|
Research In Lithium-ion Batteries
Research in lithium-ion batteries has produced many proposed refinements of lithium-ion batteries. Areas of research interest have focused on improving energy density, safety, rate capability, cycle durability, flexibility, and cost. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is becoming popular in many fields including using it for lithium-ion battery research. These methods have been used in all aspects of battery research including materials, manufacturing, characterization, and prognosis/diagnosis of batteries. Anode Lithium-ion battery anodes are most commonly made of graphite. Graphite anodes are limited to a theoretical capacity of 372 mAh/g for their fully lithiated state. Co+Li2O. Titanium dioxide In 1984, researchers at Bell Labs reported the synthesis and evaluation of a series of lithiated titanates. Of specific interest were the anatase form of titanium dioxide and the lithium spinel LiTi2O4 Anatase has been observed to have a maximum capac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium-ion Battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees significant use for grid-scale energy storage and military and aerospace applications. Compared to other rechargeable battery technologies, Li-ion batteries have high energy densities, low self-discharge, and no memory effect (although a small memory effect reported in LFP cells has been traced to poorly made cells). Chemistry, performance, cost and safety characteristics vary across types of lithium-ion batteries. Most commercial Li-ion cells use intercalation compounds as the active materials. The anode or negative electrode is usually graphite, although silicon-carbon is also being increasingly used. Cells can be manufactured to prioritize either energy or power density. Handheld electronics mostly use lithium polymer batter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese Dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the zinc–carbon battery.. is also used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese compounds, such as . It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, for example, for the oxidation of allylic alcohols. is α polymorph that can incorporate a variety of atoms (as well as water molecules) in the "tunnels" or "channels" between the manganese oxide octahedra. There is considerable interest in as a possible cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Structure Several polymorphs of are claimed, as well as a hydrated form. Like many other dioxides, crystallizes in the rutile crystal structure (this polymorph is called pyrolusite or ), with three-coordinate oxide and octahedral metal ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanofoam
Nanofoams are a class of nanostructured, porous materials (foams) containing a significant population of pores with diameters less than 100 nm. Aerogels are one example of nanofoam. Metal Overview Metallic nanofoams are a subcategorization of nanofoams; more specifically, there are nanofoams consisting of metals, often pure, that form interconnected networks of ligaments that make up the structure of the foam. A variety of metals are used, including copper, nickel, gold, and platinum. Metallic nanofoams may offer certain advantages over alternative polymer nanofoams; structurally, they retain the electrical conductivity of metals, offer increased ductility, as well as the higher surface area and nano-architecture properties offered by nanofoams. Fabrication Synthesis of metallic nanofoams may be accomplished through a variety of methods. In 2006, researchers produced metal nanofoams by igniting pellets of energetic metal bis(tetrazolato)amine complexes. Nanofoams of iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotube
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional Hexagonal tiling, hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwestern University
Northwestern University is a private research university in Evanston, Illinois. Founded in 1851, Northwestern is the oldest chartered university in Illinois and is ranked among the most prestigious academic institutions in the world. Chartered by the Illinois General Assembly in 1851, Northwestern was established to serve the former Northwest Territory. The university was initially affiliated with the Methodist Episcopal Church but later became non-sectarian. By 1900, the university was the third largest university in the United States. In 1896, Northwestern became a founding member of the Big Ten Conference, and joined the Association of American Universities as an early member in 1917. The university is composed of eleven undergraduate, graduate, and professional schools, which include the Kellogg School of Management, the Pritzker School of Law, the Feinberg School of Medicine, the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, the Bienen School of Music, the McCormick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
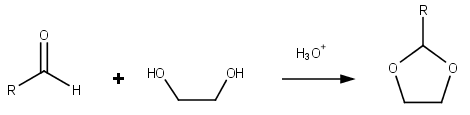
Dioxolane
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran by interchange of one oxygen for a CH2 group. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals. As a class of compounds Dioxolanes are a group of organic compounds containing the dioxolane ring. Dioxolanes can be prepared by acetalization of aldehydes and ketalization of ketones with ethylene glycol. (+)-''cis''-Dioxolane is the trivial name for which is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. Protecting groups Organic compounds containing carbonyl groups sometimes need protection so that they do not undergo reactions during transformations of other functional groups that may be present. A variety of approaches to protection and deprotection of carbonyls including as dioxolanes are kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar-Ilan University
Bar-Ilan University (BIU, he, אוניברסיטת בר-אילן, ''Universitat Bar-Ilan'') is a public research university in the Tel Aviv District city of Ramat Gan, Israel. Established in 1955, Bar Ilan is Israel's second-largest academic institution. It has about 20,000 students and 1,350 faculty members. Bar-Ilan's mission is to "blend Jewish tradition with modern technologies and scholarship and the university endeavors to ... teach the Jewish heritage to all its students while providing nacademic education." History Bar-Ilan University has Jewish-American roots: It was conceived in Atlanta in a meeting of the American Mizrahi organization in 1950, and was founded by Professor Pinkhos Churgin, an American Orthodox rabbi and educator, who was president from 1955 to 1957 where he was succeeded by Joseph H. Lookstein who was president from 1957 to 1967. When it was opened in 1955, it was described by ''The New York Times'' "as Cultural Link Between the sraeliRepu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doron Aurbach
Doron Aurbach ( he, דורון אורבך; born 3 September 1952) is an Israeli electrochemist, materials and surface scientist. Biography Doron Aurbach was born in 1952 in Israel to parents who survived the Holocaust and fought the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, grew up in Ramat Gan and studied in Blich High School. He served in Sayeret Golani reconnaissance unit, a.k.a. 631st Reconnaissance Battalion, (an Israeli special force unit) and fought west to the Suez Canal during the Yom Kippur War (1973). Later he returned to Golani Brigade as a deputy commander of a combat support company, and was discharged from reserve duty with a rank of a Major ( he, רב סרן), at the age of 46, as a patrol officer in the Armored Corps. He is married to Sara, an educational counselor by training who writes children's books. They live in Bnei Brak and have seven children and dozens of grandchildren. Academic career He obtained his BSc (1977), MSc (1979) and PhD (1983, summa cum laude) f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium–sulfur Battery
The lithium–sulfur battery (Li–S battery) is a type of rechargeable battery. It is notable for its high specific energy. The low atomic weight of lithium and moderate atomic weight of sulfur means that Li–S batteries are relatively light (about the density of water). They were used on the longest and highest-altitude unmanned solar-powered aeroplane flight (at the time) by Zephyr 6 in August 2008. Lithium–sulfur batteries may displace lithium-ion cells because of their higher energy density and reduced cost. This is due to the use of sulfur instead of cobalt, a common element in lithium-ion batteries. Li–S batteries offer specific energies on the order of 550 Wh/ kg, while lithium-ion batteries are in the range of 150260Wh/kg. Li–S batteries with up to 1,500 charge and discharge cycles were demonstrated in 2017, but cycle life tests at commercial scale and with lean electrolyte have not been completed. As of early 2021, none were commercially available. Issues th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium–air Battery
The lithium–air battery (Li–air) is a metal–air electrochemical cell or battery chemistry that uses oxidation of lithium at the anode and reduction of oxygen at the cathode to induce a current flow. Pairing lithium and ambient oxygen can theoretically lead to electrochemical cells with the highest possible specific energy. Indeed, the theoretical specific energy of a non-aqueous Li–air battery, in the charged state with Li2O2 product and excluding the oxygen mass, is ~40.1 MJ/kg = 11.14 kWh/kg of lithium. This is comparable to the theoretical specific energy of gasoline, ~46.8 MJ/kg. In practice, Li–air batteries with a specific energy of ~6.12 MJ/kg = 1.7 kWh/kg of lithium at the cell level have been demonstrated. This is about 5 times greater than that of a commercial lithium-ion battery, and is sufficient to run a 2,000 kg electric vehicle for ~ on a single charge using 60 kg of lithium (i.e. 20.4 kWh/100 km). However, the practical power and life cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
