Branchiopoda on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Branchiopoda is a class of
 The fairy shrimp of the order
The fairy shrimp of the order
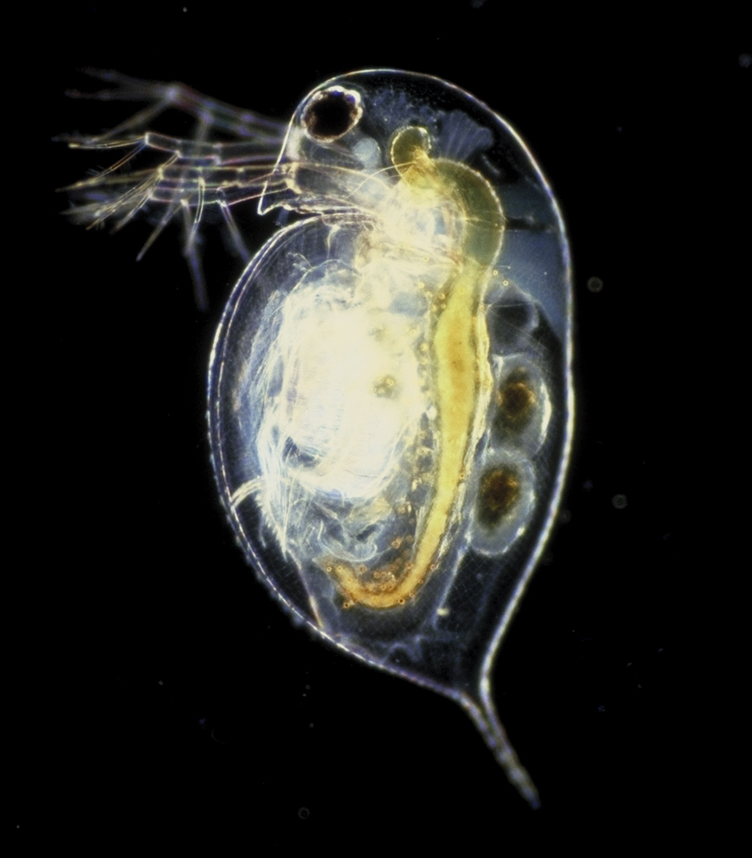 These four orders make up a group of small
These four orders make up a group of small
crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s. It comprises fairy shrimp
Anostraca is one of the four orders of crustaceans in the class Branchiopoda; its members are referred to as fairy shrimp. They live in vernal pools and hypersaline lakes across the world, and they have even been found in deserts, ice-covered mo ...
, clam shrimp
Clam shrimp are a group of bivalved branchiopod crustaceans that resemble the unrelated bivalved molluscs. They are extant and also known from the fossil record, from at least the Devonian period and perhaps before. They were originally classifi ...
, Diplostraca
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms).
Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more ...
(or Cladocera), Notostraca
The order Notostraca, containing the single family Triopsidae, is a group of crustaceans known as tadpole shrimp or shield shrimp. The two genera, ''Triops'' and '' Lepidurus'', are considered living fossils, with similar forms having existed sinc ...
and the Devonian ''Lepidocaris
''Lepidocaris rhyniensis'' is an extinct species of crustacean. It is the only species known from the order Lipostraca, and is the only abundant animal in the Pragian-aged Rhynie chert deposits. It resembles modern Anostraca, to which it is proba ...
''. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton and detritus.
Description
Members of the Branchiopoda are unified by the presence ofgill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
s on many of the animals' appendages, including some of the mouthparts. This is also responsible for the name of the group (from the grc, βράγχια, gills, akin to , windpipe
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the l ...
; el, πούς, foot). They generally possess compound eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which disti ...
s and a carapace, which may be a shell of two valves enclosing the trunk (as in most Cladocera), broad and shallow (as in the Notostraca), or entirely absent (as in the Anostraca). In the groups where the carapace prevents the use of the trunk limbs for swimming (Cladocera, clam shrimp and the extinct Lipostraca), the antennae are used for locomotion, as they are in the nauplius. Male fairy shrimp have an enlarged pair of antennae with which they grasp the female during mating, while the bottom-feeding Notostraca, the antennae are reduced to vestiges. The trunk limbs are beaten in a metachronal rhythm
A metachronal rhythm or metachronal wave refers to wavy movements produced by the sequential action (as opposed to synchronized) of structures such as cilia, segments of worms, or legs. These movements produce the appearance of a travelling wave. ...
, causing a flow of water along the midline of the animal, from which it derives oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, food and, in the case of the Anostraca and Notostraca, movement.
Ecology
Among the branchiopods, only somecladocera
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms).
Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more ...
ns are marine; all the other groups are found in continental fresh water, including temporary pools and in salt lakes. Most branchiopodans eat floating detritus or plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
, which they take using the seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for " bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. ...
e on their appendages.
Taxonomy
In early taxonomic treatments, the current members of the Branchiopoda were all placed in a single genus, ''Monoculus''. The taxon Branchiopoda was erected byPierre André Latreille
Pierre André Latreille (; 29 November 1762 – 6 February 1833) was a French zoologist, specialising in arthropods. Having trained as a Roman Catholic priest before the French Revolution, Latreille was imprisoned, and only regained his freedom ...
in 1817, initially at the rank
Rank is the relative position, value, worth, complexity, power, importance, authority, level, etc. of a person or object within a ranking, such as:
Level or position in a hierarchical organization
* Academic rank
* Diplomatic rank
* Hierarchy
* ...
of order.
The current upper-level classification of Branchiopoda, according to the World Register of Marine Species (2021), is as follows:
Class Branchiopoda Latreille, 1817
: Subclass Sarsostraca Tasch, 1969
::Order Anostraca
Anostraca is one of the four orders of crustaceans in the class Branchiopoda; its members are referred to as fairy shrimp. They live in vernal pools and hypersaline lakes across the world, and they have even been found in deserts, ice-covered m ...
Sars, 1867
:::Suborder Anostracina Weekers et al., 2002
:::Suborder Artemiina Weekers et al., 2002
: Subclass Phyllopoda
Branchiopoda is a class (biology), class of crustaceans. It comprises Anostraca, fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, Diplostraca (or Cladocera), Notostraca and the Devonian ''Lepidocaris''. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton ...
Preuss, 1951
:: Superorder Diplostraca
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms).
Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more ...
Gerstaecker, 1866
::: Order Anomopoda
Anomopoda is an order of the superorder Diplostraca. These crustaceans, a type of water flea, are members of the class Branchiopoda. The Anomopoda typically have five pairs of thoracic limbs, but sometimes have six pairs. The head of the Anomopo ...
G.O. Sars, 1865
::: Order Ctenopoda
The Ctenopoda are an order of the superorder Diplostraca, comprising the three families Holopediidae, Pseudopenilidae, and Sididae. Its members mostly live in fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or fro ...
G.O. Sars, 1865
::: Order Cyclestherida
Clam shrimp are a group of bivalved branchiopod crustaceans that resemble the unrelated bivalved molluscs. They are extant and also known from the fossil record, from at least the Devonian period and perhaps before. They were originally classifi ...
Sars G.O., 1899
::: Order Haplopoda
''Leptodora'' is a genus containing two species of large, nearly transparent predatory water fleas. They grow up to long, with two large antennae used for swimming and a single compound eye. The legs are used to catch copepods that it comes i ...
G.O. Sars, 1865
::: Order Laevicaudata
Clam shrimp are a group of bivalved branchiopod crustaceans that resemble the unrelated bivalved molluscs. They are extant and also known from the fossil record, from at least the Devonian period and perhaps before. They were originally classifi ...
Linder, 1945
::: Order Onychopoda
Onychopoda are a specialised order of branchiopod crustaceans, belonging to the superorder Cladocera.
The order Onychopoda is "one of the most morphologically distinctive groups of cladocerans". They have only four pairs of legs, compared to fiv ...
G.O. Sars, 1865
::: Order Spinicaudata
Clam shrimp are a group of bivalved branchiopod crustaceans that resemble the unrelated bivalved molluscs. They are extant and also known from the fossil record, from at least the Devonian period and perhaps before. They were originally classifi ...
Linder, 1945
:: Order Notostraca
The order Notostraca, containing the single family Triopsidae, is a group of crustaceans known as tadpole shrimp or shield shrimp. The two genera, ''Triops'' and '' Lepidurus'', are considered living fossils, with similar forms having existed sinc ...
G. O. Sars, 1867
::Genus † Cryptocaris Barrande, 1872
::Genus † Dithyrocaris
In addition, the extinct genus ''Lepidocaris
''Lepidocaris rhyniensis'' is an extinct species of crustacean. It is the only species known from the order Lipostraca, and is the only abundant animal in the Pragian-aged Rhynie chert deposits. It resembles modern Anostraca, to which it is proba ...
'' is generally placed in Branchiopoda.
Anostraca
 The fairy shrimp of the order
The fairy shrimp of the order Anostraca
Anostraca is one of the four orders of crustaceans in the class Branchiopoda; its members are referred to as fairy shrimp. They live in vernal pools and hypersaline lakes across the world, and they have even been found in deserts, ice-covered m ...
are usually long (exceptionally up to ). Most species have 20 body segments, bearing 11 pairs of leaf-like ''phyllopodia'' (swimming legs), and the body lacks a carapace. They live in vernal pool
Vernal pools, also called vernal ponds or ephemeral pools, are seasonal pools of water that provide habitat for distinctive plants and animals. They are considered to be a distinctive type of wetland usually devoid of fish, and thus allow the safe ...
s and hypersaline lakes across the world, including pools in deserts, in ice-covered mountain lakes and in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
. They swim "upside-down" and feed by filtering organic particles from the water or by scraping algae from surfaces. They are an important food for many birds and fish, and are cultured and harvested for use as fish food. There are 300 species spread across 8 families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
.
Lipostraca
Lipostraca contains a single extinct Early Devonian species, '' Lepidocaris rhyniensis'', which is the most abundant animal in theRhynie chert
The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness (a Lagerstätte). It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is locate ...
deposits. It resembles modern Anostraca, to which it is probably closely related, although its relationships to other orders remain unclear. The body is long, with 23 body segments and 19 pairs of appendages, but no carapace. It occurred chiefly among charophyte
Charophyta () is a group of freshwater green algae, called charophytes (), sometimes treated as a division, yet also as a superdivision or an unranked clade. The terrestrial plants, the Embryophyta emerged within Charophyta, possibly from terre ...
s, probably in alkaline temporary pools.
Notostraca
The orderNotostraca
The order Notostraca, containing the single family Triopsidae, is a group of crustaceans known as tadpole shrimp or shield shrimp. The two genera, ''Triops'' and '' Lepidurus'', are considered living fossils, with similar forms having existed sinc ...
comprises the single family Triopsidae, containing the tadpole shrimp or shield shrimp. The two genera, '' Triops'' and ''Lepidurus
''Lepidurus'' is a genus of small crustaceans in the order Notostraca (tadpole shrimp). It is the larger of the two extant genera of the tadpole shrimps, the other being ''Triops''. They are commonly found in vernal pools and survive dry periods ...
'', are considered living fossil
A living fossil is an extant taxon that cosmetically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living foss ...
s, having not changed significantly in outward form since the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
. They have a broad, flat carapace, which conceals the head and bears a single pair of compound eyes. The abdomen is long, appears to be segmented and bears numerous pairs of flattened legs. The telson
The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an arthropod. Depending on the definition, the telson is either considered to be the final segment of the arthropod body, or an additional division that is not a true segment on accou ...
is flanked by a pair of long, thin caudal rami. Phenotypic plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompa ...
within taxa makes species-level identification difficult, and is further compounded by variation in the mode of reproduction. The evidence of phenotypic plasticity of Arctic tadpole shrimp (''Lepidurus arcticus
Arctic tadpole shrimp ''Lepidurus arcticus'' is a species of tadpole shrimp which inhabits ephemeral pools, ponds or permanent freshwater lakes of Finland, Norway, Sweden, Svalbard, Greenland, Iceland, Russia and the Kuril Islands.Schlager, Neil, ...
'', Notostraca) has been observed in Svalbard. Notostracans are the largest branchiopodans and are omnivores living on the bottom of temporary pools, ponds and shallow lakes.
Laevicaudata, Spinicaudata and Cyclestherida (once Conchostraca)
Clam shrimp are bivalved animals which have lived since at least the Devonian. The three groups are not believed to form a clade. They have 10–32 trunk segments, decreasing in size from front to back, and each bears a pair of legs which also carrygill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
s. A strong muscle can close the two halves of the shell together.
Anomopoda, Ctenopoda, Onychopoda, and Haplopoda (once Cladocera)
 These four orders make up a group of small
These four orders make up a group of small crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s commonly called water fleas. Around 620 species have been recognised so far, with many more undescribed. They are ubiquitous in inland aquatic habitats, but rare in the oceans. Most are long, with a down-turned head, and a carapace covering the apparently unsegmented thorax and abdomen. There is a single median compound eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which disti ...
. Most species show cyclical parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
, where asexual reproduction is occasionally supplemented by sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
, which produces resting eggs that allow the species to survive harsh conditions and disperse to distant habitats.
Evolution
Thefossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
of branchiopods extends back at least into the Upper Cambrian and possibly further. The group is thought to be monophyletic, with the Anostraca
Anostraca is one of the four orders of crustaceans in the class Branchiopoda; its members are referred to as fairy shrimp. They live in vernal pools and hypersaline lakes across the world, and they have even been found in deserts, ice-covered m ...
having been the first group to branch off. It is thought that the group evolved in the seas, but was forced into temporary pools and hypersaline lakes by the evolution of bony fishes. Although they were previously considered the sister group to the remaining crustaceans, it is now widely accepted that crustaceans form a paraphyletic group, and Branchiopoda are thought to be sister to a clade comprising Xenocarida
Xenocarida (from the Greek language, Greek for ''strange shrimp'') is a proposed clade inside the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea that comprises two classes that were discovered in the 20th century: Remipedia and Cephalocarida. The clade was recov ...
(Remipedia
Remipedia is a class of blind crustaceans found in coastal aquifers which contain saline groundwater, with populations identified in almost every ocean basin so far explored, including in Australia, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean. The ...
and Cephalocarida
The Cephalocarida are a class in the subphylum Crustacea comprising only 12 benthic species. They were discovered in 1955 by Howard L. Sanders, and are commonly referred to as horseshoe shrimp. They have been grouped together with the Remipedi ...
) and Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considered ins ...
(insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s and their relatives).
See also
*''Vladicaris
''Vladicaris'' is an arthropod known from the Lower Cambrian Paseky Shale member, Czech Republic, where it occurs alongside other arthropods, namely '' Kodymirus vagans'' and ''Kockurus grandis''. It has been attributed to the Crustacea, and if i ...
''
References
{{Authority control Arthropod classes Extant Cambrian first appearances Taxa named by Pierre André Latreille