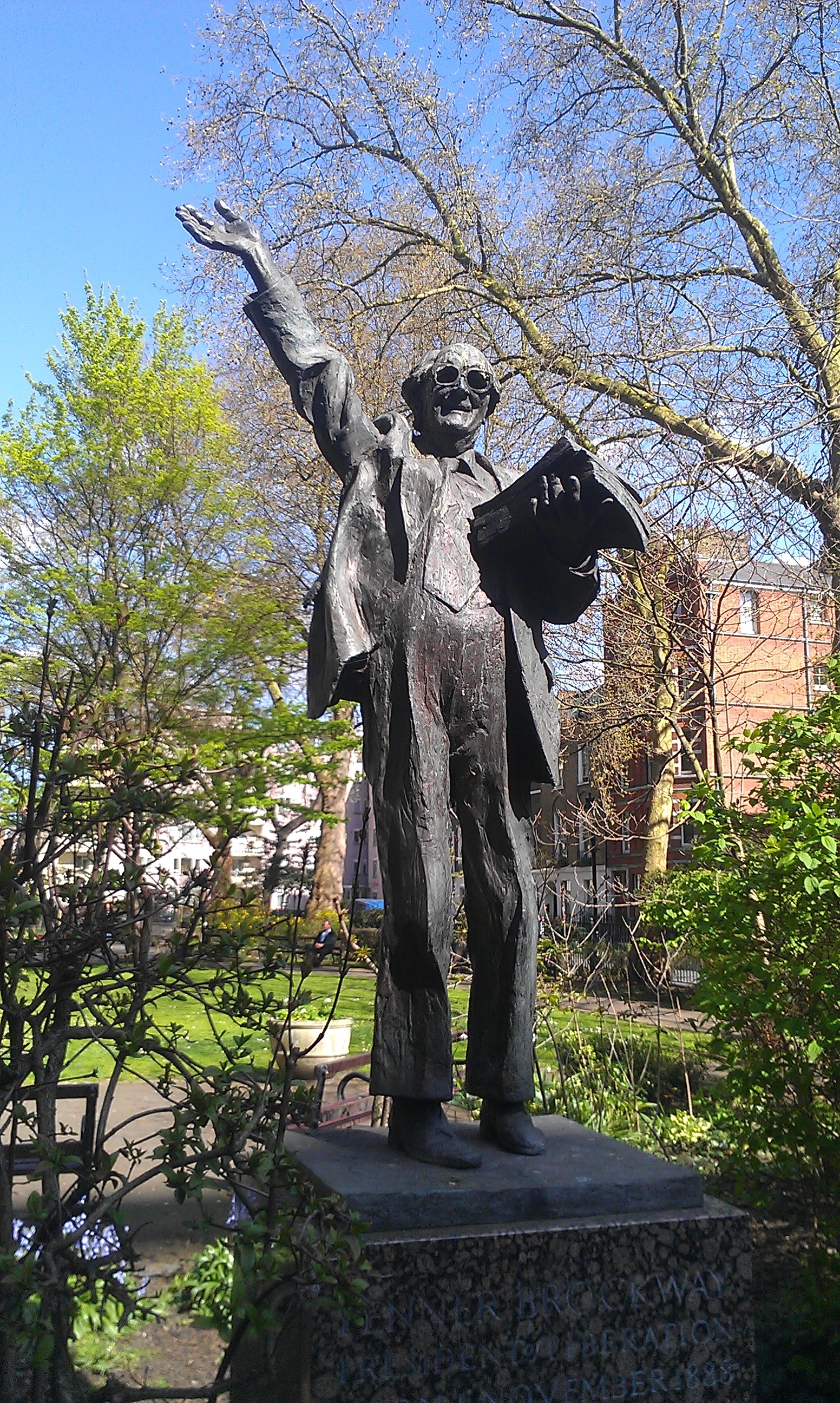|
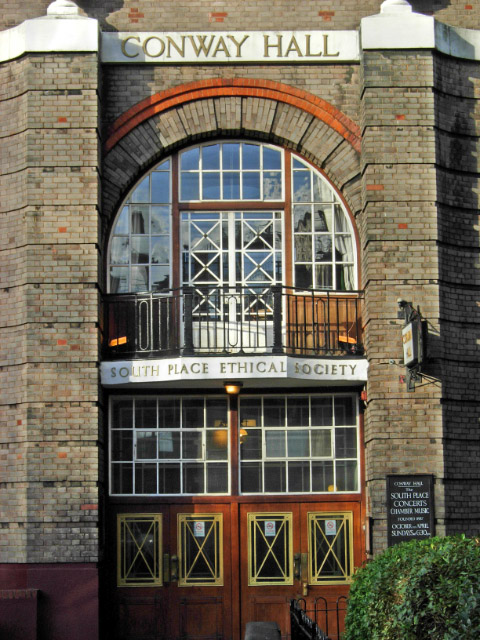
Red Lion Square Disorders
Kevin Gately (18 September 1953 – 15 June 1974) was a second-year student of mathematics at the University of Warwick who died as the result of a head injury received in the Red Lion Square disorders in London; it is not known if the injury was caused deliberately or was accidental. He was not a member of any political organisation, and the march at Red Lion Square was his first. He was the first person to die in a public demonstration in Great Britain for at least 55 years. On 15 June 1974 the National Front, a far-right, fascist political party, held a march through central London in support of the repatriation of immigrants. The march was to end at Conway Hall in Red Lion Square. A counter-demonstration was planned by Liberation, an anti-colonial pressure group. During the late 1960s and early 1970s, the London council of Liberation had been increasingly infiltrated by hard-left political activists, and they invited several hard-left organisations to join them in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a political party in the United Kingdom that has been described as an alliance of social democrats, democratic socialists and trade unionists. The Labour Party sits on the centre-left of the political spectrum. In all general elections since 1922, Labour has been either the governing party or the Official Opposition. There have been six Labour prime ministers and thirteen Labour ministries. The party holds the annual Labour Party Conference, at which party policy is formulated. The party was founded in 1900, having grown out of the trade union movement and socialist parties of the 19th century. It overtook the Liberal Party to become the main opposition to the Conservative Party in the early 1920s, forming two minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in the 1920s and early 1930s. Labour served in the wartime coalition of 1940–1945, after which Clement Attlee's Labour government established the National Health Service and expanded the welfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Unions In The United Kingdom
Trade unions in the United Kingdom were first decriminalised under the recommendation of a Royal commission in 1867, which agreed that the establishment of the organisations was to the advantage of both employers and employees. Legalised in 1871, the Trade Union Movement sought to reform socio-economic conditions for working men in British industries, and the trade unions' search for this led to the creation of a Labour Representation Committee which effectively formed the basis for today's Labour Party, which still has extensive links with the Trade Union Movement in Britain. Margaret Thatcher's governments weakened the powers of the unions in the 1980s, in particular by making it more difficult to strike legally, and some within the British trades union movement criticised Tony Blair's Labour government for not reversing some of Thatcher's changes. Most British unions are members of the TUC, the Trades Union Congress (founded in 1867), or where appropriate, the Scottish Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland. It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four traditional provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are Gaeltachtaí (Irish-speaking regions) in southern County Londonderry, the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast, and in County Donegal; collectively, these three regions are home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of Ireland. Ulster-Scots is also spoken. Lough Neagh, in the east, is the largest lake i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbon Treaty. aiming to foster economic integration among its member states. It was subsequently renamed the European Community (EC) upon becoming integrated into the first pillar of the newly formed European Union in 1993. In the popular language, however, the singular ''European Community'' was sometimes inaccuratelly used in the wider sense of the plural '' European Communities'', in spite of the latter designation covering all the three constituent entities of the first pillar. In 2009, the EC formally ceased to exist and its institutions were directly absorbed by the EU. This made the Union the formal successor institution of the Community. The Community's initial aim was to bring about economic integration, including a common market an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sam Kahn
Sam Kahn (15 December 1911 – 25 August 1987) was a South African Communist and MP from 1949 to 1952, for one of the constituencies representing native African voters. Born in Cape Town, he joined the Communist Party of South Africa and earned an LL.B. degree from the University of Cape Town in 1932. From 1938 onwards, he was nearly continuously a member of the central executive committee of the CPSA. From 1943 to 1952, he was a member of Cape Town city council, and on 17 November 1948 he was elected to House of Assembly (South Africa), South African House of Assembly as a Communist, representing native African voters in the western Cape Province (from 1937 to 1960, Black African voters voted for 'native representative' MPs instead of constituency MPs with White voters), campaigning on his disapproval of Prime Minister Daniel Malan, Malan's "nazi apartheid, doctrine of white supremacy". He made his maiden speech on 27 January 1949 during a debate on a no confidence motion mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorothy Kuya
Dorothy Kuya (April 1932 – 23 December 2013) was a leading British communist and human rights activist from Liverpool, the co-founder of Teachers Against Racism, and the general secretary of the National Assembly of Women (NAW). She was a life-long member of the Communist Party of Great Britain (CPGB), and was most famous for being Liverpool's first community relations officer, and for leading a successful campaign to establish Liverpool's International Slavery Museum. During the mid-1980s, Kuya served as the chair of the London housing association Ujima, and built the organisation into the largest black-led social enterprise in Europe. She was described by the Director of National Museums Liverpool as "Liverpool's greatest fighter against racism and racial intolerance" and "one of the country's leading figures in combating inequality." Early life Dorothy Kuya was born in Liverpool in April 1932; her father was a black man from Sierra Leone and her mother was a white Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tony Gilbert (activist)
David Gilbert (1914–1992), known to his contemporaries as "Tony", was a British political activist. He is best remembered as the head of the left-wing political organisation Liberation (formerly the Movement for Colonial Freedom) during the 1980s and 1990s. Biography Early years Tony Gilbert was born in Poplar, London to a large Jewish family in 1914. As a young man, Gilbert served as an apprentice in the fur industry, working as a nailer.John Bain"Tony Gilbert,"grahamstevenson.me.uk/ Retrieved 11 October 2010. In the early 1930s, the diminutive Gilbert was the victim of anti-semitic violence when he was attacked on the streets by members of the British Union of Fascists. Gilbert awoke from his beating in the hospital, more fervent than ever in his opposition to fascism. During the Spanish Civil War, Gilbert joined the International Brigades and went to Spain, serving as a courier for Loyalist forces fighting in defense of the Second Spanish Republic. During his Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kay Beauchamp
Kathleen Mary 'Kay' Beauchamp (27 May 1899 – 25 January 1992) was a leading light in the Communist Party of Great Britain in the 1920s. She helped found ''The Daily Worker'' (later '' The Morning Star'') and was a local councillor in Finsbury. Biography She was born to a farming family at Welton Manor Farm, Midsomer Norton, Somerset on 27 May 1899. She was sister of Joan Beauchamp, later Joan Thompson, who became a prominent suffragette and associate of Sylvia Pankhurst. The family was part of the Beauchamp family that dominated the Somerset coalfield, her father being the cousin of Sir Frank Beauchamp and Louis Beauchamp who owned coalmines in the area. Her mother died in 1904 when Kay was only four. She completed a degree in history at University College, London in 1924. In that year she married bookseller and bibliographer Graham Pollard, son of Professor Albert Pollard. She joined the Communist Party, for which she served as International Secretary. She was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Great Britain
The Communist Party of Great Britain (CPGB) was the largest communist organisation in Britain and was founded in 1920 through a merger of several smaller Marxist groups. Many miners joined the CPGB in the 1926 general strike. In 1930, the CPGB founded the ''Daily Worker'' (renamed the ''Morning Star'' in 1966). In 1936, members of the party were present at the Battle of Cable Street, helping organise resistance against the British Union of Fascists. In the Spanish Civil War the CPGB worked with the USSR to create the British Battalion of the International Brigades, which party activist Bill Alexander commanded. In World War II, the CPGB mirrored the Soviet position, opposing or supporting the war in line with the involvement of the USSR. By the end of World War II, CPGB membership had nearly tripled and the party reached the height of its popularity. Many key CPGB members became leaders of Britain's trade union movement, including most notably Jessie Eden, Abraham Lazarus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenner Brockway
Archibald Fenner Brockway, Baron Brockway (1 November 1888 – 28 April 1988) was a British socialist politician, humanist campaigner and anti-war activist. Early life and career Brockway was born to W. G. Brockway and Frances Elizabeth Abbey in Calcutta, British India. While attending the School for the Sons of Missionaries, then in Blackheath, London (now Eltham College), from 1897 to 1905, he developed an interest in politics. In 1908, Brockway became a vegetarian. Several decades later, during a debate in a House of Lords on animal cruelty, he said: "I am a vegetarian and I have been so for 70 years. On the whole, I think, physically I am a pretty good advertisement for that practice." After leaving school, he worked as a journalist for newspapers and journals including ''The Quiver'', the ''Daily News'' and the ''Christian Commonwealth''. In 1907, Brockway joined the Independent Labour Party (ILP) and was a regular visitor to the Fabian Society. He was appointed editor of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |