|
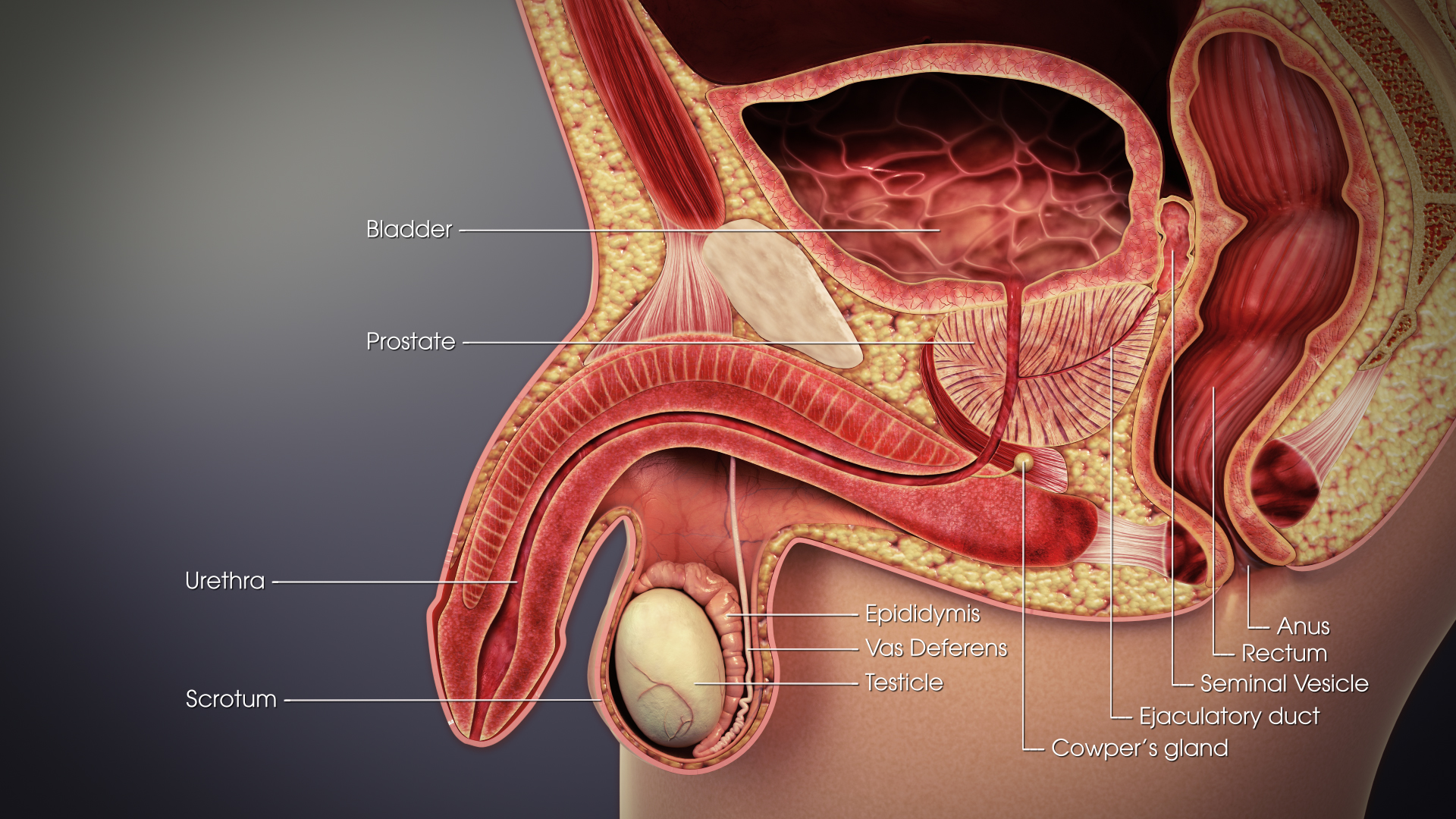
Mediastinum Testis
The mediastinum testis is a network of fibrous connective tissue that extends from the top to near the bottom of each testis. It is wider above than below. Numerous imperfect septa are given off from its front and sides, which radiate toward the surface of the testes and are attached to the tunica albuginea. These divide the interior of the testes into a number of incomplete spaces called lobules In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ (as seen for example in the brain, lung, liver, or kidney) that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to t .... These are somewhat cone-shaped, being broad at their bases at the surface of the gland, and becoming narrower as they converge to the mediastinum. The mediastinum supports the rete testis and blood vessels of the testis in their passage to and from the substance of the gland. Additional images File:gray1145.png, Transverse section thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Albuginea Of Testis
The tunica albuginea is the fibrous tissue covering of the testis. It is a dense blue-grey membrane, composed of bundles of white fibrous connective tissue, from which it derives its name '' albuginea'', which interlace in every direction. Structure The tunica albuginea is a layer of fibrous tissue capsule covering the testis. It is covered by the tunica vaginalis, except at the points of attachment of the epididymis to the testis, and along its posterior border, where the spermatic vessels enter the gland. It is thicker than the tunica albuginea of the ovary. The tunica albuginea is applied to the tunica vasculosa over the glandular substance of the testis, and, at its posterior border, is reflected into the interior of the gland, forming an incomplete vertical septum, called the mediastinum testis (corpus Highmori). Additional images File:Gray1145.png, Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis. File:Gray1114.png, Section of a genital c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis is the pouch of serous membrane that covers the testes. It is derived from the vaginal process of the peritoneum, which in the fetus precedes the descent of the testes from the abdomen into the scrotum. After its descent, that portion of the pouch which extends from the abdominal inguinal ring to near the upper part of the gland becomes obliterated; the lower portion remains as a shut sac, which invests the surface of each testis, and is reflected on to the internal surface of the scrotum; hence it may be described as consisting of a visceral and a parietal lamina. Visceral lamina The visceral lamina (lamina visceralis) covers the greater part of the testis and epididymis, connecting the latter to the testis by means of a distinct fold. From the posterior border of the gland it is reflected on to the internal surface of the scrotum. Parietal lamina The parietal lamina (lamina parietalis) is far more extensive than the visceral, extending upward for some di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobules Of Testis
The glandular structure of the testis consists of numerous lobules. Their number, in a single testis, is estimated by Berres at 250, and by Krause at 400. Anatomic studies have demonstrated figures of 250–290 for the same. They differ in size according to their position, those in the middle of the gland being larger and longer. The lobules are conical in shape, the base being directed toward the circumference of the organ, the apex toward the mediastinum testis. Each lobule is contained in one of the intervals between the fibrous septa The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people in five c ... which extend between the mediastinum testis and the tunica albuginea, and consists of from one to three, or more, minute convoluted tubes, the tubuli seminiferi. Additional images File:Gray114 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septa Of Testis
Each lobule of the testis is contained in one of the intervals between the fibrous septa which extend between the mediastinum testis The mediastinum testis is a network of fibrous connective tissue that extends from the top to near the bottom of each testis. It is wider above than below. Numerous imperfect septa are given off from its front and sides, which radiate toward the s ... and the tunica albuginea, and consists of from one to three, or more, minute convoluted tubes, the tubuli seminiferi. Additional images File:Gray1145.png, Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis. File:Gray1149.png, Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts. References External links * - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: The Cross-Section of the Testis" Mammal male reproductive system {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use calipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side. Structure The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: * ''external spermatic fascia'', an extension of the innominate fascia that overlies the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. * '' cremasteric muscle and fascia'', formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia. * '' internal spermatic fascia'', continuous with the transversalis fascia. The normal diameter of the spermatic cord is about 16 mm (range 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms. Etymology The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word παρέγχυμα ''parenchyma'' meaning 'visceral flesh', and from παρεγχεῖν ''parenchyma'' meaning 'to pour in' from παρα- ''para-'' 'beside' + ἐν ''en-'' 'in' + χεῖν ''chyma'' 'to pour'. Originally, Erasistratus and other anatomists used it to refer to certain human tissues. Later, it was also applied to plant tissues by Nehemiah Grew. Structure The parenchyma is the ''functional'' parts of an organ, or of a structure such as a tumour in the body. This is in contrast to the stroma, which refers to the ''structural'' tissue of organs or of structures, namely, the connective tissues. Brain The brain parenchyma refers to the functional tissue in the brain that is made up of the two types of brain cell, neurons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel"; the plural version is ''vasa deferentia''. ''Ductus deferens'' is also Latin, meaning "carrying-away duct"; the plural version is ''ducti deferentes''. Structure There are two vasa deferentia, connecting the left and right epididymis with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct in order to move sperm. The (human) vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. The vas deferens is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis. The vas deferens exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septula Testis
Each lobule of the testis is contained in one of the intervals between the fibrous septa which extend between the mediastinum testis and the tunica albuginea, and consists of from one to three, or more, minute convoluted tubes, the tubuli seminiferi. Additional images File:Gray1145.png, Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis. File:Gray1149.png, Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts. References External links * - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: The Cross-Section of the Testis" Mammal male reproductive system {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymis
The epididymis (; plural: epididymides or ) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, in length. It serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Anatomy The epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head ( la, caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinum testis, mediastinium of the testis at the superior pole of the testis. The head is characterized histologically by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia (described below) and a little smooth muscle. It is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductuli Efferentes Testis
The efferent ducts (or efferent ductules or ductuli efferentes or ductus efferentes or vasa efferentia) connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.Hess 2018 There are two basic designs for efferent ductule structure: * a) multiple entries into the epididymis, as seen in most large mammals. In humans and other large mammals, there are approximately 15 to 20 efferent ducts, which also occupy nearly one third of the head of the epididymis. * b) single entry, as seen in most small animals such as rodent Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...s, where by the 3–6 ductules merge into a single small ductule prior to entering the epididymis. The ductuli are unilaminar and composed of columnar ciliated and non-ciliated (absorptive) cells. The ciliate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |