|
Red King Hypothesis
The Red King hypothesis contrasts with the Red Queen hypothesis, where mutualistic and cooperative interactions favor the fitness of a set of individuals through slow evolution, as opposed to having competitive interactions or having an " arms race". The hypothesis posits that individuals from different communities can establish positive interactions for long periods of time when there is a great benefit for both parties, also through mutual help, individuals from different species (communities) can share different tasks to build a niche (Black Queen hypothesis The Black Queen hypothesis (BQH) is reductive evolution theory which seeks to explain how natural selection (as opposed to genetic drift) can drive gene loss. In a microbial community, different members may have genes which produce certain chemic ...), which avoid spending energy in competing and increasing their resilience over environmental stress. The types of interaction between species determine how fast they coev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
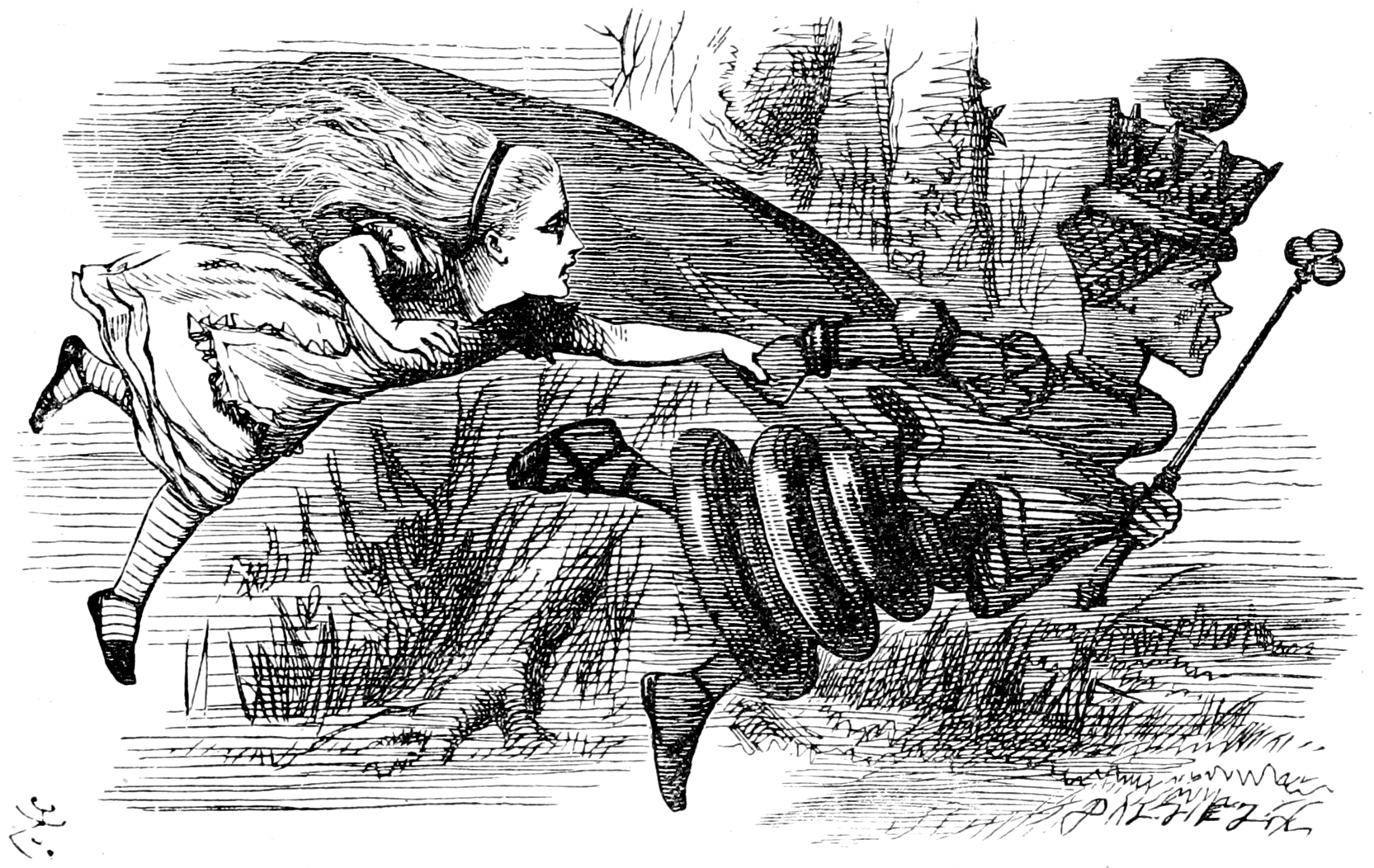
Red Queen Hypothesis
The Red Queen hypothesis is a hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposed in 1973, that species must constantly adapt, evolve, and proliferate in order to survive while pitted against ever-evolving opposing species. The hypothesis was intended to explain the constant (age-independent) extinction probability as observed in the paleontological record caused by co-evolution between competing species; however, it has also been suggested that the Red Queen hypothesis explains the advantage of sexual reproduction (as opposed to asexual reproduction) at the level of individuals,Bell, G. (1982). The Masterpiece Of Nature: The Evolution and Genetics of Sexuality. University of California Press, Berkeley, 378 pp. and the positive correlation between speciation and extinction rates in most higher taxa. Origin In 1973, Leigh Van Valen proposed the hypothesis as an "explanatory tangent" to explain the "law of extinction" known as "Van Valen's law", which states that the probability of ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples include most vascular plants engaged in mutualistic interactions with mycorrhizae, flowering plants being pollinated by animals, vascular plants being dispersed by animals, and corals with zooxanthellae, among many others. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and exploitation, or parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites and Messmates'' to mean "mutual aid among species". Mutualism is often conflated with two other types of ecological phenomena: cooperation and symbiosis. Cooperation most commonly refers to increases in fitness through within-species (intraspecific) interactions, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness (biology)
Fitness (often denoted w or ω in population genetics models) is the quantitative representation of individual reproductive success. It is also equal to the average contribution to the gene pool of the next generation, made by the same individuals of the specified genotype or phenotype. Fitness can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment or time. The fitness of a genotype is manifested through its phenotype, which is also affected by the developmental environment. The fitness of a given phenotype can also be different in different selective environments. With asexual reproduction, it is sufficient to assign fitnesses to genotypes. With sexual reproduction, recombination scrambles alleles into different genotypes every generation; in this case, fitness values can be assigned to alleles by averaging over possible genetic backgrounds. Natural selection tends to make alleles with higher fitness more common over time, resulting in Darw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Arms Race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling an arms race. These are often described as examples of positive feedback.Dawkins, R. 1996. '' The Blind Watchmaker'' New York: W. W. Norton. Note: This book was also published by Penguin in 1991. While the text is identical, page numbers differ The co-evolving gene sets may be in different species, as in an evolutionary arms race between a predator species and its prey (Vermeij, 1987), or a parasite and its host. Alternatively, the arms race may be between members of the same species, as in the manipulation/sales resistance model of communication (Dawkins & Krebs, 1979) or as in runaway evolution or Red Queen effects. One example of an evolutionary arms race is in sexual conflict between the sexes, often described with the term Fisher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Interaction
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition, harmful to both partners. Interactions can be indirect, through intermediaries such as shared resources or common enemies. This type of relationship can be shown by net effect based on individual effects on both organisms arising out of relationship. Several recent studies have suggested non-trophic species interactions such as habitat modification and mutualisms can be important determinants of food web structures. However, it remains unclear whether these findings g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Queen Hypothesis
The Black Queen hypothesis (BQH) is reductive evolution theory which seeks to explain how natural selection (as opposed to genetic drift) can drive gene loss. In a microbial community, different members may have genes which produce certain chemicals or resources in a "leaky fashion" making them accessible to other members of that community. If this resource is available to certain members of a community in a way that allows them to sufficiently access that resource without generating it themselves, these other members in the community may lose the biological function (or the gene) involved in producing that chemical. Put another way, the black queen hypothesis is concerned with the conditions under which it is advantageous to lose certain biological functions. By accessing resources without the need to generate it themselves, these microbes conserve energy and streamline their genomes to enable faster replication. Jeffrey Morris proposed the Black Queen hypothesis in his 2011 PhD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coevolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well as gene-culture coevolution. Charles Darwin mentioned evolutionary interactions between flowering plants and insects in ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Although he did not use the word coevolution, he suggested how plants and insects could evolve through reciprocal evolutionary changes. Naturalists in the late 1800s studied other examples of how interactions among species could result in reciprocal evolutionary change. Beginning in the 1940s, plant pathologists developed breeding programs that were examples of human-induced coevolution. Development of new crop plant varieties that were resistant to some diseases favored rapid evolution in pathogen populations to overcome those plant defenses. That, in turn, required the development o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Gradient Hypothesis
The stress gradient hypothesis (SGH) is an evolutionary theory in microbial ecology and community ecology In ecology, a community is a group or association (ecology), association of Population ecology, populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time, also known as a biocoenosis, biotic community, ... that provides a framework to predict when positive or negative interactions should be observed in an habitat. The SGH states that facilitation, cooperation or mutualism should be more common in stressful environments, compared with benign environments (i.e nutrient excess) where competition or parasitism should be more common. The stress gradient hypothesis, in which ecological interactions shift in a positive direction with increasing environmental stress, is controversial among ecologists, in part because of contradictory support, yet a 2021 meta analysis study compared SGH across different organisms with intraspecificity and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism Parasitism Continuum
The hypothesis or paradigm of Mutualism Parasitism Continuum postulates that compatible host-symbiont associations can occupy a broad continuum of interactions with different fitness outcomes for each member. At one end of the continuum lies obligate mutualism where both host and symbiont benefit from the interaction and are dependent on it for survival. At the other end of the continuum highly parasitic interactions can occur, where one member gains a fitness benefit at the expense of the others survival. Between these extremes many different types of interaction are possible. The degree of change between mutualism or parasitism varies depending on the availability of resources, where there is environmental stress generated by few resources, symbiotic relationships are formed while in environments where there is an excess of resources, biological interactions turn to competition and parasitism. Classically the transmission mode of the symbiont can also be important in predicting w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Facilitation
Ecological facilitation or probiosis describes species interactions that benefit at least one of the participants and cause harm to neither.Stachowicz, J. J. 2001. Mutualism, facilitation, and the structure of ecological communities. BioScience 51: 235-246. Facilitations can be categorized as mutualisms, in which both species benefit, or commensalisms, in which one species benefits and the other is unaffected.Boucher, D. H., S. James, and K. H. Keeler. 1982. The ecology of mutualism. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 13: 315-347.Callaway, R. M. 1995. Positive interactions among plants (Interpreting botanical progress). The Botanical Review 61: 306-349.Bruno, J. F., J. J. Stachowicz, and M. D. Bertness. 2003. Inclusion of facilitation into ecological theory. TREE 18: 119-125.Tirado, R. and F. I. Pugnaire. 2005. Community structure and positive interactions in constraining environments. OIKOS 111: 437-444. This article addresses both the mechanisms of facilitation and the incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |