|
Red-headed Myzomela
The red-headed myzomela or red-headed honeyeater (''Myzomela erythrocephala'') is a passerine bird of the honeyeater family Meliphagidae found in Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. It was described by John Gould in 1840. Two subspecies are recognised, with the nominate race ''M. e. erythrocephala'' distributed around the tropical coastline of Australia, and ''M. e. infuscata'' in New Guinea. Though widely distributed, the species is not abundant within this range. While the IUCN lists the Australian population of ''M. e. infuscata'' as being near threatened, as a whole the widespread range means that its conservation is of least concern. At , it is a small honeyeater with a short tail and relatively long down-curved bill. It is sexually dimorphic; the male has a glossy red head and brown upperparts and paler grey-brown underparts while the female has predominantly grey-brown plumage. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical mangrove forests. It is very active whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gould
John Gould (; 14 September 1804 – 3 February 1881) was an English ornithologist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates produced by his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists, including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart. He has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed "Darwin's finches" played a role in the inception of Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. Gould's work is referenced in Charles Darwin's book, ''On the Origin of Species''. Early life Gould was born in Lyme Regis, the first son of a gardener. Both father and son probably had little education. After working on Dowager Lady Poulett's glass house, his father obtained a position on an estate near Guildford, Surrey, and then in 1818, Gould Snr became foreman in the Royal Gardens of Windsor. Gould then be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Sound
King Sound is a large gulf in northern Western Australia. It expands from the mouth of the Fitzroy River, one of Australia's largest watercourses, and opens to the Indian Ocean. It is about long, and averages about in width. The port town of Derby lies near the mouth of the Fitzroy River on the eastern shore of King Sound. King Sound has the highest tides in Australia, and amongst the highest in the world, reaching a maximum tidal range of at Derby.Derby tides at derbytourism.com.au . Retrieved 7 January 2007 The tidal range and water dynamic were researched in 1997–1998. Waters within the sound are generally turbid. The turbidity is associated with the erosion of |
Myzomela
''Myzomela'' is a genus of bird in the honeyeater family Meliphagidae. It is the largest genus of honeyeaters, with 39 species, and the most geographically widespread. It ranges from Indonesia to Australia and into the islands of the Pacific Ocean as far as Micronesia and Samoa. The genus was introduced by the naturalists Nicholas Vigors and Thomas Horsfield in 1827. The type species is the scarlet myzomela (''Myzomela sanguinolenta''). The title page is dated 1826. The genus contains the following 40 species: * Drab myzomela (''Myzomela blasii'') * White-chinned myzomela (''Myzomela albigula'') * Ashy myzomela (''Myzomela cineracea'') * Ruby-throated myzomela (''Myzomela eques'') *Moluccan myzomela (''Myzomela simplex'') * Red-tinged myzomela (''Myzomela rubrotincta'') *Biak myzomela (''Myzomela rubrobrunnea'') * Dusky myzomela (''Myzomela obscura'') * Red myzomela (''Myzomela cruentata'') *Reddish myzomela (''Myzomela erythrina'') * Papuan black myzomela (''Myzomela nigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
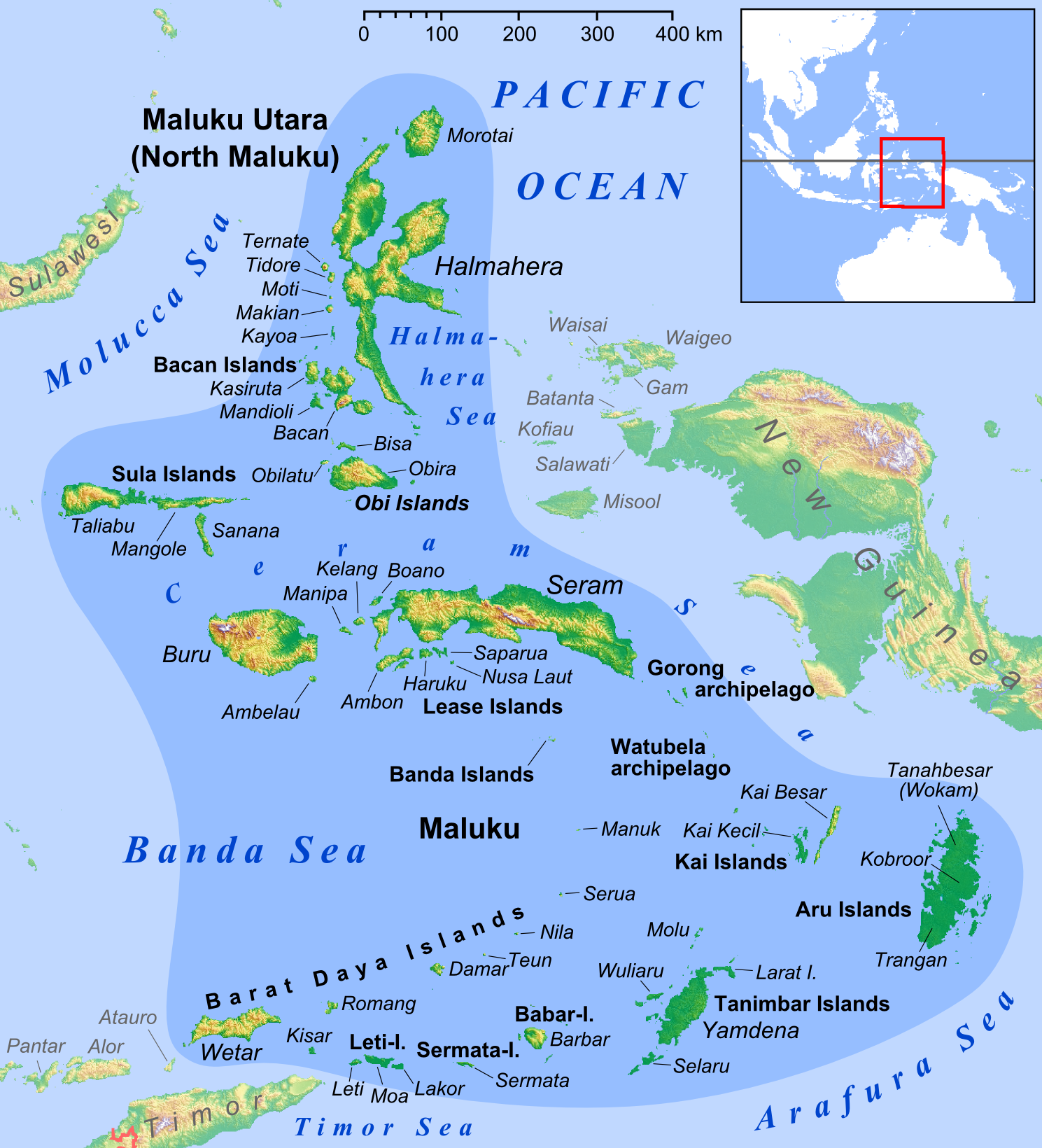
Wetar
Wetar is a tropical island which belongs to the Indonesian province of Maluku and is the largest island of the Maluku Barat Daya Islands (literally ''Southwest Islands'') of the Maluku Islands. It lies east of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which include nearby Alor and Timor, but it is politically part of the Maluku Islands. To the south, across the Wetar Strait, lies the island of Timor; at its closest it is 50 km away. To the west, across the Ombai Strait, lies the island of Alor. To the southwest is the very small island of Liran, which is also part of Wetar district (''kecamatan'') and, further southwest, the small East Timorese island of Atauro. To the north is the Banda Sea and to the east lie Romang and Damar Islands, while to the southeast lie the other principal islands of the Barat Daya Islands. Including Liran, Wetar has an area of 2,651.9 km2, and had a population of 7,916 at the 2010 Census. Wetar is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetar Myzomela
The Wetar myzomela or crimson-hooded myzomela (''Myzomela kuehni'') is a species of bird in the family Meliphagidae. It is endemic to Wetar. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, and rural gardens. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby .... References crimson-hooded myzomela Birds of Wetar crimson-hooded myzomela Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Meliphagidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumba Myzomela
The Sumba myzomela (''Myzomela dammermani'') is a species of bird in the family Meliphagidae. It is endemic to Sumba in the western Lesser Sunda Islands of Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ..., where it is found in forest with a significant component of deciduous trees. References Sumba myzomela Birds of Sumba Sumba myzomela Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Meliphagidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Alexander Forbes
William Alexander Forbes (25 June 1855 – 14 January 1883) was an English zoologist. He was the son of James Staats Forbes (1823–1904). Forbes studied natural sciences at St John's College, Cambridge, and later taught at Rhodes College (then known as Stewart College). In 1879 he was appointed prosector to the Zoological Society of London on the death of the previous incumbent, Alfred Henry Garrod, who was Forbes's friend and whose literary executor Forbes became. Forbes lectured on comparative anatomy at Charing Cross Hospital Medical School. As an anatomist, he wrote valuable papers on the muscular structure and voice organs of birds. On 8 February 1878, Forbes was elected Secretary of the Cambridge Natural History Society. He also edited the book compiling the late Alfred Henry Garrod's scientific papers; the book was published in 1881 along with a memoir of Garrod written by Forbes. In 1880 Forbes visited the forests of Pernambuco, Brazil, and published an account of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race (biology)
In biological taxonomy, race is an informal rank in the taxonomic hierarchy for which various definitions exist. Sometimes it is used to denote a level below that of subspecies, while at other times it is used as a synonym for subspecies. It has been used as a higher rank than strain, with several strains making up one race. Races may be genetically distinct populations of individuals within the same species, Republished without known revision several times since 1999, and originally published as: or they may be defined in other ways, e.g. geographically, or physiologically. Genetic isolation between races is not complete, but genetic differences may have accumulated that are not (yet) sufficient to separate species. The term is recognized by some, but not governed by any of the formal codes of biological nomenclature. Taxonomic units below the level of subspecies are not typically applied to animals. Other terms In botany, the Latin words ''stirps'' and ''proles'' were trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Ornithological Committee
The International Ornithologists' Union, formerly known as the International Ornithological Committee, is a group of about 200 international ornithologists, and is responsible for the International Ornithological Congress and other international ornithological activities, undertaken by its standing committees. International Ornithological Congress The International Ornithological Congress series forms the oldest and largest international series of meetings of ornithologists. It is organised by the International Ornithologists' Union. The first meeting was in 1884; subsequent meetings were irregular until 1926 since when meetings have been held every four years, except for two missed meetings during and in the immediate aftermath of the Second World War. Meetings See also * '' Birds of the World: Recommended English Names'', a book written by Frank Gill Frank Gill may refer to: * Frank Gill (Australian footballer) (1908–1970), Australian rules footballer with Carlton * Frank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectarivore
In zoology, a nectarivore is an animal which derives its energy and nutrient requirements from a diet consisting mainly or exclusively of the sugar-rich nectar produced by flowering plants. Nectar as a food source presents a number of benefits as well as challenges. It is essentially a solution of (as much as 80%) the simple sugars sucrose, glucose and fructose, which are easily ingested and digested, representing a rich and efficient source of nutrition. This solution is often diluted either by the plant that produces it or by rain falling on a flower and many nectarivores possess adaptations to effectively rid themselves of any excess water ingested this way. However, nectar is an incomplete source of nutrition. While it does contain proteins and amino acids, these are found in low quantities, and it is severely deficient in minerals and vitamins. Very few organisms consume nectar exclusively over their whole life cycle, either supplementing it with other sources, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_by_John_Gould.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
