|
Redondasuchus
''Redondasuchus'' is an extinct genus of aetosaur. It may be a junior synonym of '' Typothorax coccinarum'', another aetosaur. ''Redondasuchus'' is a member of the clade Typothoracisinae within the subfamily Aetosaurinae, and lived during the middle Norian stage of the Late Triassic. Material belonging to the genus has been found from the Redonda Formation in east-central New Mexico. The type species, ''R. reseri'', was named in 1991 after having been referred to as a species of ''Typothorax'' since 1985. A second species, ''R. rineharti'', was described in 2006. Description and species ''Redondasuchus'' was first named with the description of the type species, ''R. reseri'', in 1991. ''R. reseri'' was named on the basis of isolated scutes found at Apache Canyon and Shark Tooth Hill in Quay County, New Mexico. ''R. rineharti'' was described in 2006 from several scutes and part of a right femur found from Apache Canyon. While other aetosaurs have scutes covered in pits and groove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typothorax
''Typothorax'' is an extinct genus of typothoracine aetosaur that lived in the Late Triassic. Its remains have been found in North America. Two species are known: ''T. coccinarum'', the type species, and ''T. antiquum''. Description ''Typothorax'' was an aetosaur, a pseudosuchian distantly related to modern crocodilians. Unlike modern crocodilians, aetosaurs were herbivorous. ''Typothorax'' and other aetosaurs possess small, leaf-shaped teeth that were unsuited for a diet consisting of meat.Martz, J.W. 2002. The morphology and ontogeny of Typothorax coccinarum (Archosauria, Stagonolepididae) from the Upper Triassic of the American southwest. M.S. thesis, Geosciences, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, 279 pp. Unlike some aetosaurs such as ''Desmatosuchus'', ''Typothorax'' does not have large shoulder spikes. It does, however, have a pair of enlarged spikes on the neck projecting from the third row of scutes. It has lateral scutes that bear horns that are posteriorly hooked along it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
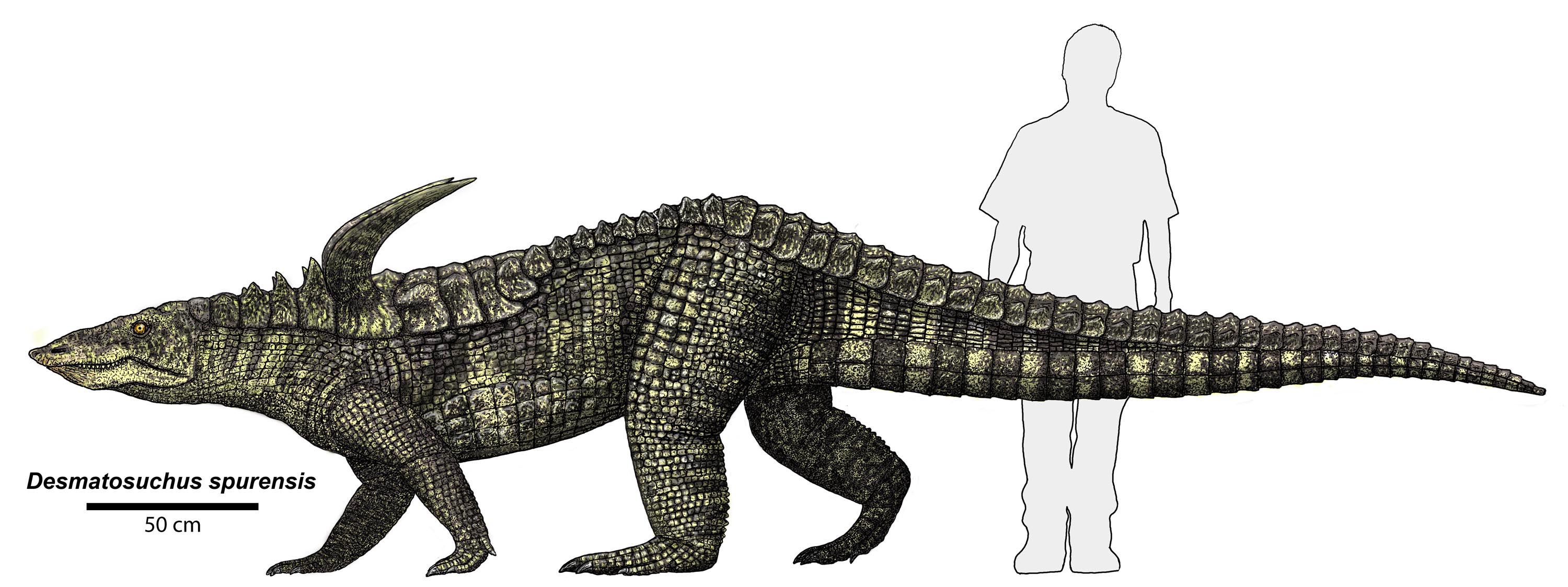
Desmatosuchus
''Desmatosuchus'' (, from Greek δεσμός ''desmos'' 'link' + σοῦχος ''soûkhos'' 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosaur belonging to the Order Aetosauria. It lived during the Late Triassic. Description ''Desmatosuchus'' was a large quadrupedal reptile upwards of to in lengthvon Baczko, M. B., Desojo, J. B., Gower, D. J., Ridgely, R., Bona, P., & Witmer, L. M. (2021)New digital braincase endocasts of two species of Desmatosuchus and neurocranial diversity within Aetosauria (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia) The Anatomical Record, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24798 and in weight. Its vertebral column had amphicoelus centra and 3 sacral vertebrae. This archosaur's most distinguishing anatomical characteristics were its scapulae which possessed large acromion processes commonly referred to as "shoulder spikes". The forelimbs were much shorter than the hindlimbs, with humeri less than two-thirds the length of the femurs. The pelvic girdle consisted of a long pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redonda Formation
The Redonda Formation is a geologic formation exposed in eastern New Mexico.Dobrovolny and Summerson 1947 It contains vertebrate fossils of the late Triassic Period.Griggs and Read 1959 Fossil theropod tracks have been reported from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. Description The formation consists of interbedded fine-grained red-brown sandstone and mudstone. It conformably overlies the Bull Canyon FormationLucas and Hunt 1989 and underlies the Entrada Formation. The formation is interpreted as having been deposited in a lake with an area of about . Fossils The formation has few fossil plants, with only '' Neocalamites'' reported, but it contains abundant invertebrate fossils (conchostracans and ostracods) and a diverse assemblage of vertebrate fossils. Vertebrate fauna Fish Stereospondyls Synapsids Archosauriforms History of investigation The unit was first named as the Redonda Member of the Chinle Formation by D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typothoracisinae
Typothoracinae is a clade of aetosaurs within the subfamily Aetosaurinae. It was originally defined as a stem-based taxon including all aetosaurs closer to ''Typothorax'' than to ''Stagonolepis'' or ''Desmatosuchus''. This definition was later expanded to specifically exclude ''Aetosaurus''; as of 2016, Typothoracinae is defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Typothorax'' and '' Paratypothorax'', but not ''Aetosaurus,'' ''Stagonolepis'', or ''Desmatosuchus''. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Typothoracisinae, after its namesake ''Typothorax''. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Typothoracinae in 2016. Typothoracines can be distinguished by their wide bodies. The transverse processes of the dorsal (trunk) vertebrae are reinforced and elongated, more than twice the width of the centrum. Their neural spines, on the other hand, are short. The overlying carapace A carapace is a D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rioarribasuchus
''Rioarribasuchus'' is a genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Chinle Formation in Arizona and New Mexico that date back to the upper Late Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. History ''"Desmatosuchus" chamaensis'' was named in 2003 and found from the Petrified Forest Member of the Chinle Formation in New Mexico. It was suggested to be more closely related to '' Paratypothorax'', and so Parker gave it the name ''Heliocanthus''. However, this new generic name was first proposed in an unpublished thesis, and thus did not meet ICZN regulations for the naming of a new taxon. Later published papers reasserted the genetic separation of ''"D". chamaensis'' from ''Desmatosuchus'', but the name ''Heliocanthus'' remained a ''nomen nudum'' until 2007, where it was thoroughly rediscribed in a paper published by the ''Journal of Systematic Palaeontology''. However, a paper previously published in late 2006 assigned ''"D". chamaensis'' to the new genus ''Rioarribasuchus''. As a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico Museum Of Natural History And Science
The New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science is a natural history and science museum in Albuquerque, New Mexico near Old Town Albuquerque. The Museum was founded in 1986. It operates as a public revenue facility of the New Mexico Department of Cultural Affairs. Permanent exhibits The Museum's permanent exhibit halls illustrate a journey through time, covering the birth of the Universe (≈13.6 billion years ago) to the Ice Age (≈10,000 years ago). The eight journey through time halls are as follows: *Origins *Dawn of the Dinosaurs *Jurassic Age of Super Giants *New Mexico's Seacoast *Age of Volcanoes *Rise of the Recent - Evolving Grasslands *Cave Experience *New Mexico's Ice Age Other permanent exhibits include an interactive planetarium where programs are held daily. There is also a floor of exhibit galleries dedicated to astronomy and space exploration, as well as an observation deck for viewing through the telescope. The observatory opens only occasionally, usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darren Naish
Darren William Naish is a British vertebrate palaeontologist, author and science communicator. As a researcher, he is best known for his work describing and reevaluating dinosaurs and other Mesozoic reptiles, including ''Eotyrannus'', ''Xenoposeidon'', and azhdarchid pterosaurs. Much of his research has focused on Wealden Group fossils from the Isle of Wight. He is founder of the vertebrate palaeozoology blog Tetrapod Zoology, and has written several popular science books. Naish also makes frequent media appearances and is a scientific consultant and advisor for film, television, museums and exhibitions. Naish is also known for his skepticism and work examining cryptozoology and sea monster sightings and beliefs from a scientific perspective. Research He obtained a geology degree at the University of Southampton and later studied vertebrate palaeontology under British palaeontologist David Martill at the University of Portsmouth, where he obtained both an M. Phil. and PhD. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico Department Of Cultural Affairs
The New Mexico Department of Cultural Affairs is a state agency of the New Mexico government. Created as the Office of Cultural Affairs (OCA) in 1980, the New Mexico Department of Cultural Affairs was elevated to a state Cabinet-level agency in 2004. The department oversees the state museum, monument, art, library, heritage preservation, and archaeology programs. The Department of Cultural Affairs is currently directed by Cabinet Secretary Debra Garcia y Griego, who was nominated by Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham on December 26, 2018. The Cabinet Secretary appoints all of the Directors of the divisions Divisions * Museum Resources Division * Administrative Services Division * New Mexico Arts * New Mexico Historic Preservation Division * New Mexico State Library * National Hispanic Cultural Center * Museum of New Mexico * New Mexico Museum of Space History * Farm and Ranch Heritage Museum History The Cultural Affairs Department Act was passed by the New Mexico Legislature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetogate
''Rioarribasuchus'' is a genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Chinle Formation in Arizona and New Mexico that date back to the upper Late Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. History ''"Desmatosuchus" chamaensis'' was named in 2003 and found from the Petrified Forest Member of the Chinle Formation in New Mexico. It was suggested to be more closely related to '' Paratypothorax'', and so Parker gave it the name ''Heliocanthus''. However, this new generic name was first proposed in an unpublished thesis, and thus did not meet ICZN regulations for the naming of a new taxon. Later published papers reasserted the genetic separation of ''"D". chamaensis'' from ''Desmatosuchus'', but the name ''Heliocanthus'' remained a ''nomen nudum'' until 2007, where it was thoroughly rediscribed in a paper published by the ''Journal of Systematic Palaeontology''. However, a paper previously published in late 2006 assigned ''"D". chamaensis'' to the new genus ''Rioarribasuchus''. As a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |