|
Reichsbahnausbesserungswerk Meiningen
The Meiningen Steam Locomotive Works (german: Dampflokwerk Meiningen) is a railway repair shop in Meiningen, Germany. It is owned by Deutsche Bahn and has specialised in the maintenance of museum steam locomotives since 1990, having extensive experience in maintaining steam engines. Today, customers of the factory include railway museums and museum railways from all over Europe. The factory is responsible for the safety inspections of all operational German steam locomotives. Dampflokwerk Meiningen is the only facility in Europe capable of constructing new locomotive boilers up to modern standards of construction, performance, and safety. The newly built British steam locomotive 60163 ''Tornado'' that was delivered in 2008 had her all-steel, high-performance boiler made at Meiningen; the only part that could not be made in Britain. History In 1863 the Werra Railway (''Werrabahn'') built a locomotive repair shop opposite Meiningen station, which became a main workshop for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ausbesserungswerk
An Ausbesserungswerk (abbreviation AW or Aw) is a railway facility in German-speaking countries, the primary function of which is the repair (and formerly also the construction) of railway vehicles or their components. It is thus equivalent to a 'repair shop' or 'works'. It is also referred to as a Centralwerkstatt or Zentralwerkstatt (central workshop) or Hauptwerkstatt (main workshop). During the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG) period between the two world wars these facilities were called Reichsbahnausbesserungswerke (RAW) (Reichsbahn repair shops). Terminology Whilst the term ''Ausbesserungswerk'' was used by the former Deutsche Bundesbahn in West Germany after the war, the railway workshops in the Deutsche Reichsbahn in East Germany continued to refer to them as ''Reichsbahnausbesserungswerke'' until 1992. The term ''Hauptwerkstatt'' was also commonly used by state railways ('' Länderbahn'') or private railways and they are still called that today, for example, in Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 44
The Class 44 (German: ''Baureihe 44'' or ''BR 44'') was a ten-coupled, heavy goods train steam locomotive built for the Deutsche Reichsbahn as a standard steam engine class (''Einheitsdampflokomotive''). Its sub-class was G 56.20 and it had triple cylinders. It was intended for hauling goods trains of up to on the routes through Germany's hilly regions (''Mittelgebirge'') and up to on steep inclines. They were numbered 44 001-44 1989. History The first 10 examples were built in 1926. These engines had a somewhat higher steam consumption than the first ten units of the DRG Class 43 procured in parallel for comparison purposes, and which were equipped with two cylinders. Not until 1937 were further 44s procured, because by then the rising demands of rail transportation could be better met with a triple-cylinder configuration. From 1926 to 1949, a total of 1,989 locomotives were manufactured. During the Second World War an austerity variant was built with simplified constructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogies
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transport. A bogie may remain normally attached (as on many railroad cars and semi-trailers) or be quickly detachable (as the dolly in a road train or in railway bogie exchange); it may contain a suspension within it (as most rail and trucking bogies do), or be solid and in turn be suspended (as most bogies of tracked vehicles are); it may be mounted on a swivel, as traditionally on a railway carriage or locomotive, additionally jointed and sprung (as in the landing gear of an airliner), or held in place by other means (centreless bogies). In Scotland, the term is used for a child’s (usually home-made) wooden cart. While ''bogie'' is the preferred spelling and first-listed variant in various dictionaries, bogey and bogy are also used. Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
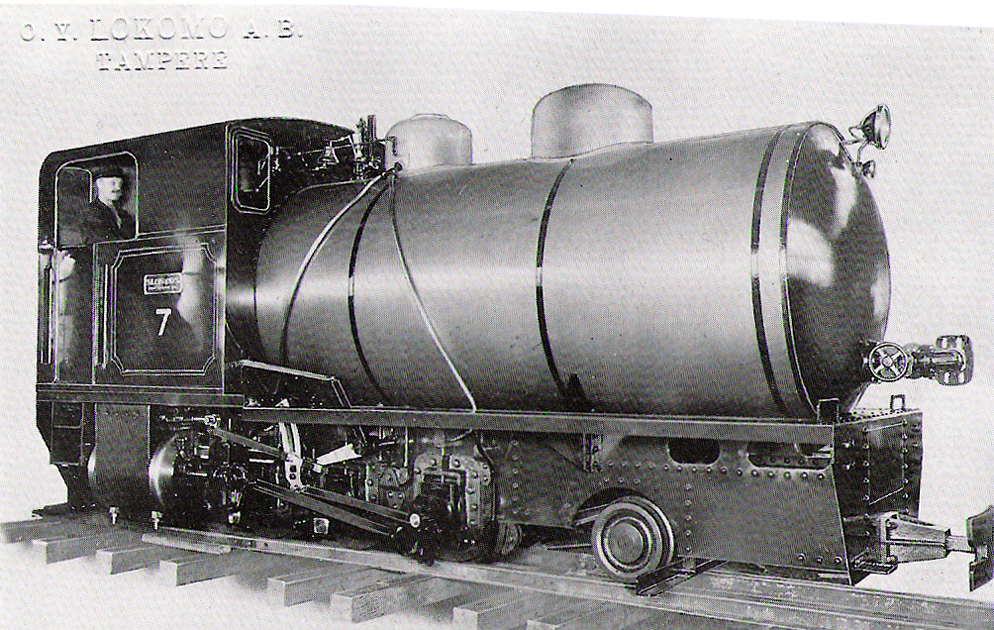
Fireless Locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of locomotive which uses reciprocating engines powered from a reservoir of compressed air or steam, which is filled at intervals from an external source. They offer advantages over conventional steam locomotives of lower cost per unit, cleanliness, and decreased risk from fire or boiler explosion; these are counterbalanced by the need for a source to refill the locomotive, and by the limited range afforded by the reservoir. They were desirable in situations where smoke from a firebox would be too noxious, or where there was risk of fire or explosion. Typical usage was in a mine, or a food or chemical factory. They were also used where a source of air or steam was readily available, and for moving loads within limited areas, such as a switch yard or within an industrial factory. They were eventually replaced for most uses by diesel and battery electric locomotives fitted with protective appliances; these are described as flame-proof locomotives. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR 18 201
The German express locomotive, number 18 201 of the Deutsche Reichsbahn in East Germany, appeared in 1960–61 at Meiningen Steam Locomotive Works as a conversion of the Henschel-Wegmann train locomotive 61 002, the tender from 44 468 and parts of H 45 024 and Class 41. It is the fastest operational steam locomotive in the world. Origin The motivation for the conversion was firstly that, as a one-off, locomotive 61 002 could not really be used for scheduled services, and secondly that the research institute at VES-M Halle urgently needed locomotives that could do at least 160 km/h in order to test passenger coaches. For the conversion a DR Class 22 new-design boiler, parts of the unsuccessful high pressure locomotive, H 45 024, (outside cylinders, trailing wheels and rear section of the locomotive frame) as well as the tender of locomotive 44 468 were used. The inside cylinder of the three-cylinder engine was not however taken from 61 002, rather a new one was made. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 61
The two German DRG Class 61 Steam locomotive, steam engines were express train locomotives specifically built by Henschel for the Henschel-Wegmann train in service with the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft, Deutsche Reichsbahn. The Henschel-Wegmann train was an initiative of the German locomotive construction industry, intended to be able to demonstrate a powerful steam locomotive-hauled train alongside the emerging express diesel multiple units, such as the DRG Class SVT 877, Hamburg Flyer. Construction Because it was planned to run the train in shuttle services to a tight time schedule, it was necessary that the engine could run at top speed in both directions. This resulted in a tank locomotive rather than the Tender (rail), tender locomotive design otherwise used for long-distance high-speed links. In order to be able to attain the high running performance aimed at, locomotives and coaches were designed to be especially light, albeit the coal and water supplies still had to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
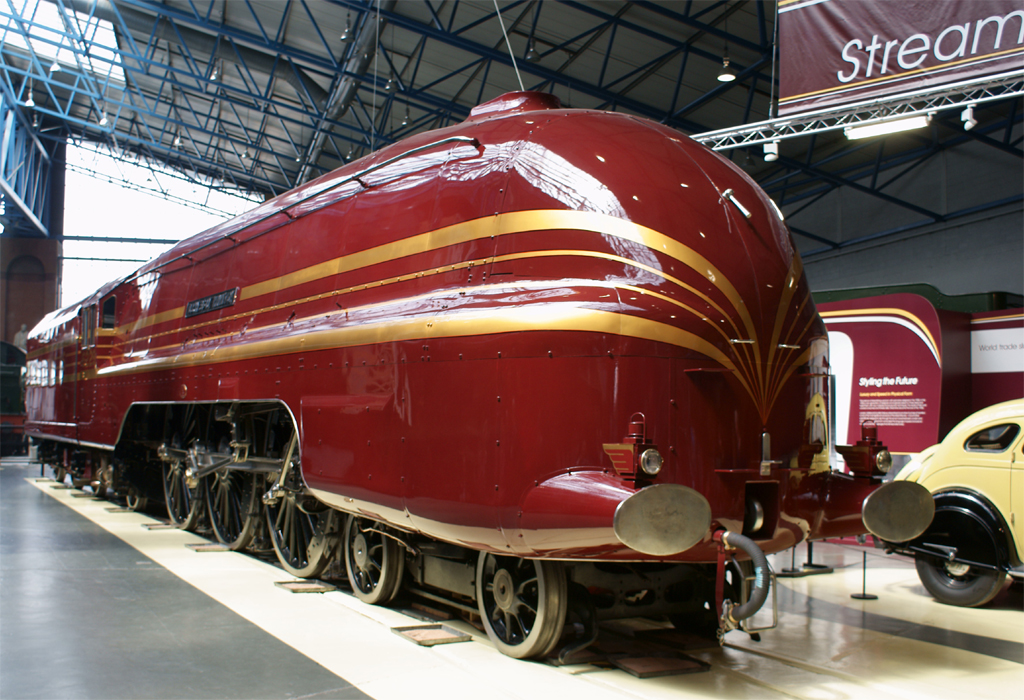
Streamliner
A streamliner is a vehicle incorporating wikt:streamline, streamlining in a shape providing reduced air resistance. The term is applied to high-speed railway trainsets of the 1930s to 1950s, and to their successor "High-speed rail, bullet trains". Less commonly, the term is applied to fully Bicycle fairing, faired upright and recumbent bicycles. As part of the Streamline Moderne trend, the term was applied to passenger cars, trucks, and other types of light-, medium-, or heavy-duty vehicles, but now vehicle streamlining is so prevalent that it is not an outstanding characteristic. In Land speed record, land speed racing, it is a term applied to the long, slender, custom built, high-speed vehicles with enclosed wheels. Trains Before World War II Europe The first high-speed streamliner in Germany was the "Schienenzeppelin", an experimental propeller driven single car, built in 1930. On 21 June 1931, the car set a speed record of on a run between Berlin and Hamburg. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Locomotives
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels. Early internal combustion locomotives and railcars used kerosene and gasoline as their fuel. Rudolf Diesel patented his first compression-ignition engine in 1898, and steady improvements to the design of diesel engines reduced their physical size and improved their power-to-weight ratios to a point where one could be mounted in a locomotive. Internal combustion engines only operate efficiently within a limited power band, and while low power gasoline engines could be coupled to mechanical transmissions, the more powerful diesel engines required the development of new forms of transmission. This is because clutches would need to be very large at these power levels and would not fit in a standard -wide locomotive frame, or wear too quickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Reichsbahn (East Germany)
The Deutsche Reichsbahn or DR ''(German Reich Railways)'' was the operating name of state owned railways in the German Democratic Republic (East Germany), and after German reunification until 1 January 1994. In 1949, occupied Germany's railways were returned to German control after four years of Allied control following World War II. Those in the Soviet occupation zone (which became the German Democratic Republic or GDR on 7 October 1949) continued to run as the Deutsche Reichsbahn, the name given to the German national railways in 1937. In West Germany, the Reichsbahn was succeeded by the Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB). Both the Reichsbahn and the Bundesbahn continued as separate entities until 1994, when they merged to form the Deutsche Bahn. Organisation The DR was the largest employer in the GDR and as a state-owned firm was directly subordinated to the GDR Ministry of Transport ''(Ministerium für Verkehr der DDR)''. From November 1954 until November 1989, the GDR Minister o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Plough
A snowplow (also snow plow, snowplough or snow plough) is a device intended for mounting on a vehicle, used for removing snow and ice from outdoor surfaces, typically those serving transportation purposes. Although this term is often used to refer to vehicles mounting such devices, more accurately they are known as winter service vehicles, especially in areas that regularly receive large amounts of snow every year, or in specific environments such as airfields. In other cases, pickup trucks and front end loaders are outfitted with attachments to fulfill this purpose. Some regions that do not frequently see snow may use graders to remove compacted snow and ice off the streets. Snowplows can also be mounted on rail cars or locomotives to clear railway tracks. Usage A snowplow works by using a blade to push snow to the side to clear it from a surface. Modern plows may include technology to make it easier to perform the work and stay on the road. These include Global Positioning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 95
The German DRG Class 95 was a ten-coupled tank locomotive with a 2-10-2 wheel arrangement, which was procured by the Deutsche Reichsbahn (also referred to later as the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft or ''DRG'') in 1922 for hauling heavy goods trains on steep main lines. Because the development of this class was begun by the Prussian state railways, it was designated as the Prussian Class T 20. History The first ten locomotives, built in 1922, were ordered as ''T 20 Magdeburg 9201–9210'' and, because they were at first intended to be grouped into Class 77, were supplied as numbers 77 001 to 77 010. By 1923 they had been renumbered to 95 001–010. A total of 45 locomotives were built by 1924. Their areas of operations included the Sonneberg–Probstzella line, the Spessart ramp, the Franconian Forest Railway, the Geislingen ramp (''Geislinger Steige''), the Schiefe Ebene and the Rübeland Railway, where they earned their nickname ''Bergkönigin'' ('mountain queen'). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |