|
Resistome
The resistome has been used to describe to two similar yet separate concepts: * All the antibiotic resistance genes in communities of both pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria. * All of the resistance genes in an organism, how they are inherited, and how their transcription levels vary to defend against pathogens like viruses and bacteria. Discovery and Current Data The resistome was first used to describe the resistance capabilities of bacteria preventing the effectiveness of antibiotics . Although antibiotics and their accompanying antibiotic resistant genes come from natural habitats, before next-generation sequencing, most studies of antibiotic resistance had been confined to the laboratory. Increased availability of whole-genome and metagenomic next-generation sequencing techniques have revealed significant reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria outside of clinical settings. Repeated testing of soil metagenomes revealed that in urban, agricultural, and forest environ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Resistance
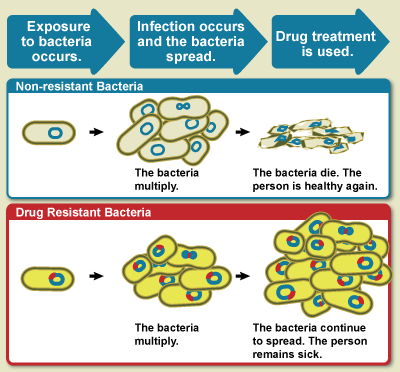
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major subset ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major subset o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of DNA sequencing, gene sequencing at Single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metagenomics
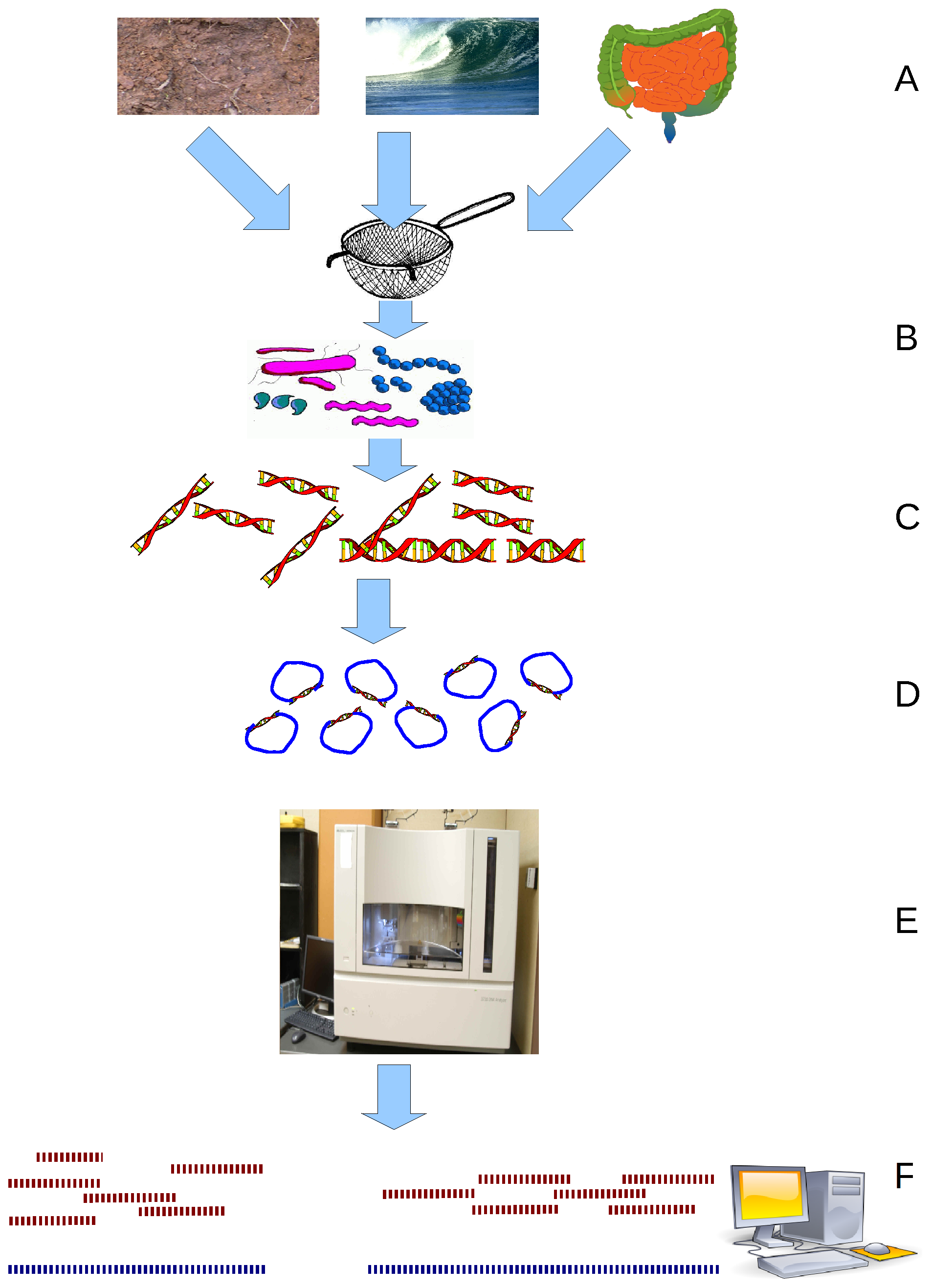
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contig
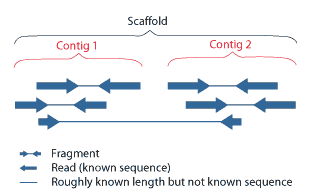
A contig (from ''contiguous'') is a set of overlapping DNA segments that together represent a consensus region of DNA.Gregory, S. ''Contig Assembly''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. In bottom-up sequencing projects, a contig refers to overlapping sequence data ( reads); in top-down sequencing projects, contig refers to the overlapping clones that form a physical map of the genome that is used to guide sequencing and assembly.Dear, P. H. ''Genome Mapping''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. . Contigs can thus refer both to overlapping DNA sequences and to overlapping physical segments (fragments) contained in clones depending on the context. Original definition of contig In 1980, Staden wrote: ''In order to make it easier to talk about our data gained by the shotgun method of sequencing we have invented the word "contig". A contig is a set of gel readings that are related to one another by overlap of their sequences. All gel readings belong to one and only one con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created Bactericide, pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves Temperateness (virology), temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Genetic Elements
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) sometimes called selfish genetic elements are a type of genetic material that can move around within a genome, or that can be transferred from one species or replicon to another. MGEs are found in all organisms. In humans, approximately 50% of the genome is thought to be MGEs. MGEs play a distinct role in evolution. Gene duplication events can also happen through the mechanism of MGEs. MGEs can also cause mutations in protein coding regions, which alters the protein functions. These mechanisms can also rearrange genes in the host genome generating variation. These mechanism can increase fitness by gaining new or additional functions. An example of MGEs in evolutionary context are that virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes of MGEs can be transported to share genetic code with neighboring bacteria. However, MGEs can also decrease fitness by introducing disease-causing alleles or mutations. The set of MGEs in an organism is called a mobilome, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Cassette
In biology, a gene cassette is a type of mobile genetic element that contains a gene and a recombination site. Each cassette usually contains a single gene and tends to be very small; on the order of 500–1000 base pairs. They may exist incorporated into an integron or freely as circular DNA. Gene cassettes can move around within an organism's genome or be transferred to another organism in the environment via horizontal gene transfer. These cassettes often carry antibiotic resistance genes. An example would be the '' kanMX'' cassette which confers kanamycin (an antibiotic) resistance upon bacteria. Integrons Integrons are genetic structures in bacteria which express and are capable of acquiring and exchanging gene cassettes. The integron consists of a promoter, an attachment site, and an integrase gene that encodes a site-specific recombinase There are three classes of integrons described. The mobile units that insert into integrons are gene cassettes. For cassettes that ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
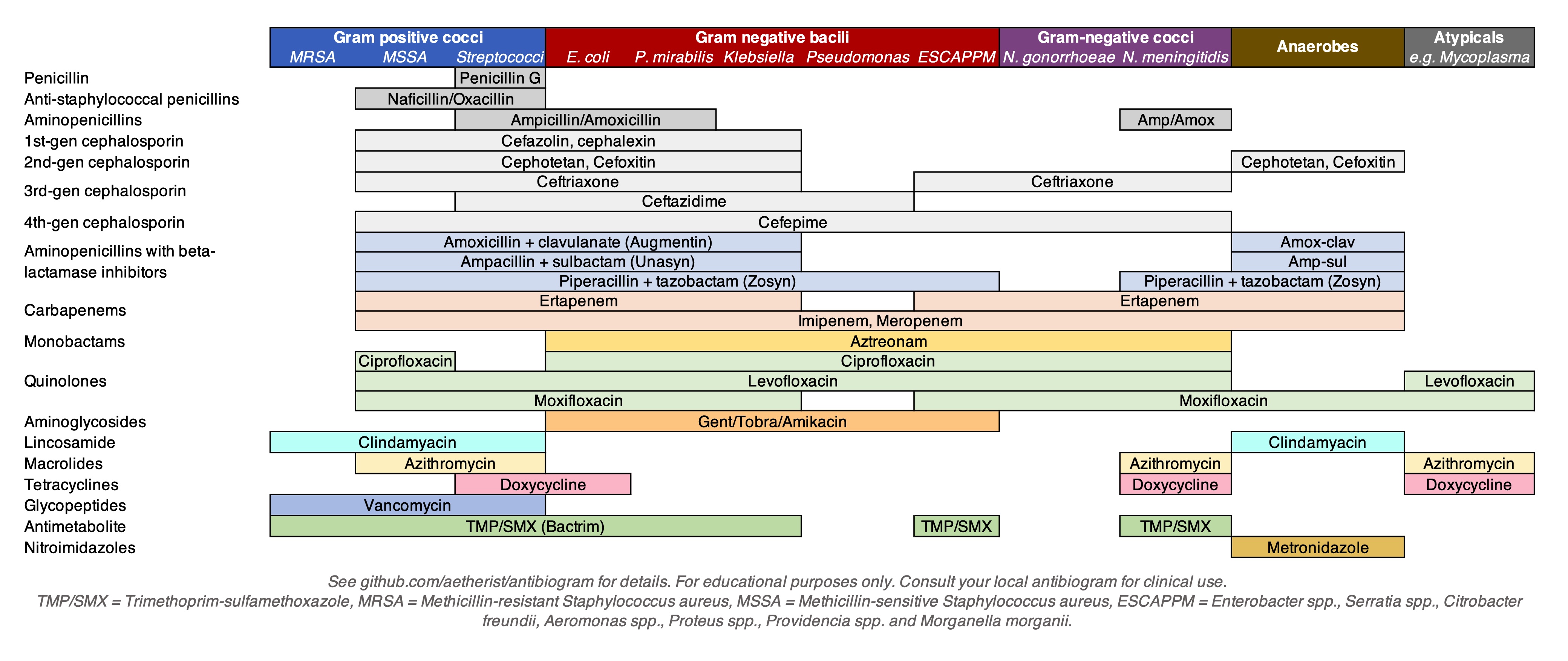
Antibiotic Classes
The following is a list of antibiotics. The highest division between antibiotics is bactericidal and bacteriostatic. Bactericidals kill bacteria directly, whereas bacteriostatics prevent them from dividing. However, these classifications are based on laboratory behavior.The development of antibiotics has had a profound effect on health in people for many years. Also, for both people and animals have used antibiotics to treat infections and diseases. In practice, both treat a bacterial infection. By coverage The following are lists of antibiotics for specific microbial coverage. MRSA Antibiotics that cover methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA): * Vancomycin * Teicoplanin * Linezolid * Daptomycin * Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole * Doxycycline * Ceftobiprole (5th generation) * Ceftaroline (5th generation) * Clindamycin * Dalbavancin * Fusidic acid * Mupirocin (topical) * Omadacycline * Oritavancin * Tedizolid * Telavancin * Tigecycline (also covers gram negatives) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |