|
Rete Tubular Ectasia
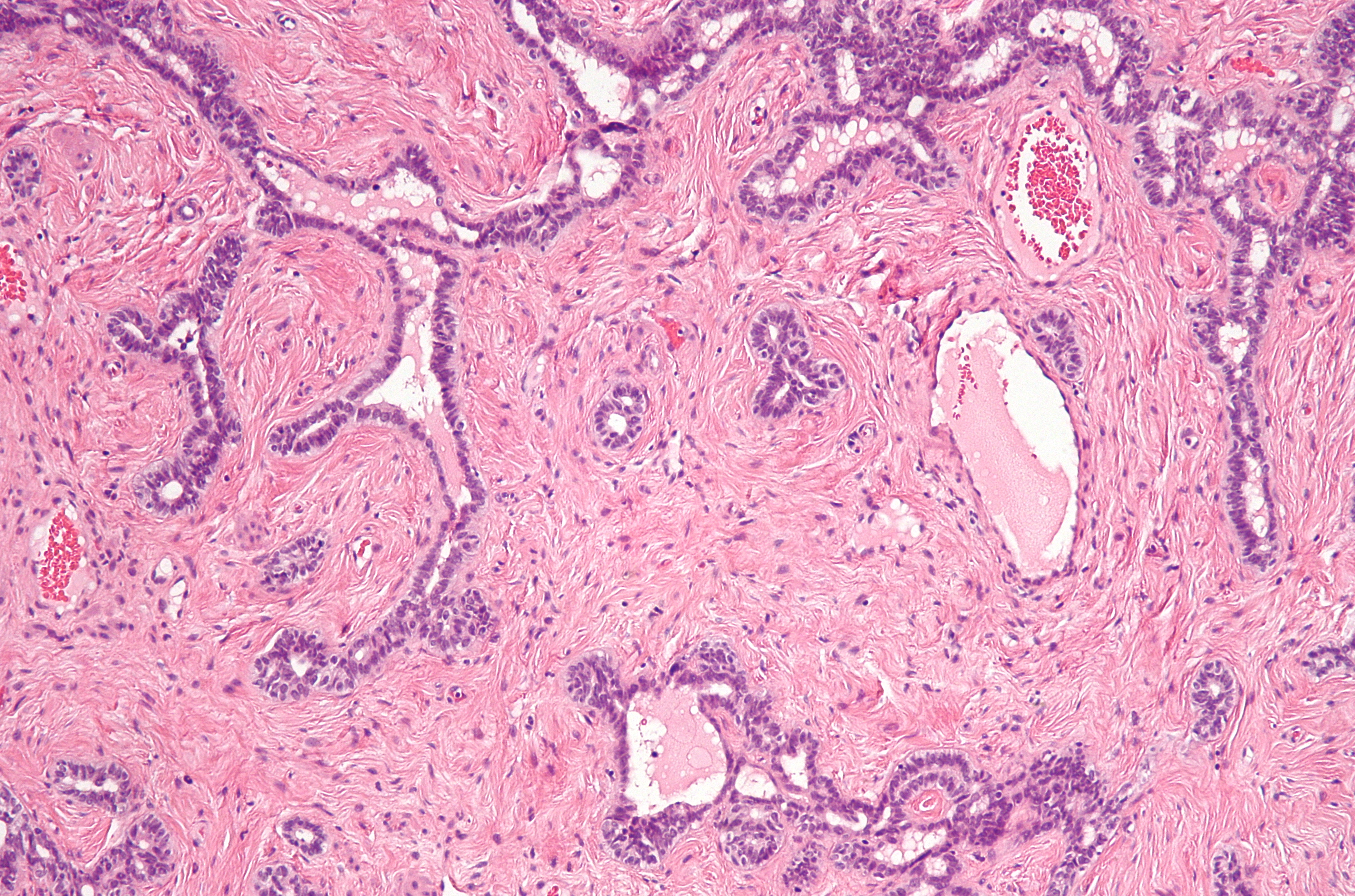
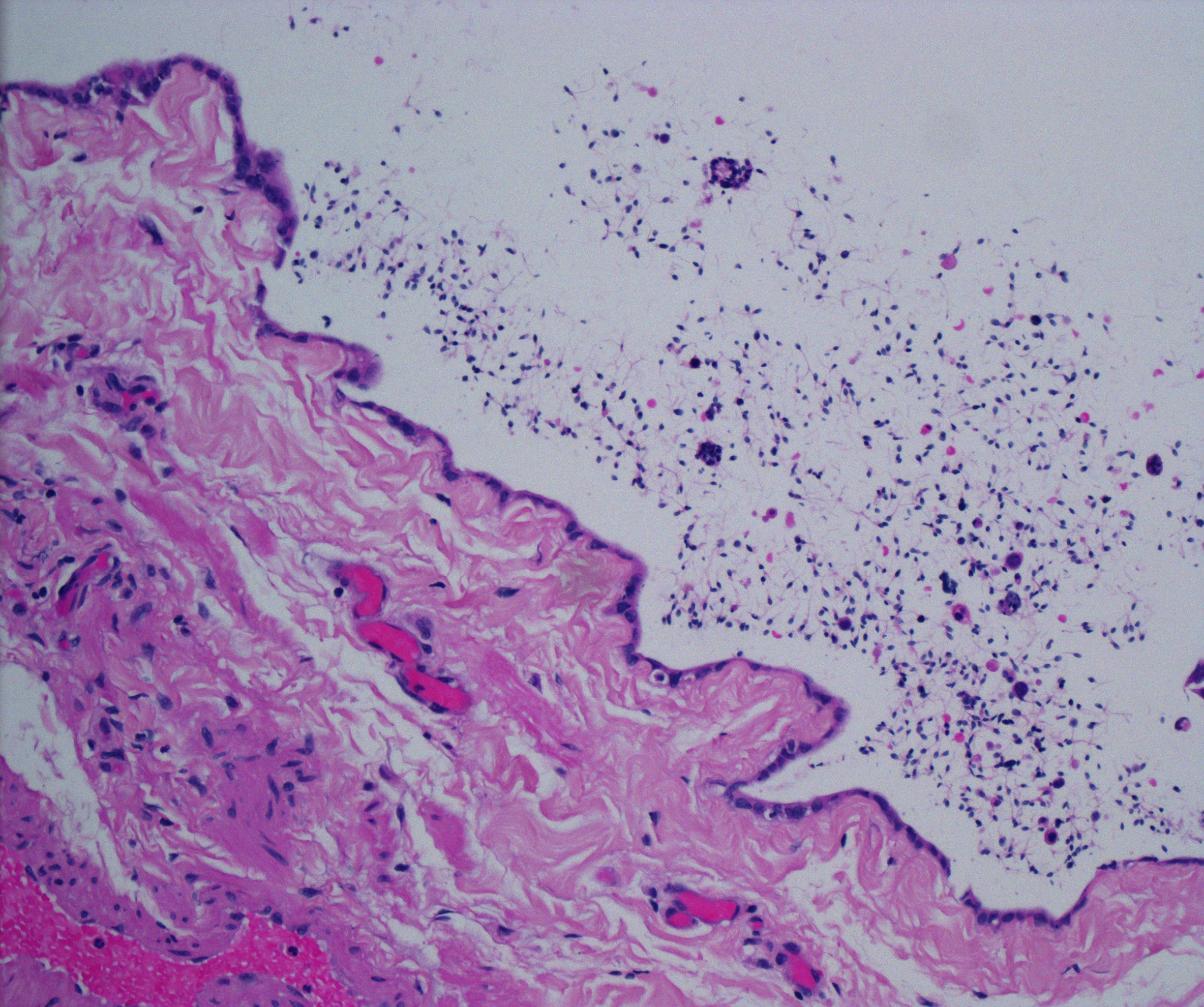
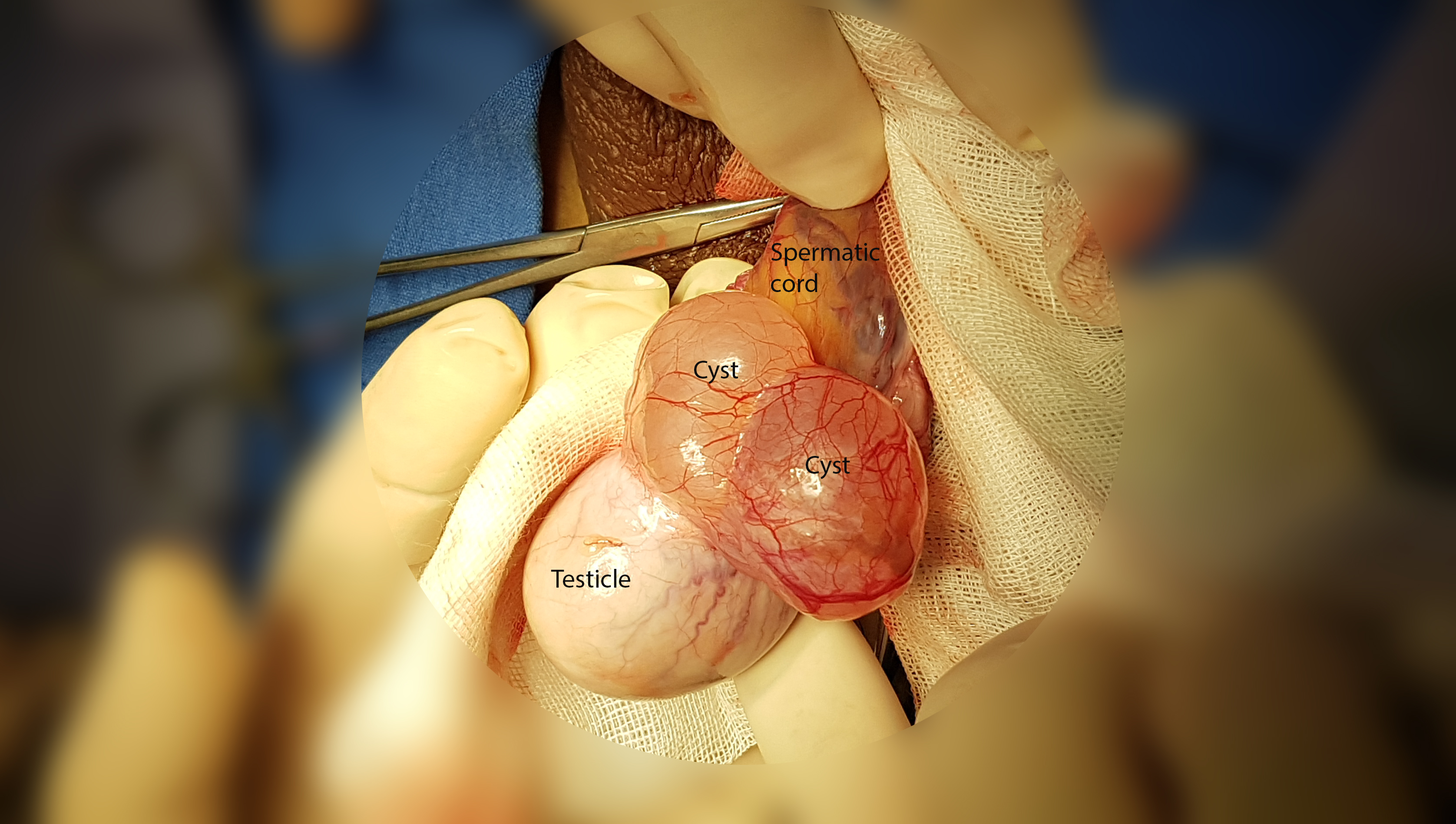
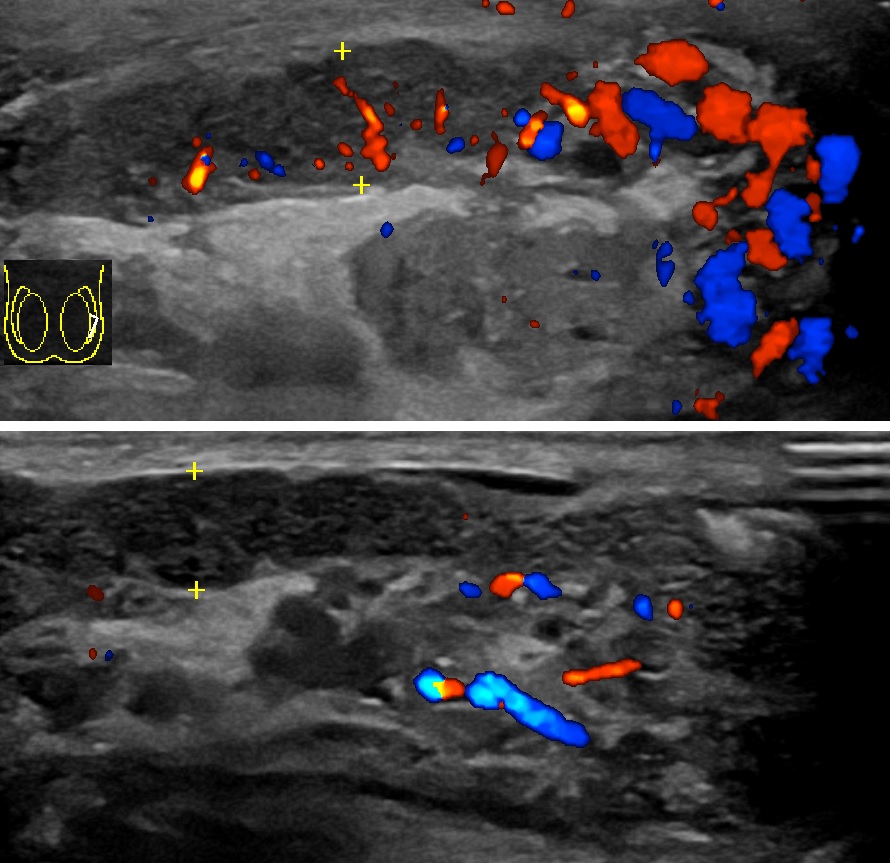
Rete tubular ectasia , also known as cystic transformation of rete testis is a benign condition, usually found in older men, involving numerous small, tubular cystic structures within the rete testis. Presentation It is usually found in men older than 55 years and is frequently found on bilateral testes but often asymmetrical. Mechanism The formation of cysts in the rete testis is associated with the obstruction of the efferent ducts, which connect the rete testis with the head of the epididymis. They are often bilateral. Diagnosis The condition can be detected with ultrasonography. Cystic lesions us usually found at the mediastinum testis with elongated shaped lesion displacing the mediastinum. It is commonly associated with epididymal abnormalities, such as spermatocele, epididymal cyst, and epididymitis. The condition shares a common location with cystic dysplasia of the testis and intratesticular cysts. Unlike cystic neoplasms, they don't present specific tumor markers. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubular Ectasia Of Rete Testis - 81jm - Sono
Tubular may refer to: *having the form of a hollow cylinder, or tube *having the form of a cylinder *''Tubular'', a television-related entertainment blog on the ''Houston Chronicle'' website *''Tubular'', a level in the video game ''Super Mario World'' * Tubular, surf culture slang for cool or awesome, derived from catching a wave and getting in the tube *Tubular people, a former ethnic group in Russia The adjective is often applied to items which are somewhat tubular in shape: *Tubular bells, musical instruments (also known as chimes) in the percussion family *Tubular bridge, a bridge built as a rigid box girder section, with the traffic carried within the section *Tubular chassis or superleggera, a type of automobile construction technique used only in expensive sports cars *Tubular Gallery, a large diameter, round, tubular steel structure used to enclose a troughed conveyor belt *Tubular pin tumbler lock, or tubular lock, a type of lock using a tubular key *Tubular NDT, nondestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse. Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. Cancers usually show tumour heterogeneity, containing multiple subclones. They also frequently have reduced expression of DNA repair enzymes due to epigenetic methylation of DNA repair genes or altered microRNAs that control DNA repair gene expression. Tumours can be detected through the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rete Testis
The rete testis ( ) is an anastomosing network of delicate tubules located in the hilum of the testicle (mediastinum testis) that carries sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the efferent ducts. It is the counterpart of the rete ovarii in females. Its function is to provide a site for fluid reabsorption. Structure The rete testis is the network of interconnecting tubules where the straight seminiferous tubules (the terminal part of the seminiferous tubules) empty. It is located within a highly vascular connective tissue in the mediastinum testis. The epithelial cells form a single layer that lines the inner surface of the tubules. These cells are cuboidal, with microvilli and a single cilium on their surface. Development In the development of the urinary and reproductive organs, the testis is developed in much the same way as the ovary, originating from mesothelium as well as mesonephros. Like the ovary, in its earliest stages it consists of a central mass covered by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efferent Ducts
The efferent ducts (or efferent ductules or ductuli efferentes or ductus efferentes or vasa efferentia) connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.Hess 2018 There are two basic designs for efferent ductule structure: * a) multiple entries into the epididymis, as seen in most large mammals. In humans and other large mammals, there are approximately 15 to 20 efferent ducts, which also occupy nearly one third of the head of the epididymis. * b) single entry, as seen in most small animals such as rodents, where by the 3–6 ductules merge into a single small ductule prior to entering the epididymis. The ductuli are unilaminar and composed of columnar ciliated and non-ciliated (absorptive) cells. The ciliated cells serve to stir the luminal fluids, possibly to help ensure homogeneous absorption of water from the fluid produced by the testis, which results in an increase in the concentration of luminal sperm. The epithelium is surrounded by a band of smooth m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymis
The epididymis (; plural: epididymides or ) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, in length. It serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Anatomy The epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head ( la, caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinum testis, mediastinium of the testis at the superior pole of the testis. The head is characterized histologically by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia (described below) and a little smooth muscle. It is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum Testis
The mediastinum testis is a network of fibrous connective tissue that extends from the top to near the bottom of each testis. It is wider above than below. Numerous imperfect septa are given off from its front and sides, which radiate toward the surface of the testes and are attached to the tunica albuginea. These divide the interior of the testes into a number of incomplete spaces called lobules In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ (as seen for example in the brain, lung, liver, or kidney) that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to t .... These are somewhat cone-shaped, being broad at their bases at the surface of the gland, and becoming narrower as they converge to the mediastinum. The mediastinum supports the rete testis and blood vessels of the testis in their passage to and from the substance of the gland. Additional images File:gray1145.png, Transverse section thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatocele
Spermatocele is a fluid-filled cyst that develops at the top of the testicle of the epididymis. The fluid is usually a clear or milky white color and may contain sperm. Spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa and they can vary in size from several millimeters to many centimeters. Small spermatoceles are relatively common, occurring in an estimated 30 percent of males. They are generally not painful. However, some people may experience discomfort such as a dull pain in the scrotum from larger spermatoceles. They are not cancerous, nor do they cause an increased risk of testicular cancer. Additionally, unlike varicoceles, they do not reduce fertility. History "Spermatocele" is originally derived from the ''Greek'' term ''spermatos'' (sperm) and ''kele'' (cavity or mass). Oftentimes, "epididymal cyst" has been used interchangeably with "spermatocele." However, it is important to note their differences. Epididymal cysts may appear anywhere along or within the epididymis a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymal Cyst
An epididymal cyst is a cyst of the epididymis containing serous liquid. They are difficult to differentiate from a spermatocele Spermatocele is a fluid-filled cyst that develops at the top of the testicle of the epididymis. The fluid is usually a clear or milky white color and may contain sperm. Spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa and they can vary in size ... except by aspiration, since a spermatocele contains milky-appearing sperm. References Cysts Epididymis disorders {{genitourinary-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the epididymis, a curved structure at the back of the testicle. Onset of pain is typically over a day or two. The pain may improve with raising the testicle. Other symptoms may include swelling of the testicle, burning with urination, or frequent urination. Inflammation of the testicle is commonly also present. In those who are young and sexually active gonorrhea and chlamydia are frequently the underlying cause. In older males and men who practice insertive anal sex, enteric bacteria are a common cause. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms. Conditions that may result in similar symptoms include testicular torsion, inguinal hernia, and testicular cancer. Ultrasound can be useful if the diagnosis is unclear. Treatment may include pain medications, NSAIDs, and elevation. Recommended antibiotics in those who are young and sexually active are ceftriaxone and doxycycline. Among those who are older, ofloxacin m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Dysplasia
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use calipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |