|
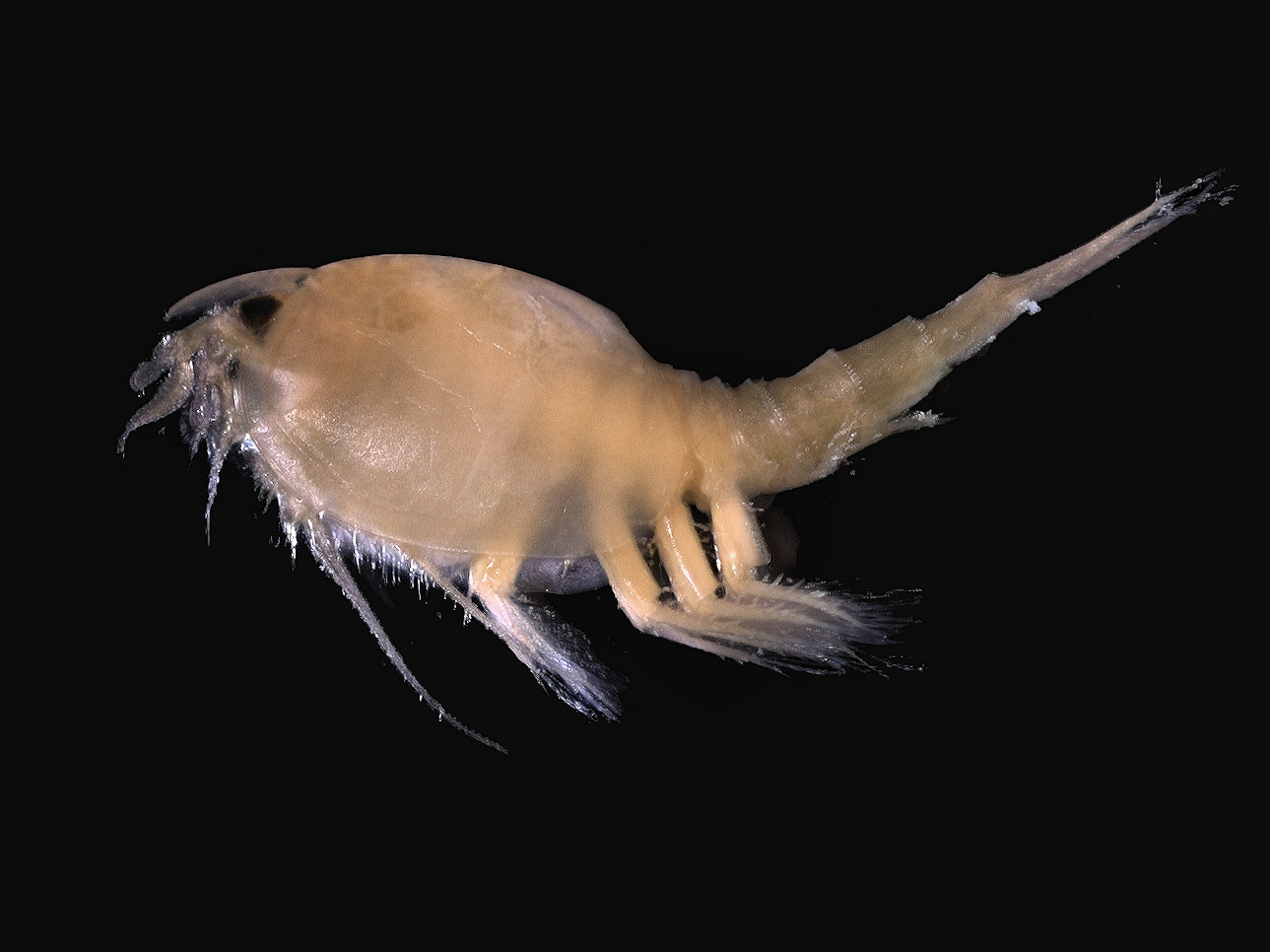
Remipedia
Remipedia is a class of blind crustaceans found in coastal aquifers which contain saline groundwater, with populations identified in almost every ocean basin so far explored, including in Australia, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean. The first described remipede was the fossil '' Tesnusocaris goldichi'' (Lower Pennsylvanian). Since 1979, at least seventeen living species have been identified in subtropical regions around the world. Description Remipedes are long and comprise a head and an elongate trunk of up to thirty-two similar body segments. Pigmentation and eyes are absent. Biramous swimming appendages are laterally present on each segment. The animals swim on their backs and are generally slow-moving. They are the only known venomous crustaceans, and have fangs connected to secretory glands, which inject a combination of digestive enzymes and venom into their prey, but they also feed through filter feeding. Being hermaphrodites, the female pore is located on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancrustacea
Pancrustacea is the clade that comprises all crustaceans and hexapods. This grouping is contrary to the Atelocerata hypothesis, in which Myriapoda and Hexapoda are sister taxa, and Crustacea are only more distantly related. As of 2010, the Pancrustacea taxon is considered well accepted, with most studies recovering Hexapoda within Crustacea. The clade has also been called Tetraconata, referring to having four cone cells in the ommatidia. This name is preferred by some scientists as a means of avoiding confusion with the use of "pan-" to indicate a clade that includes a crown group and all of its stem group representatives. Molecular studies A monophyletic Pancrustacea has been supported by several molecular studies, in most of which the subphylum Crustacea is paraphyletic with regard to hexapods (that is, that hexapods, including insects, are derived from crustacean ancestors). The evidence for this clade derives from molecular data and morphological characteristics. The m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godzilliidae
Godzilliidae is a family of remipede Remipedia is a class of blind crustaceans found in coastal aquifers which contain saline groundwater, with populations identified in almost every ocean basin so far explored, including in Australia, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean. The ...s in the order Nectiopoda. There are at least two genera and four described species in Godzilliidae. Genera These two genera belong to the family Godzilliidae: * '' Godzilliognomus'' Yager, 1989 * '' Godzillius'' Schram, Yager & Emerson, 1986 References Further reading * * Remipedia Articles created by Qbugbot Crustacean families {{crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesnusocaris Goldichi
''Tesnusocaris goldichi'' is an extinct species of remipedian crustacean that lived in the Pennsylvanian period, the one of the two representatives of the extinct remipedian Order Enantiopoda. Its fossil is from the Lower Pennsylvanian (Paleozoic, Carboniferous) Tesnus formation, Texas. The other known enantiopod remipedian is '' Cryptocaris hootchi'' of the Mazon Creek The Mazon Creek fossil beds are a conservation ' found near Morris, in Grundy County, Illinois. The fossils are preserved in ironstone concretions, formed approximately in the mid- Pennsylvanian epoch of the Carboniferous period. These concreti ... fauna. References Remipedia Carboniferous crustaceans Monotypic arthropod genera Carboniferous animals of North America {{paleo-crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleonectidae
Speleonectidae is a family of remipedes in the order Nectiopoda. There are at least two genera and about seven described species in Speleonectidae. Genera These two genera and seven species belong to the family Speleonectidae: * '' Lasionectes'' Yager & Schram, 1986 ** '' Lasionectes entrichoma'' Yager & Schram, 1986 * '' Speleonectes'' Yager, 1981 ** '' Speleonectes epilimnius'' Yager & Carpenter, 1999 ** '' Speleonectes gironensis'' Yager, 1994 ** '' Speleonectes kakuki'' Daenekas, Iliffe, Yager & Koenemann, 2009 ** '' Speleonectes lucayensis'' Yager, 1981 ** '' Speleonectes minnsi'' Koenemann, Iliffe & van der Ham, 2003 ** '' Speleonectes tanumekes'' Koenemann, Iliffe & van der Ham, 2003 Several former ''Speleonectes'' species have recently been transferred to other genera: * ''Speleonectes atlantida'' (to ''Morlockia atlantida'') * ''Speleonectes benjamini'' (to '' Angirasu benjamini'') * ''Speleonectes tulumensis'' (to ''Xibalbanus tulumensis ''Xibalbanus tulumensis'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branchiopoda
Branchiopoda is a class of crustaceans. It comprises fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, Diplostraca (or Cladocera), Notostraca and the Devonian '' Lepidocaris''. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton and detritus. Description Members of the Branchiopoda are unified by the presence of gills on many of the animals' appendages, including some of the mouthparts. This is also responsible for the name of the group (from the grc, βράγχια, gills, akin to , windpipe; el, πούς, foot). They generally possess compound eyes and a carapace, which may be a shell of two valves enclosing the trunk (as in most Cladocera), broad and shallow (as in the Notostraca), or entirely absent (as in the Anostraca). In the groups where the carapace prevents the use of the trunk limbs for swimming (Cladocera, clam shrimp and the extinct Lipostraca), the antennae are used for locomotion, as they are in the nauplius. Male fairy shrimp have an enlarged pair of antennae with w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malacostraca
Malacostraca (from New Latin; ) is the largest of the six classes of crustaceans, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, amphipods, mantis shrimp, tongue-eating lice and many other less familiar animals. They are abundant in all marine environments and have colonised freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are segmented animals, united by a common body plan comprising 20 body segments (rarely 21), and divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. Etymology The name Malacostraca was coined by a French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802. He was curator of the arthropod collection at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris. The name comes from the Greek roots (', meaning "soft") and (', meaning "shell"). The name is misleading, since the shell is soft only immediately after moulting, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalocarida
The Cephalocarida are a class in the subphylum Crustacea comprising only 12 benthic species. They were discovered in 1955 by Howard L. Sanders, and are commonly referred to as horseshoe shrimp. They have been grouped together with the Remipedia in the Xenocarida. Although a second family, Lightiellidae, is sometimes used, all cephalocaridans are generally considered to belong in just one family: Hutchinsoniellidae. Though no fossil record of cephalocaridans has been found, most specialists believe them to be primitive among crustaceans. Taxonomy * Class Cephalocarida Sanders 1955 ** Order Brachypoda Birshteyn 1960 *** Family Hutchinsoniellidae Sanders 1955 **** Genus '' Chiltoniella'' Knox & Fenwick 1977 ***** ''Chiltoniella elongata'' Knox & Fenwick 1977 **** Genus '' Hampsonellus'' Hessler & Wakabara 2000 ***** ''Hampsonellus brasiliensis'' Hessler & Wakabara 2000 **** Genus ''Hutchinsoniella'' Sanders 1955 ***** ''Hutchinsoniella macracantha'' Sanders 1955 **** Genus '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibulata
Mandibulata, termed "mandibulates", is a clade of arthropods that comprises the extant subphyla Myriapoda (millipedes and others), Crustacea and Hexapoda (insects and others). Mandibulata is currently believed to be the sister group of the clade Arachnomorpha, which comprises the rest of arthropods (Chelicerata and Trilobita). The mandibulates constitute the largest and most varied arthropod group. The name "Mandibulata" refers to the mandibles or jaws, which are the characterizing feature of its member arthropods. Molecular phylogenetic studies suggest that the living arthropods are related as shown in the cladogram below. Crustaceans do not form a monophyletic group as insects and other hexapods have evolved from within them. See also * Atelocerata *Marrellomorpha * Myriochelata *Pancrustacea Pancrustacea is the clade that comprises all crustaceans and hexapods. This grouping is contrary to the Atelocerata hypothesis, in which Myriapoda and Hexapoda are sister ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
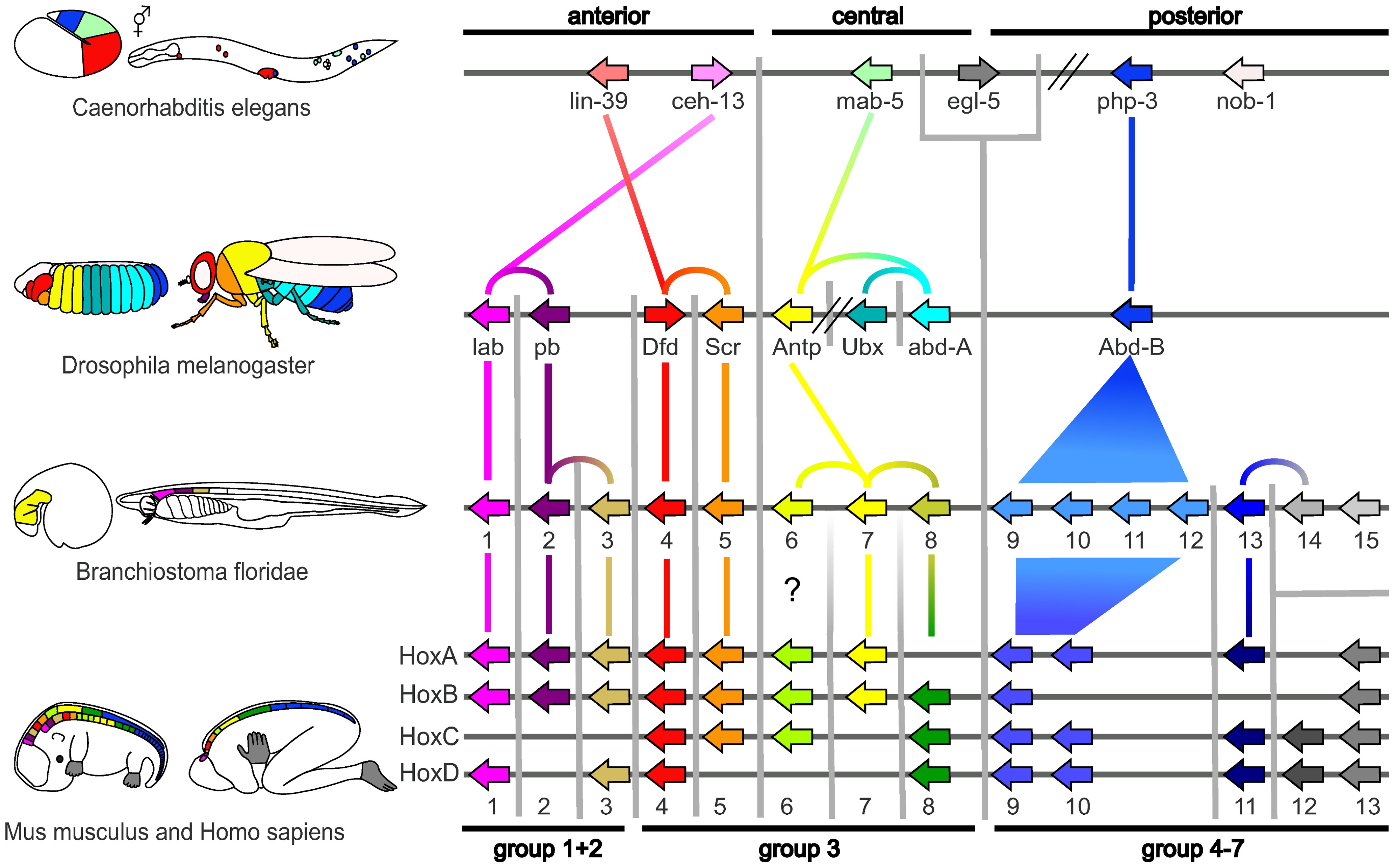
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoologists did not know how embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are controlled by similar genes such as ''pax-6'', from the evo-devo gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considered insects). The Collembola (or springtails) are very abundant in terrestrial environments. ''Hexapods'' are named for their most distinctive feature: a consolidated thorax with three pairs of legs (six legs). Most other arthropods have more than three pairs of legs. Most recent studies have recovered Hexapoda as a subgroup of Crustacea. Morphology Hexapods have bodies ranging in length from 0.5 mm to over 300 mm which are divided into an anterior head, thorax, and posterior abdomen. The head is composed of a presegmental ''acron'' that usually bears eyes (absent in Protura and Diplura), followed by six segments, all closely fused together, with the following appendages: :Segment I. None :Segment II. Antennae (sensory), absent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |