|
Republic Of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ), is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 1,726,000. It borders Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south-east. Guinea-Bissau was once part of the kingdom of Kaabu, as well as part of the Mali Empire. Parts of this kingdom persisted until the 18th century, while a few others were under some rule by the Portuguese Empire since the 16th century. In the 19th century, it was colonised as Portuguese Guinea. Portuguese control was restricted and weak until the early 20th century with the pacification campaigns, these campaigns solidified Portuguese sovereignty in the area. The final Portuguese victory over the remaining bastion of mainland resistance, the Papel ruled Kingdom of Bissau in 1915 by the Portugue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of member states of the African Union, 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The bloc was founded on 26 May 2001 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and launched on 9 July 2002 in Durban, South Africa. The intention of the AU was to replace the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa by 32 signatory governments; the OAU was disbanded on 9 July 2002. The most important decisions of the AU are made by the Assembly of the African Union, a semi-annual meeting of the heads of state and government of its member states. The AU's secretariat, the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa. The largest city in the AU is Lagos, Nigeria, while the list of urban areas in Africa by population, largest urban agglomeration is Cairo, Egypt. The African U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bissau
Bissau () is the capital, and largest city of Guinea-Bissau. Bissau had a population of 492,004. Bissau is located on the Geba River estuary, off the Atlantic Ocean, and is Guinea-Bissau's largest city, major port, and its administrative and military centre. Etymology The term Bissau may have come from the name of a clan N'nssassun, in its plural form Bôssassun.direct link to pdf Intchassu (Bôssassu) was the name given to the nephew of King Mecau—the first sovereign of the island of Bissau—, son of his sister Pungenhum. Bôssassu formed a clan of the Papel peoples. History The city was founded in 1687 by Portugal as a fortified port and trading center. In 1942 the capital of Portuguese Guinea was transferred from Bolama to Bissau. After the declaration of independence by the anti-colonial guerrillas of PAIGC in 1973, the capital of the rebel territories was declared to be Madina do Boe, while Bissau remained the colonial capital. When Portugal granted independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic
A republic () is a "sovereign state, state in which Power (social and political), power rests with the people or their Representative democracy, representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th centuries, the term was used to imply a state with a Democracy, democratic or Representative democracy, representative constitution (constitutional republic), but more recently it has also been used of autocratic or dictatorial states not ruled by a monarch. It is now chiefly used to denote any non-monarchical state headed by an elected or appointed president. , List of countries by system of government, 159 of the world's List of sovereign states, 206 sovereign states use the word "republic" as part of their official names. Not all of these are republics in the sense of having elected governments, nor is the word "republic" used in the names of all states with elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-presidential System
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has a popularly elected head of state and from the presidential system in that the cabinet, although named by the president, is responsible to the legislature, which may force the cabinet to resign through a motion of no confidence. While the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) and Finland (from 1919 to 2000) exemplified early semi-presidential systems, the term "semi-presidential" was first introduced in 1959 in an article by journalist Hubert Beuve-Méry, and popularized by a 1978 work written by political scientist Maurice Duverger, both of whom intended to describe the French Fifth Republic (established in 1958). Definition Maurice Duverger's original definition of semi-presidentialism stated that the president had to be elected, poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unitary State
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only the powers that the central government chooses to delegate. Although Power (social and political), political power may be delegated through devolution to regional or local governments by statute, the central government may abrogate the acts of Devolution, devolved governments or curtail (or expand) their powers. Unitary states stand in contrast with federations, also known as ''federal states''. A large majority of the world's sovereign states (166 of the 193 Member states of the United Nations, UN member states) have a unitary system of government. Devolution compared with federalism A unitary system of government can be considered the opposite of federalism. In federations, the provincial/regional governments share powers with the centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and antitheism. Social scientists tend to define irreligion as a purely naturalist worldview that excludes a belief in anything supernatural. The broadest and loosest definition, serving as an upper limit, is the lack of religious identification, though many non-identifiers express metaphysical and even religious beliefs. The narrowest and strictest is subscribing to positive atheism. According to the Pew Research Center's 2012 global study of 230 countries and territories, 16% of the world's population does not identify with any religion. The population of the religiously unaffiliated, sometimes referred to as "nones", has grown significantly in recent years. Measurement of irreligiosity requires great cultural sensitivity, especially outside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Guinea-Bissau
Religion in Guinea-Bissau is diverse, with no particular religion comprising an absolute majority of the population. Islam is the most widely professed faith, and significant populations of Christians and adherents of Traditional Faiths are also present in the country. The CIA World Factbook (2020 estimate) states that around 46.1% of the population are Muslims, 30.6% adhere to Folk religions, 18.9% are Christians, and 4.4% are non-religious or practice other religions. Meanwhile, the US State Department mentions that estimates vary greatly and cites the Pew Forum data (2020) of 46% Muslim, 31% indigenous religious practices, and 19% Christian. Sunni Islam, including that of Sufi-oriented, are most concentrated in the northern and northeastern parts of the country. Practitioners of traditional indigenous religious beliefs generally live in all but the northern parts of the country. Christians are mostly found along the coastal regions, and belong to the Roman Catholic Church (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious .... It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional African Religions
The traditional beliefs and practices of African people are highly diverse beliefs that include various ethnic religions.Encyclopedia of African Religion (Sage, 2009) Molefi Kete Asante Generally, these traditions are oral rather than scriptural and passed down from one generation to another through folk tales, songs, and festivals, include belief in an amount of higher and lower gods, sometimes including a supreme creator or force, belief in spirits, veneration of the dead, use of magic and traditional African medicine. Most religions can be described as animistic with various polytheistic and pantheistic aspects. The role of humanity is generally seen as one of harmonizing nature with the supernatural. Spread Adherents of traditional religions in Africa are distributed among 43 countries and are estimated to number over 100 million.''Britannica Book of the Year'' (2003), ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2003) p.306 According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', as of mid- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) " e Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, with its followers ranging between 1-1.8 billion globally, or around a quarter of the world' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papel People
Papels also known as Moium, Oium, Papei, Pepel or Pelels, are an ethnic group primarily located in Guinea Bissau, though are also found in Casamance (Senegal) and Guinea. Its population in Guinea Bissau is 183,000, with 9,000 living outside of the country. They traditionally engaged in hunting and agriculture. History Origins Oral history on their origins is as follows, the son of a king from the Kingdom of Quinara on the south of the river Geba called Mecau, arrived at Bissau on one of his hunting trips. Finding Bissau to hold good fertile soil and habitation he opted to reside there establishing a kingdom. From his homeland Quinara he brought his sister Punguenhum who was already with child, and his six wives Intende, Djokom, Mala, Intsoma, Kliker and Intchipolo. Mecau invited other subjects from his fathers kingdom to settle the area of Bissau alongside him. From his sister and six wives seven main Papel clans arose. * The first clan called N'nssassun (plural, bossassun) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
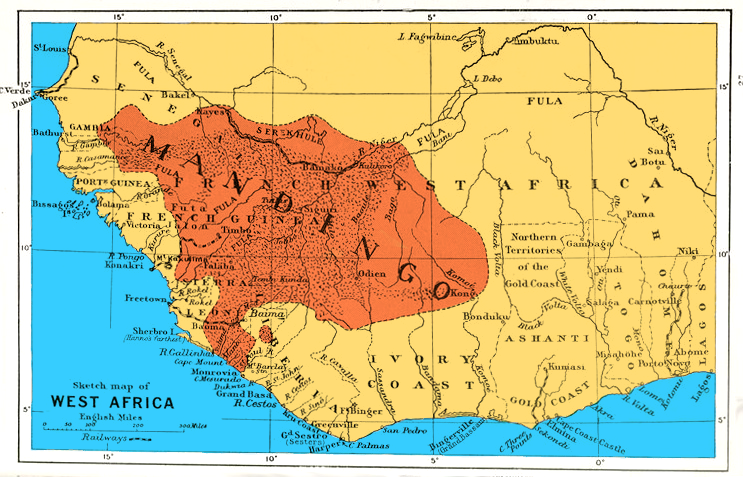
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a '' lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Sene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)