|
Reservation In India
Reservation is a system of affirmative action in India that provides historically disadvantaged groups representation in education, employment, government schemes, scholarships and politics. Based on provisions in the Indian Constitution, it allows the Union Government and the States and Territories of India to set ''reserved quotas or seats'', at particular percentage in Education Admissions, Employments, Political Bodys, Promotions, etcb for "socially and educationally backward citizens." History Before independence Quota systems favouring certain castes and other communities existed before independence in several areas of British India. Demands for various forms of positive discrimination had been made, for example, in 1882 and 1891. Rajarshi Shahu, the Maharaja of the princely state of Kolhapur, introduced reservation in favor of non-Brahmin and backward classes, much of which came into force in 1902. He provided free education to everyone and opened several hostels to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pieces of tribal and privately held land being treated as separate enclaves. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political and legal difficulties. The total area of all reservations is , approximately 2.3% of the total area of the United States and about the size of the state of Idaho. While most reservations are small c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Councils Act 1909
The Indian Councils Act 1909, commonly known as the Morley–Minto or Minto–Morley Reforms, was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that brought about a limited increase in the involvement of Indians in the governance of British India. Named after Viceroy Lord Minto and Secretary of State John Morley, the act introduced elections to legislative councils and admitted Indians to councils of the Secretary of State for India, the viceroy, and to the executive councils of Bombay and Madras states. Muslims were granted separate electorates according to the demands of the Muslim League. Background In 1885, the Indian National Congress was founded at Gokuldas Tejpal Sanskrit College in Bombay, gathering a small group of colonial India's educated elite. One of their main grievances was the difficulty Indians faced when trying to enter the civil service and administrative roles. Queen Victoria had promised racial equality in the selection of civil servants for the govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandal Commission
The ''Mandal Commission'' or the Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission (SEBC), was established in India in 1979 by the Janata Party government under Prime Minister Morarji Desai with a mandate to "identify the socially or educationally backward classes" of India.Bhattacharya, Amit. ''Times of India'', 8 April 2006. It was headed by B.P. Mandal, an Indian parliamentarian, to consider the question of reservations for people to redress caste discrimination, and used eleven social, economic, and educational indicators to determine backwardness. In 1980, based on its rationale that OBCs ("Other backward classes") identified on the basis of caste, social, economic indicators made up 52% of India's population, the commission's report recommended that members of Other Backward Classes (OBC) be granted reservations to 27% of jobs under the Central government and public sector undertakings, thus making the total number of reservations for SC, ST and OBC to 49%. Though t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
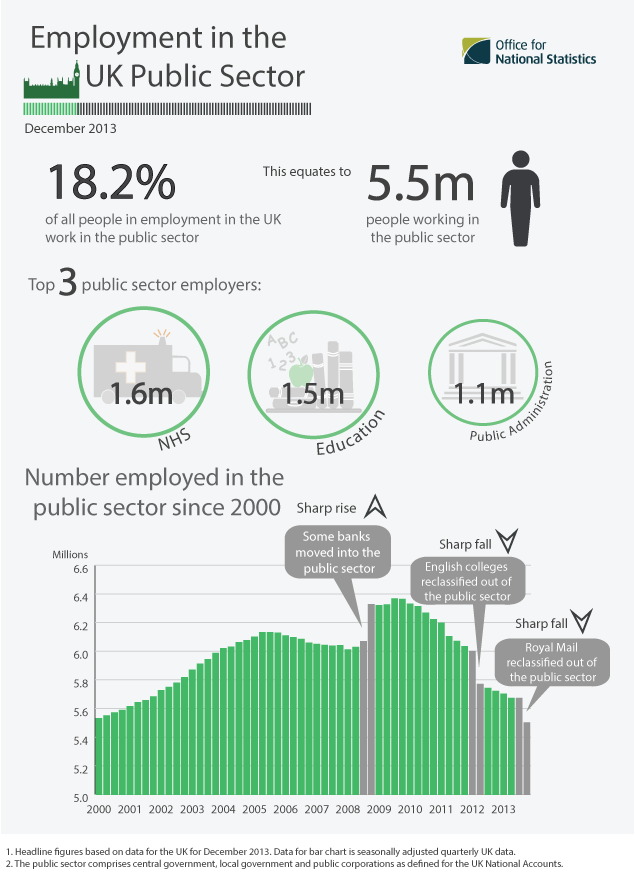
Public Sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, infrastructure, public transit, public education, along with health care and those working for the government itself, such as elected officials. The public sector might provide services that a non-payer cannot be excluded from (such as street lighting), services which benefit all of society rather than just the individual who uses the service. Public enterprises, or state-owned enterprises, are self-financing commercial enterprises that are under public ownership which provide various private goods and services for sale and usually operate on a commercial basis. Organizations that are not part of the public sector are either part of the private sector or voluntary sector. The private sector is composed of the economic sectors that are intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poona Pact
The Poona Pact was an agreement between Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B. R. Ambedkar on behalf of Dalits, depressed classes, and upper caste Hindu leaders on the reservation of electoral seats for the depressed classes in the legislature of British India in 1932. It was made on 24 September 1932 at Yerwada Central Jail in Poona, India. It was signed by Dr. Ambedkar on behalf of the depressed classes and by Madan Mohan Malviya on behalf of upper caste Hindus, Faraz Shah, Sana Ejaz and Gandhi. Gandhi, currently imprisoned by the British, had embarked on a fast unto death to protest against the decision made by British prime minister Ramsay MacDonald, responding to arguments made by Ambedkar in the Round Table Conferences, to give separate electorates to depressed classes for the election of members of provincial legislative assemblies in British India. He wrote that separate electorates would "vivisect and disrupt" Hinduism. Ambedkar, for his part, argued that upper-caste reformers co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalits
Dalit (from sa, दलित, dalita meaning "broken/scattered"), also previously known as untouchable, is the lowest stratum of the castes in India. Dalits were excluded from the four-fold varna system of Hinduism and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Dalits now profess various religious beliefs, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, Islam. Scheduled Castes is the official term for Dalits as per the Constitution of India. History The term ''Dalit'' is a self-applied concept for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste hierarchy. Economist and reformer B. R. Ambedkar (1891–1956) said that untouchability came into Indian society around 400 CE, due to the struggle for supremacy between Buddhism and Brahmanism (an ancient term for Brahmanical Hinduism). Some Hindu priests befriended untouchables and were demoted to low-caste ranks. Eknath, another excommunicated Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) count 87 distinct "''peoples of Europe''", of which 33 form the majority population in at least one sovereign state, while the remaining 54 constitute ethnic minorities. The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of 770 million Europeans.Christoph Pan, Beate Sibylle Pfeil (2002), Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als2006 reprint by Springer(Amazon, no preview) . The Russians are the most populous among Europeans, with a population of roughly 120 million. There are no universally accepted and precise definitions of the terms " ethnic group" and "nationality". In the context of European ethnography in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Indians
Anglo-Indian people fall into two different groups: those with mixed Indian and British ancestry, and people of British descent born or residing in India. The latter sense is now mainly historical, but confusions can arise. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'', for example, gives ''three'' possibilities: "Of mixed British and Indian parentage, of Indian descent but born or living in Britain or (chiefly historical) of English descent or birth but living or having lived long in India". People fitting the middle definition are more usually known as British Asian or British Indian. This article focuses primarily on the modern definition, a distinct minority community of mixed Eurasian ancestry, whose first language is English. The All India Anglo-Indian Association, founded in 1926, has long represented the interests of this ethnic group; it holds that Anglo-Indians are unique in that they are Christians, speak English as their mother tongue, and have a historical link to both Europe a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Christians
Christianity is India's third-largest religion with about 27.8 million adherents, making up 2.3 percent of the population as of the 2011 census. The written records of the Saint Thomas Christians state that Christianity was introduced to the Indian subcontinent by Thomas the Apostle, who sailed to the Malabar region in the present-day Kerala state in 52 AD. The Acts of Thomas mentions that the first converts were Malabarese Jews, who had settled in India before the birth of Christ. Thomas who was a Jew by birth came in search of Indian Jews. Following years of evangelising, Thomas was martyred and his remains were buried at St. Thomas Mount in Mylapore. A scholarly consensus exists that Christian communities had firmly established in the Malabar by 600 AD at the latest. These communities were composed mainly of the Oriental Orthodox Eastern Christians, belonging to the Church of the East in India, that used Syriac as their liturgical language. Following the discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'. Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh'' ('lion'/'tiger') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world. Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar'' ('baptism by Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of their initiation known as Khalsa, and they m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_according_to_Indian_Caste_System_-_1942.jpg)


.jpg)

