|
Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering is a process in which a solder paste (a sticky mixture of powdered solder and flux) is used to temporarily attach one or thousands of tiny electrical components to their contact pads, after which the entire assembly is subjected to controlled heat. The solder paste reflows in a molten state, creating permanent solder joints. Heating may be accomplished by passing the assembly through a reflow oven, under an infrared lamp, or (unconventionally) by soldering individual joints with a desoldering hot air pencil. Reflow soldering with long industrial convection ovens is the preferred method of soldering surface mount technology components or SMT to a printed circuit board or PCB. Each segment of the oven has a regulated temperature, according to the specific thermal requirements of each assembly. Reflow ovens meant specifically for the soldering of surface mount components may also be used for through-hole components by filling the holes with solder paste and inse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Example Ramp To Spike Thermal Profile
Example may refer to: * '' exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, example.edu, second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially uniform and temporally constant. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium are always in thermal equilibrium, but the converse is not always true. If the connection between the systems allows transfer of energy as 'change in internal energy' but does not allow transfer of matter or transfer of energy as work, the two systems may reach thermal equilibrium without reaching thermodynamic equilibrium. Two varieties of thermal equilibrium Relation of thermal equilibrium between two thermally connected bodies The relation of thermal equilibrium is an instance of equilibrium between two bodies, which means that it refers to transfer through a selectively permeable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
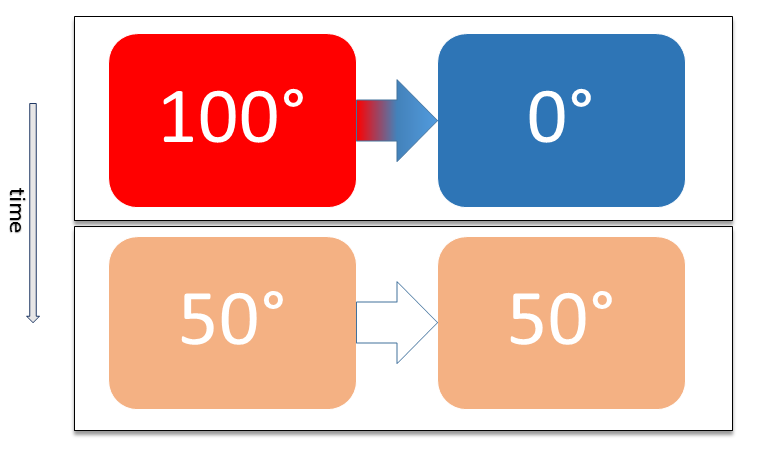
Thermal Profiling
A thermal profile is a complex set of time-temperature data typically associated with the measurement of thermal temperatures in an oven (ex: reflow oven). The thermal profile is often measured along a variety of dimensions such as slope, soak, time above liquidus (TAL), and peak. A thermal profile can be ranked on how it fits in a process window (the specification or tolerance limit). Raw temperature values are normalized in terms of a percentage relative to both the process mean and the window limits. The center of the process window is defined as zero, and the extreme edges of the process window are ±99%. A Process Window Index (PWI) greater than or equal to 100% indicates the profile is outside of the process limitations. A PWI of 99% indicates that the profile is within process limitations, but runs at the edge of the process window. For example, if the process mean is set at 200 °C with the process window calibrated at 180 °C and 220 °C respectively, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Of Hazardous Substances Directive
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS 1), short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union. The initiative was to prevent an overabundance of chemicals in electronics. Thus, as a result electronics were restricted. The RoHS 1 directive took effect on 1 July 2006, and is required to be enforced and became a law in each member state. This directive restricts (with exceptions) the use of ten hazardous materials in the manufacture of various types of electronic and electrical equipment. In addition to the exceptions, there are exclusions for products such as solar panels. It is closely linked with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) 2002/96/EC (now superseded) which sets collection, recycling and recovery targets for electrical goods and is part of a legislative initiative to solve the problem of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflow Oven
A reflow oven is a machine used primarily for reflow soldering of surface mount electronic components to printed circuit boards (PCBs). In commercial high-volume use, reflow ovens take the form of a long tunnel containing a conveyor belt along which PCBs travel. For prototyping or hobbyist use PCBs can be placed in a small oven with a door. Commercial conveyorised reflow ovens contain multiple individually heated zones, which can be individually controlled for temperature. PCBs being processed travel through the oven and through each zone at a controlled rate. Technicians adjust the conveyor speed and zone temperatures to achieve a known time and temperature profile. The profile in use may vary depending on the requirements of the PCBs being processed at the time. Types of reflow ovens Infrared and convection ovens In infrared reflow ovens, the heat source is normally ceramic infrared heaters above and below the conveyor, which transfer heat to the PCBs by means of radiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video platform, online video sharing and social media, social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the List of most visited websites, second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's Google AdSens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, opacity (optics), opacity, and lustre (mineralogy), luster, but may have properties that differ from those of the pure metals, such as increased strength or hardness. In some cases, an alloy may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the mixture imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Alloys are defined by a metallic bonding character. The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass percentage for practical applications, and in Atomic ratio, atomic fraction for basic science studies. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is a type of rapidly transient mechanical load. By definition, it is a mechanical load caused by a rapid change of temperature of a certain point. It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient, which makes different parts of an object expand by different amounts. This differential expansion can be more directly understood in terms of strain, than in terms of stress, as it is shown in the following. At some point, this stress can exceed the tensile strength of the material, causing a crack to form. If nothing stops this crack from propagating through the material, it will cause the object's structure to fail. Failure due to thermal shock can be prevented by: # Reducing the thermal gradient seen by the object, by changing its temperature more slowly or increasing the material's thermal conductivity # Reducing the material's coefficient of thermal expansion # Increasing its strength # Introducing built-in compressive stress, as for example in tempered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. This happens in presence of a gaseous phase or another liquid phase not miscible with the first one. The degree of wetting (wettability) is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces. Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of two materials. Wetting and the surface forces that control wetting are also responsible for other related effects, including capillary effects. There are two types of wetting: non-reactive wetting and reactive wetting. Wetting deals with three phases of matter: gas, liquid, and solid. It is now a center of attention in nanotechnology and nanoscience studies due to the advent of many nanomaterials in the past two decades (e.g. graphene, Carbon nano tube, carbon nanotube, boron nitride nanomesh). Explanation Adhesive forces between a liquid and solid cause a liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Example Thermal Profiler
Example may refer to: * '' exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, example.edu, second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermetallic
An intermetallic (also called an intermetallic compound, intermetallic alloy, ordered intermetallic alloy, and a long-range-ordered alloy) is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic elements. Intermetallics are generally hard and brittle, with good high-temperature mechanical properties. They can be classified as stoichiometric or nonstoichiometic intermetallic compounds. Although the term "intermetallic compounds", as it applies to solid phases, has been in use for many years, its introduction was regretted, for example by Hume-Rothery in 1955. Definitions Research definition Schulze in 1967 defined intermetallic compounds as ''solid phases containing two or more metallic elements, with optionally one or more non-metallic elements, whose crystal structure differs from that of the other constituents''. Under this definition, the following are included: #Electron (or Hume-Rothery) compounds #Size packing phases. e.g. Lav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |