|
Respirology
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty . Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas. Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to intensive care medicine ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
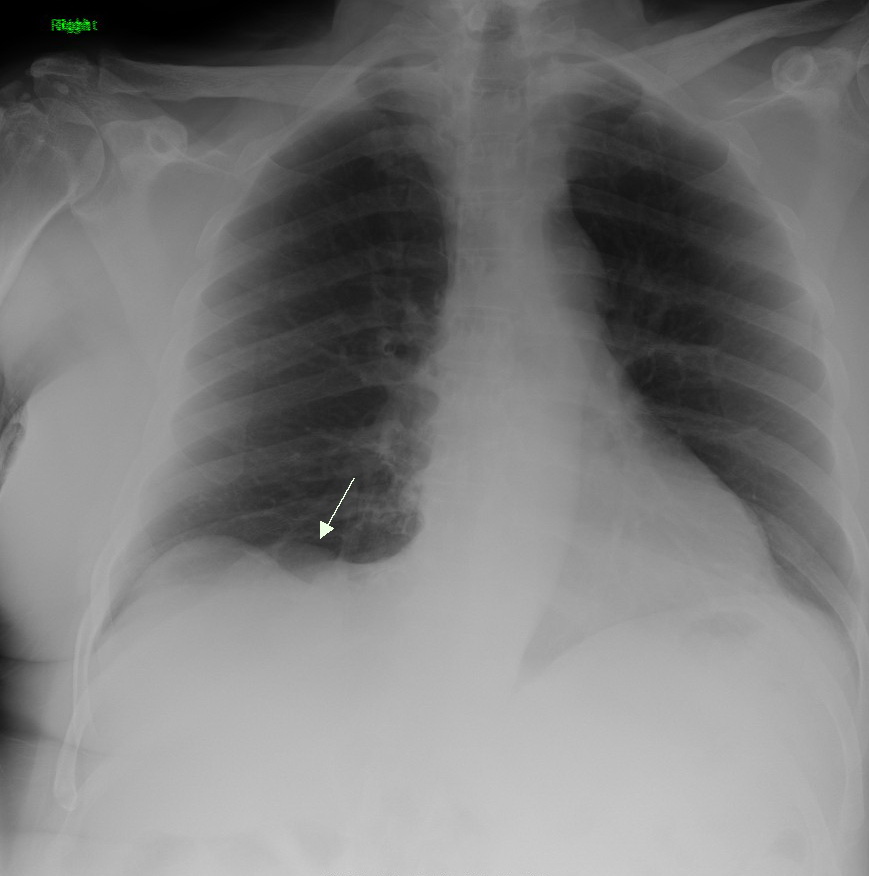
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled growth can metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory System Complete En
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' " breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
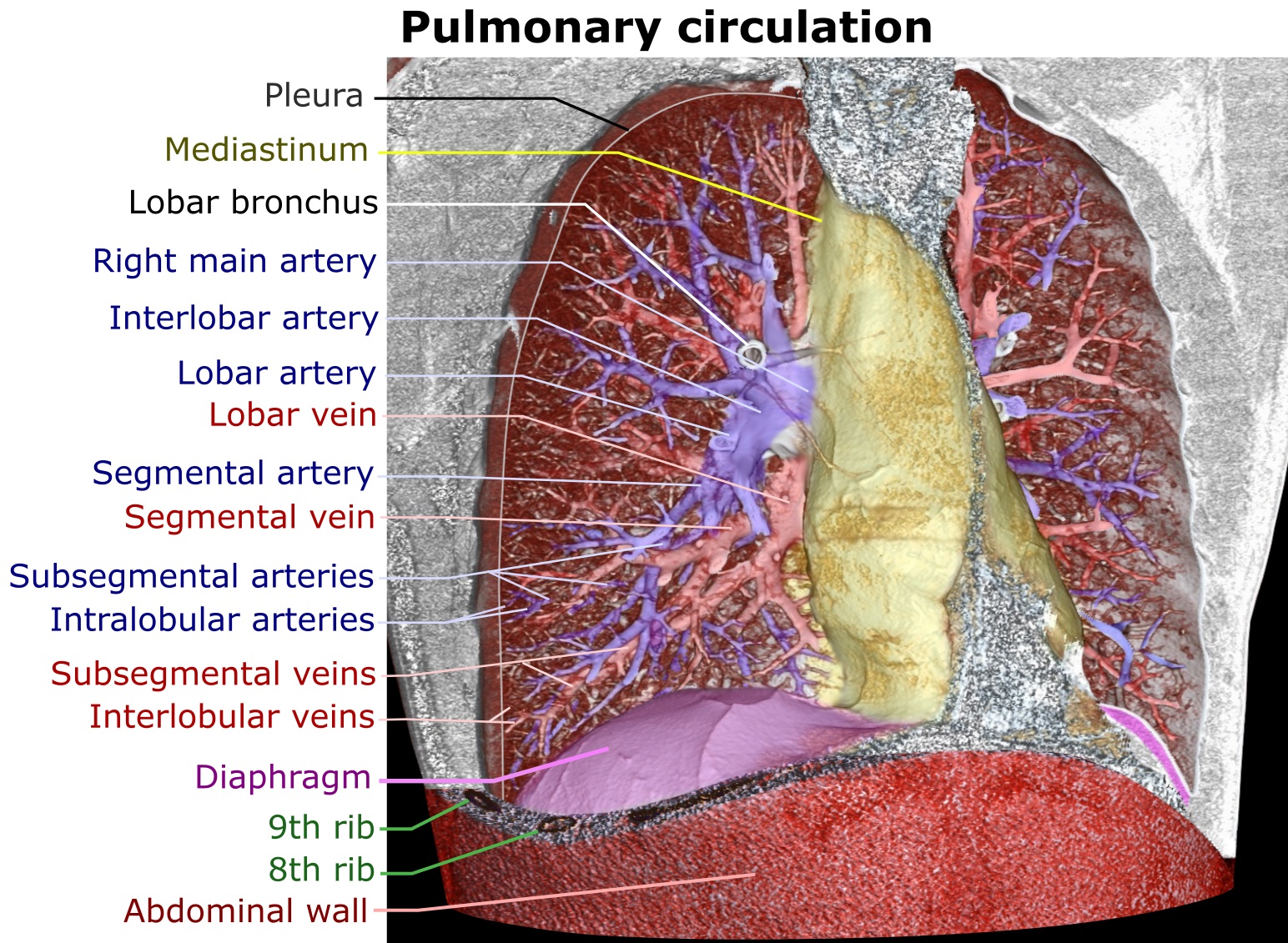
Pulmonary Circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. In the lungs the blood is oxygenated and returned to the left atrium to complete the circuit. The other division of the circulatory system is the systemic circulation that begins with receiving the oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circulation into the left atrium. From the atrium the oxygenated blood enters the left ventricle where it is pumped out to the rest of the body, returning as deoxygenated blood back to the pulmonary circulation. The blood vessels of the pulmonary circulation are the pulmonary arteries and the pulmonary veins. A separate circulatory circuit known as the bronchial circulation supplies oxygenated blood to the tissue of the larger airways of the lung. Structure De-oxygenated blood leaves the heart, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Respiratory Society
The European Respiratory Society, or ERS, is a non-profit organization with offices in Lausanne, Brussels and Sheffield. It was founded in 1990 in the field of respiratory medicine. The organization was formed with the merger of the Societas Europaea Physiologiae Clinicae Respoiratoriae (founded in 1966) and the European Society of Pneumology (founded 1981). The organization's membership is made up of medical professionals and scientists working in the area of respiratory medicine. ERS founded thEuropean Lung Foundation(ELF) in 2000. The foundation aims to bring together patients and the public with respiratory professionals to positively influence lung health. Activities The ERS publishes academic journals and books as well as hosting events aimed at educating health professionals, including a large annual congress. The organization's stated goal is to "promote lung health in order to alleviate suffering from disease and drive standards for respiratory medicine globally". Publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Thoracic Society
The British Thoracic Society (BTS) was formed in 1982 by the amalgamation of the British Thoracic Association and the Thoracic Society. It is a registered charity and a company limited by guarantee. Function The society's main charitable objective is to improve the care of people with respiratory and associated disorders, which it aims to achieve by: * promoting optimum standards of care (the Clinical Information section of the BTS website contains treatment Guidelines, good practice guides and related audit tools) * promoting and advancing knowledge about the causes, prevention and treatment of respiratory diseases (the society runs two large conferences each year and a range of short courses and are currently developing an e-learning resource - more details of these can be found in the Education Hub) * promoting and disseminating research (the society's Winter Meeting is the main showcase for this activity, as well as the journal Thorax, published jointly with the British Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Thoracic Society
The American Thoracic Society (ATS) is a nonprofit organization focused on improving care for pulmonary diseases, critical illnesses and sleep-related breathing disorders. It was established in 1905 as the American Sanatorium Association, and changed its name in 1938 to the American Trudeau Society. In 1960, it changed its name again to the American Thoracic Society. Originally the medical section of the American Lung Association, the Society became independently incorporated in 2000 as a 501 (c) (3) organization. Medical and scientific areas of interest Pulmonology, critical care, sleep medicine, infectious disease, pediatrics, allergy/immunology, thoracic surgery, behavioral science, environmental and occupational medicine, physiology, molecular biology, among others. Membership More than 15,000 physicians, research scientists, and nurses and other allied healthcare professionals (32 percent of whom work outside the United States). ATS Assemblies The interests of member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Lung Association
The American Lung Association is a voluntary health organization whose mission is to save lives by improving lung health and preventing lung disease through education, advocacy and research. History The organization was founded in 1904 to fight tuberculosis (TB) as the National Association for the Study and Prevention of Tuberculosis by Edward Livingston Trudeau, Robert Hall Babcock, Henry Martyn Hall, Lawrence Flick, and S. Adolphus Knopf. Earlier in 1892, Flick had founded the Pennsylvania Society for the Prevention of Tuberculosis, the world's first society dedicated to the prevention of TB. The NASPT was Renamed the National Tuberculosis Association (NTA) in 1918, and then the National Tuberculosis and Respiratory Disease Association (NTRDA) in 1968; it adopted its current name in 1973. Taglines that the association has used in its public-service messages have included: * "It's a matter of life and breath," * "When you can't breathe, nothing else matters," and, currently, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Chest Physicians
The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) is a medical association in the United States consisting of physician A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...s and non-physician specialists in the field of chest medicine, which includes pulmonology, critical care medicine, and sleep medicine. The group was founded in 1935. It has a membership of over 19,000. See also * ''Chest'' (journal) References External linksOfficial website* {{authority control Medical associations based in the United States Professional titles and certifications Pulmonology and respiratory therapy organizations Scientific organizations established in 1935 Medical and health professional associations in Chicago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |