|
Black Queen Hypothesis
The Black Queen hypothesis (BQH) is reductive evolution theory which seeks to explain how natural selection (as opposed to genetic drift) can drive gene loss. In a microbial community, different members may have genes which produce certain chemicals or resources in a "leaky fashion" making them accessible to other members of that community. If this resource is available to certain members of a community in a way that allows them to sufficiently access that resource without generating it themselves, these other members in the community may lose the biological function (or the gene) involved in producing that chemical. Put another way, the black queen hypothesis is concerned with the conditions under which it is advantageous to lose certain biological functions. By accessing resources without the need to generate it themselves, these microbes conserve energy and streamline their genomes to enable faster replication. Jeffrey Morris proposed the Black Queen hypothesis in his 2011 PhD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Evolution
Reductive evolution is the process by which microorganisms remove genes from their genome. It can occur when bacteria found in a free-living state enter a restrictive state (either as endosymbionts or parasites) or are completely absorbed by another organism becoming intracellular ( symbiogenesis). The bacteria will adapt to survive and thrive in the restrictive state by altering and reducing its genome to get rid of the newly redundant pathways that are provided by the host. In an endosymbiont or symbiogenesis relationship where both the guest and host benefit, the host can also undergo reductive evolution to eliminate pathways that are more efficiently provided for by the guest. Examples Endosymbiont or parasitic microorganisms such as '' Rickettsia prowazekii'', '' Chlorella'' in '' Paramecium'', '' Buchnera aphidicola'' in aphids, and '' Wolbachia'' bacteria in '' Wuchereria bancrofti'' have all been studied and fully sequenced which is why they are used as examples of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using ... due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as specicide, widespread violence or intentional culling, and human population planning. Such events can reduce the variation in the gene pool of a population; thereafter, a smaller population, with a smaller genetic diversity, remains to pass on genes to future generations of offspring through sexual reproduction. Genetic diversity remains lower, increasing only when gene flow from another population occurs or very slowly increasing with time as random mutations occur. This results in a reduction in the robustness of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable. In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Evolution
Reductive evolution is the process by which microorganisms remove genes from their genome. It can occur when bacteria found in a free-living state enter a restrictive state (either as endosymbionts or parasites) or are completely absorbed by another organism becoming intracellular ( symbiogenesis). The bacteria will adapt to survive and thrive in the restrictive state by altering and reducing its genome to get rid of the newly redundant pathways that are provided by the host. In an endosymbiont or symbiogenesis relationship where both the guest and host benefit, the host can also undergo reductive evolution to eliminate pathways that are more efficiently provided for by the guest. Examples Endosymbiont or parasitic microorganisms such as '' Rickettsia prowazekii'', '' Chlorella'' in '' Paramecium'', '' Buchnera aphidicola'' in aphids, and '' Wolbachia'' bacteria in '' Wuchereria bancrofti'' have all been studied and fully sequenced which is why they are used as examples of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holobiont
A holobiont is an assemblage of a host and the many other species living in or around it, which together form a discrete ecological unit through symbiosis, though there is controversy over this discreteness. The components of a holobiont are individual species or bionts, while the combined genome of all bionts is the hologenome. The holobiont concept was initially introduced by the German theoretical biologist Adolf Meyer-Abich in 1943, and then apparently independently by Dr. Lynn Margulis in her 1991 book ''Symbiosis as a Source of Evolutionary Innovation''. The concept has evolved since the original formulations. Holobionts include the host, virome, microbiome, and any other organisms which contribute in some way to the functioning of the whole. Well-studied holobionts include reef-building corals and humans. Overview A holobiont is a collection of closely associated species that have complex interactions, such as a plant species and the members of its microbiome. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a pan-genome (pangenome or supragenome) is the entire set of genes from all Strain (biology), strains within a clade. More generally, it is the union (set theory), union of all the genomes of a clade. The pan-genome can be broken down into a "core pangenome" that contains genes present in all individuals, a "shell pangenome" that contains genes present in two or more strains, and a "cloud pangenome" that contains genes only found in a single strain. Some authors also refer to the cloud genome as "accessory genome" containing 'dispensable' genes present in a subset of the strains and strain-specific genes. Note that the use of the term 'dispensable' has been questioned, at least in plant genomes, as accessory genes play "an important role in genome evolution and in the complex interplay between the genome and the environment". The field of study of the pangenome is called pangenomics. The genetic repertoire of a bacterial species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbialite
Microbialite is a benthic sedimentary deposit made of carbonate mud (particle diameter < 5 μm) that is formed with the mediation of microbes. The constituent carbonate mud is a type of automicrite, or authigenic mud, and therefore it precipitates in situ instead of being transported and deposited. Being formed in situ, a microbialite can be seen as a type of boundstone where reef builders are microbes, and precipitation of carbonate is biotically induced instead of forming tests, shells or skeletons. Microbialites can also be defined as |
Genome Streamlining
Genomic streamlining is a theory in evolutionary biology and microbial ecology that suggests that there is a reproductive benefit to prokaryotes having a smaller genome size with less non-coding DNA and fewer non-essential genes. There is a lot of variation in prokaryotic genome size, with the smallest free-living cell's genome being roughly ten times smaller than the largest prokaryote. Two of the bacterial taxa with the smallest genomes are ''Prochlorococcus'' and ''Pelagibacter ubique,'' both highly abundant marine bacteria commonly found in oligotrophic regions. Similar reduced genomes have been found in uncultured marine bacteria, suggesting that genomic streamlining is a common feature of bacterioplankton. This theory is typically used with reference to free-living organisms in oligotrophic environments. Overview Genome streamlining theory states that certain prokaryotic genomes tend to be small in size in comparison to other prokaryotes, and all eukaryotes, due to selection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Selection (natural Selection)
In natural selection, negative selection or purifying selection is the selective removal of alleles that are deleterious. This can result in stabilising selection through the purging of deleterious genetic polymorphisms that arise through random mutations. Purging of deleterious alleles can be achieved on the population genetics level, with as little as a single point mutation being the unit of selection. In such a case, carriers of the harmful point mutation have fewer offspring each generation, reducing the frequency of the mutation in the gene pool. In the case of strong negative selection on a locus, the purging of deleterious variants will result in the occasional removal of linked variation, producing a decrease in the level of variation surrounding the locus under selection. The incidental purging of non-deleterious alleles due to such spatial proximity to deleterious alleles is called background selection. This effect increases with lower mutation rate but decreases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructive Neutral Evolution
Constructive neutral evolution (CNE) is a theory that seeks to explain how complex systems can evolve through neutral transitions and spread through a population by chance fixation (genetic drift). Constructive neutral evolution is a competitor for both adaptationist explanations for the emergence of complex traits and hypotheses positing that a complex trait emerged as a response to a deleterious development in an organism. Constructive neutral evolution often leads to irreversible or "irremediable" complexity and produces systems which, instead of being finely adapted for performing a task, represent an excess complexity that has been described with terms such as "runaway bureaucracy" or even a "Rube Goldberg machine". The groundworks for the concept of CNE were laid by two papers in the 1990s, although first explicitly proposed by Arlin Stoltzfus in 1999. The first proposals for the role CNE was in the evolutionary origins of complex macromolecular machines such as the spliceoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
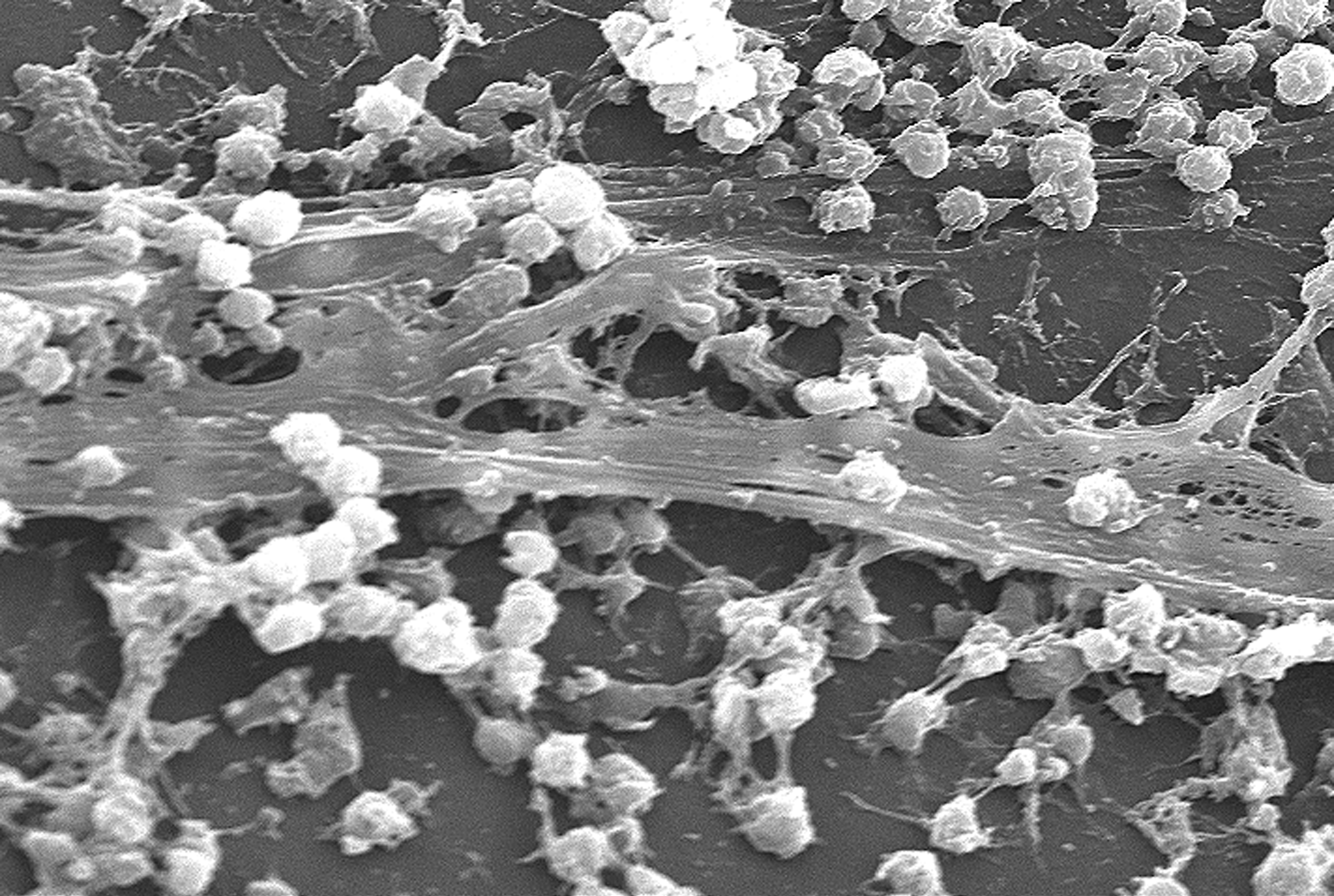
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples include most vascular plants engaged in mutualistic interactions with mycorrhizae, flowering plants being pollinated by animals, vascular plants being dispersed by animals, and corals with zooxanthellae, among many others. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and exploitation, or parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites and Messmates'' to mean "mutual aid among species". Mutualism is often conflated with two other types of ecological phenomena: cooperation and symbiosis. Cooperation most commonly refers to increases in fitness through within-species (intraspecific) interactions, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |