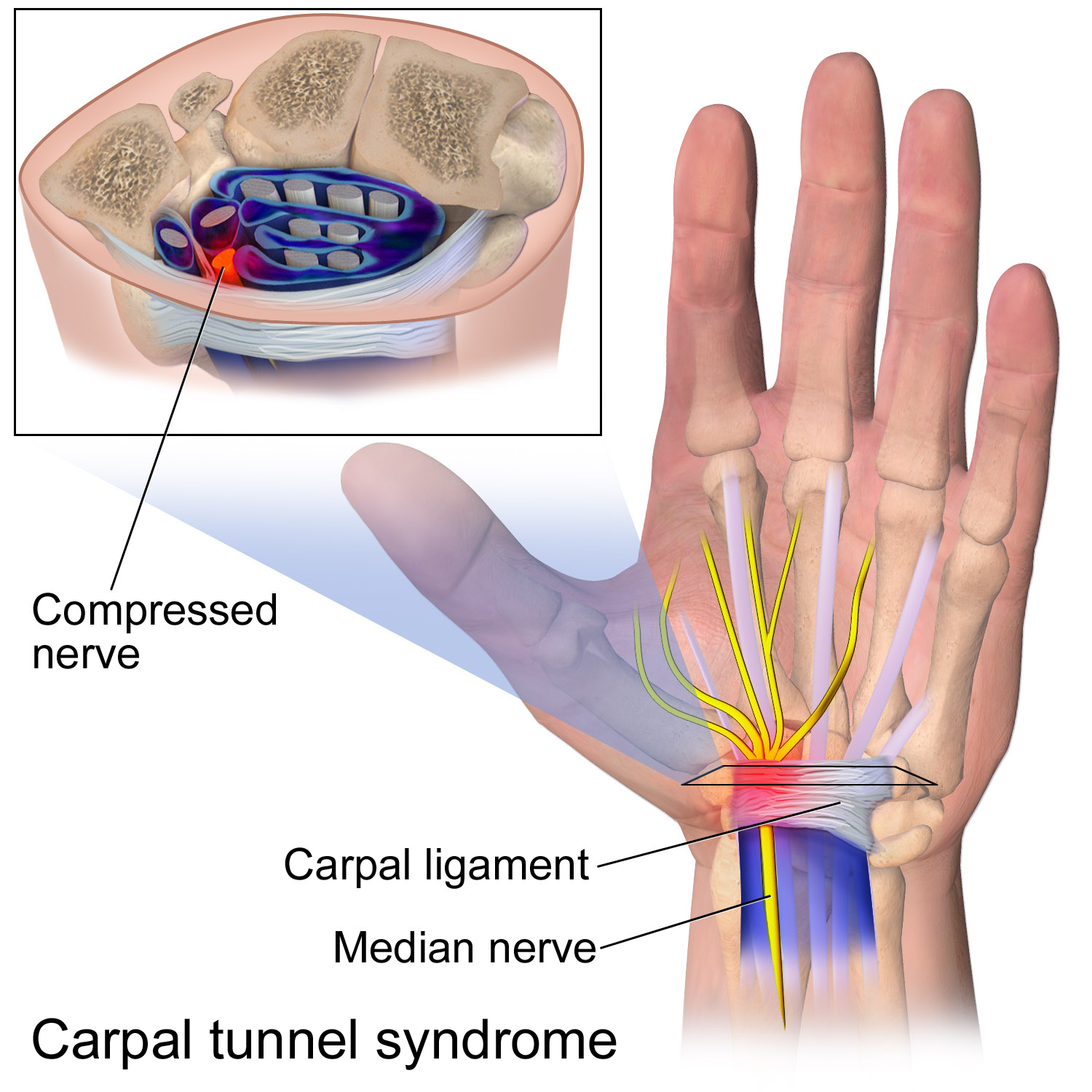
Flexor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament, or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel. Structure The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone. The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, and deeper with the palmar aponeurosis. The ulnar artery and ulnar nerve, and the cutaneous branches of the median and ulnar nerves, pass on top of the flexor retinaculum. On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The extensor retinaculum (dorsal carpal ligament, or posterior annular ligament) is an anatomical term for the thickened part of the antebrachial fascia that holds the tendons of the extensor muscles in place. It is located on the back of the forearm, just proximal to the hand. It is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, which is located on the anterior side of the forearm. Structure The extensor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band, extending obliquely downward and medialward across the back of the wrist. It consists of part of the deep fascia of the back of the forearm, strengthened by the addition of some transverse fibers. The extensor retinaculum is attached laterally to the lateral margin of the radius. However, it is not attached to the ulna, as the distance between these two bones varies with supination and pronation of the forearm. Instead the medial attachment is to the pisiform bone and triquetral bone. Other authors may state the medial attachment of extensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Extensor Retinaculum Of Foot
The superior extensor retinaculum of the foot (transverse crural ligament) is the upper part of the extensor retinaculum of foot which extends from the ankle to the heelbone. The superior extensor retinaculum binds down the tendons of extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, peroneus tertius, and tibialis anterior as they descend on the front of the tibia and fibula; under it are found also the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve. It is found on the lateral side of the lower leg, attached laterally to the lower end of the fibula, and medially to the tibia; above it is continuous with the fascia of the leg. Additional images File:Gray437.png, Muscles of the front of the leg. See also * Peroneal retinacula The fibular retinacula (also known as peroneal retinacula) are fibrous retaining bands that bind down the tendons of the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles as they run across the side of the ankle. (''Retinaculum'' is Latin for "retaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Retinaculum Of Foot
The flexor retinaculum of foot (laciniate ligament, internal annular ligament) is a strong fibrous band in the foot. Structure The flexor retinaculum of the foot extends from the medial malleolus above, to the calcaneus below. This converts a series of bony grooves into canals for the passage of the tendons of the flexor muscles and the posterior tibial vessels and tibial nerve into the sole of the foot, known as the tarsal tunnel. It is continuous by its upper border with the deep fascia of the leg, and by its lower border with the plantar aponeurosis and the fibers of origin of the abductor hallucis muscle. Enumerated from the medial side, the four canals which it forms transmit the tendons of the tibialis posterior and flexor digitorum longus muscles; the posterior tibial artery and tibial nerve, which run through a broad space beneath the ligament; and lastly, in a canal formed partly by the talus, the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus. Clinical significance Tarsal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Extensor Retinaculum Of Foot
The inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot (cruciate crural ligament, lower part of anterior annular ligament) is a Y-shaped band placed in front of the ankle-joint, the stem of the Y being attached laterally to the upper surface of the calcaneus, in front of the depression for the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament; it is directed medialward as a double layer, one lamina passing in front of, and the other behind, the tendons of the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus. At the medial border of the latter tendon, these two layers join, forming a compartment in which the tendons are enclosed. From the medial extremity of this sheath, the two limbs of the Y diverge: one is directed upward and medialward, to be attached to the tibial malleolus, passing over the extensor hallucis longus and the vessels and nerves but enclosing the tibialis anterior by a splitting of its fibers. The other limb extends downward and medialward, to be attached to the border of the plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Retinaculum
The lateral retinaculum is the fibrous tissue on the lateral (outer) side of the kneecap (patella). The kneecap has both a medial (on the inner aspect) and a lateral (on the outer side) retinaculum, and these help to support the kneecap in its position in relation to the femur bone underneath it. The lateral retinaculum is an extension of the fibrous 'aponeurosis' of the vastus lateralis muscle (itself a part of the quadriceps muscle The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...s making up the 'lap'). External links Patello-femoral Pain Syndrome {{Authority control Tissues (biology) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis. It is often termed a ''compound joint'' having tibiofemoral and patellofemoral components. (The fibular collateral ligament is often considered with tibiofemoral components.) Structure The knee is a modified hinge joint, a type of synovial joint, which is composed of three functional compartments: the patellofemoral articulation, consisting of the patella, or "kneecap", and the patellar groove on the front of the femur through which it slides; and the medial and lateral tibiofemoral articulations linking the femur, or thigh bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Fascia
Deep fascia (or investing fascia) is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments. This fibrous connective tissue interpenetrates and surrounds the muscles, bones, nerves, and blood vessels of the body. It provides connection and communication in the form of aponeuroses, ligaments, tendons, retinacula, joint capsules, and septa. The deep fasciae envelop all bone (periosteum and endosteum); cartilage (perichondrium), and blood vessels (tunica externa) and become specialized in muscles (epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium) and nerves (epineurium, perineurium, and endoneurium). The high density of collagen fibers gives the deep fascia its strength and integrity. The amount of elastin fiber determines how much extensibility and resilience it will have. Examples Examples include: * Fascia lata * Deep fascia of leg * Brachial fascia * Buck's fascia Fascial dynamics Deep fascia is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments; both are made of collagen. Ligaments connect one bone to another, while tendons connect muscle to bone. Structure Histologically, tendons consist of dense regular connective tissue. The main cellular component of tendons are specialized fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tenocytes synthesize the extracellular matrix of tendons, abundant in densely packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are parallel to each other and organized into tendon fascicles. Individual fascicles are bound by the endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibres. Groups of fascicles are bounded by the epitenon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Latin
New Latin (also called Neo-Latin or Modern Latin) is the revival of Literary Latin used in original, scholarly, and scientific works since about 1500. Modern scholarly and technical nomenclature, such as in zoological and botanical taxonomy and international scientific vocabulary, draws extensively from New Latin vocabulary, often in the form of classical or neoclassical compounds. New Latin includes extensive new word formation. As a language for full expression in prose or poetry, however, it is often distinguished from its successor, Contemporary Latin. Extent Classicists use the term "Neo-Latin" to describe the Latin that developed in Renaissance Italy as a result of renewed interest in classical civilization in the 14th and 15th centuries. Neo-Latin also describes the use of the Latin language for any purpose, scientific or literary, during and after the Renaissance. The beginning of the period cannot be precisely identified; however, the spread of secular education, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italy (geographical region), Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a fusional language, highly inflected language, with three distinct grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |