|
Reconvilier - Vue D'ensemble Vers 1919
Reconvilier is a municipality in the Jura bernois administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is located in the French-speaking Bernese Jura (''Jura Bernois''). History Reconvilier is first mentioned in 884 as ''Roconis villare''. The former German name Rokwiler is no longer used today. The oldest trace of a settlement in the area are two ceramic and three bronze bowls which probably come from a Roman villa from the 2nd or 3rd century. In 884, the village appears as an estate belonging to Moutier-Grandval Abbey. The noble Reconvilier family appears in historical records beginning in the 12th century and lasting until the 15th. The village remained under the Abbey's control until it was secularized around 1531. Then Reconvilier came under the authority of the provost of Moutier-Grandval who represented the Prince-Bishop of Basel. After the 1797 French victory and the Treaty of Campo Formio, Reconvilier became part of the French Département of Mont-T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jura Bernois (administrative District)
Bernese Jura (french: Jura bernois, ) is the name for the French-speaking area of the Swiss canton of Bern, and from 2010 one of ten administrative divisions of the canton. Comprising the three French-speaking districts in the northern part of the canton, it contains 40 municipalities with an area of and a population () of . More than 90% of the population of the three districts speak French. The Bernese Jura of today comprises only three out of a total of seven districts which were known as the Bernese Jura during the period of 1815–1979. Of the remaining four, three seceded as the canton of Jura in 1979, while the fourth, the Laufen district, joined the canton of Basel-Landschaft in 1994. Additionally, Moutier, a municipality, voted to secede from Bern in a referendum in 2021 and join Jura, with the changeover expected to be implemented by 2026. History Most of the territory of the Bernese Jura was passed from the County of Burgundy to the Bishopric of Basel in AD 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
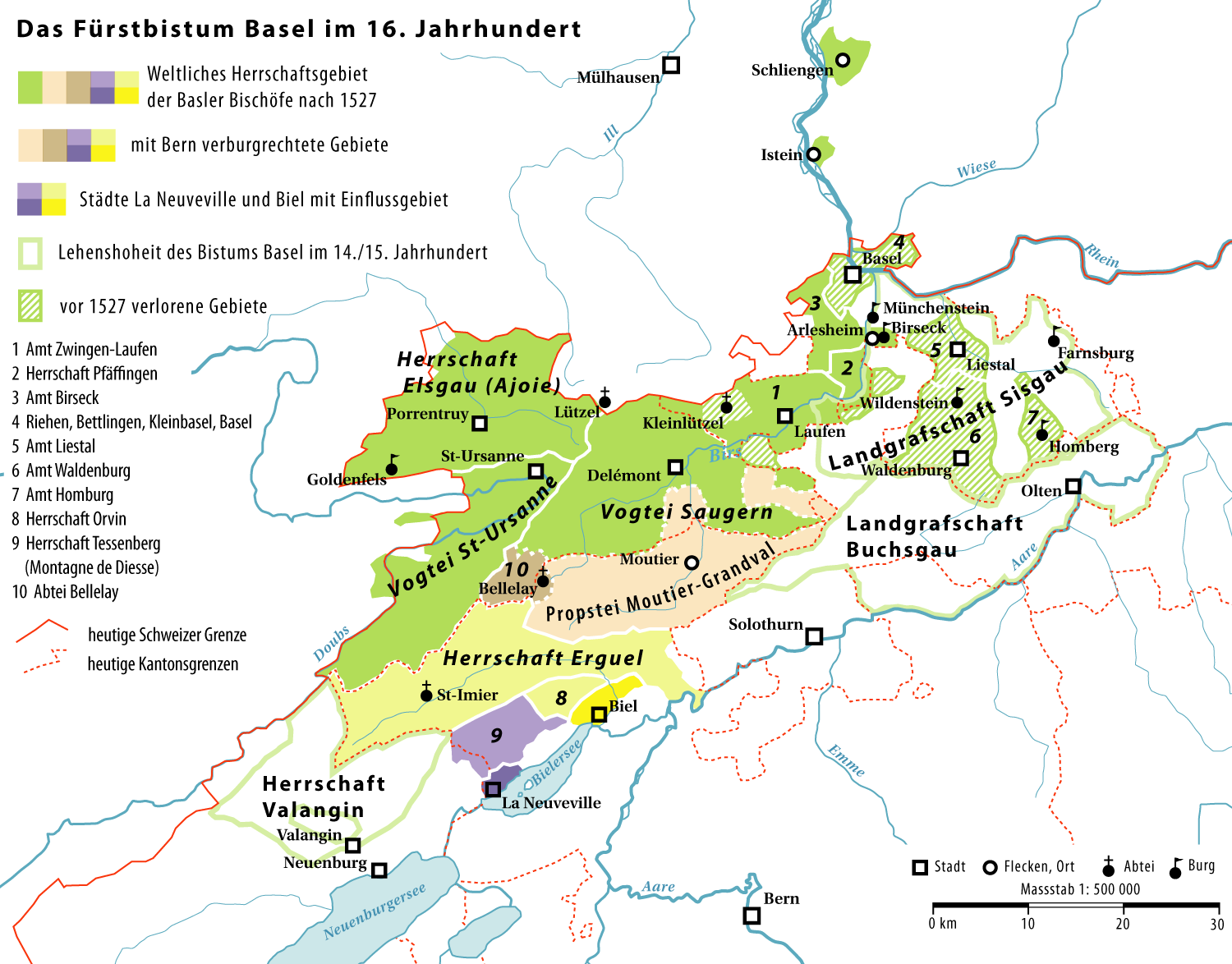
Moutier-Grandval Abbey
Moutier-Grandval Abbey was a Benedictine abbey near the villages of Moutier and Grandval in today's Jura bernois administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It was founded around 640, when Grandval already existed; Moutier grew up around the abbey. History The abbey was founded as a dependency of Luxeuil Abbey, on land granted by Gundoin, Duke of Alsace on the old route leading to the Pierre Pertuis Pass. The abbot of Luxeuil, Saint Waldebert, sent Saint Germanus of Granfelden, who served 35 years as the first abbot, with Saint Randoald of Grandval as his prior. Both were martyred in 675 by Adalrich, Duke of Alsace after they protested against his expulsion of the population of the Sorgenau valley. The abbey became, like some others, the secular ruler of a local territory, and by the 9th or 10th century had property and influence all the way to Lake Biel and into the Balsthal valley, but was regarded as a fief of the king of Burgundy. There was to be a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May 1521 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavannes
Tavannes is a municipality in the Jura bernois administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is located in the French-speaking part of the canton in the Jura mountains. History The area around Tavannes was traversed by the early inhabitants of the Helvetic plain because of the natural tunnel through the Jura between the valley of the Suze and the valley of the Birse. Under the Emperor Marcus Aurelius, the Romans improved this road between 161 and 169 AD. The Roman administrator left an inscription in the cliff at Pierre-Pertuis to this effect. Early mills were built along the Birse, utilizing its water as a source of power. Tavannes was one of the earliest inhabited locations in the district. Its name comes from the ancient Germanic words 'Þahs-winja, ancien haut allemand dahs, germanique *þahsu, « blaireau », et gothique vinja, germanique *venjô, « pâturage » errenot ',which means the same as the older German name 'Dachsfelden'. In the fourth cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or more curates, and who operates from a parish church. Historically, a parish often covered the same geographical area as a manor. Its association with the parish church remains paramount. By extension the term ''parish'' refers not only to the territorial entity but to the people of its community or congregation as well as to church property within it. In England this church property was technically in ownership of the parish priest ''ex-officio'', vested in him on his institution to that parish. Etymology and use First attested in English in the late, 13th century, the word ''parish'' comes from the Old French ''paroisse'', in turn from la, paroecia, the latinisation of the grc, παροικία, paroikia, "sojourning in a foreign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers and other stakeholders, chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars without the use of (military) violence. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More fundamentally, strongly generalising, conservative thinking leaders like Von Metternich also sought to restrain or eliminate republicanism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means ''Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is the smaller and less populated of the two departments of the former administrative Alsace region, the other being the Bas-Rhin (Lower Rhine). Especially after the 1871 cession of the southern territory known since 1922 as Territoire de Belfort, although it is still densely populated compared to the rest of metropolitan France. It had a population of 767,086 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 68 Haut-Rhin INSEE On 1 January 2021, the departments of |
Mont-Terrible
Mont-Terrible was a department of the First French Republic, with its seat at Porrentruy. The Mont Terrible for which the department was named is now known as , a peak of 804 metres near Courgenay (now in the canton of Jura, Switzerland). The toponym of was formed by popular etymology from an earlier Frainc-Comtou ''Mont Tairi'', from "arid, dry". The department was created in 1793 with the annexation of the short-lived Rauracian Republic, which had been created in December 1792 from a part of the Prince-Bishopric of Basel. In 1797, the former Württemberg-owned Principality of Montbéliard, which had previously been given to Haute-Saône, was reattached to Mont-Terrible, together with the remaining Swiss part of the Bishopric of Basel after the French attack to the Elvetic nation. The department was abolished in 1800. Its territory was annexed to the Haut-Rhin, within which it formed the two arrondissements of Delémont and Porrentruy. In 1815, the territory that had pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The treaty followed the armistice of Leoben (18 April 1797), which had been forced on the Habsburgs by Napoleon's victorious campaign in Italy. It ended the War of the First Coalition and left Great Britain fighting alone against revolutionary France. The treaty's public articles concerned only France and Austria and called for a Congress of Rastatt to be held to negotiate a final peace for the Holy Roman Empire. In the treaty's secret articles, Austria as the personal state of the Emperor promised to work with France to certain ends at the congress. Among other provisions, the treaty meant the definitive end to the ancient Republic of Venice, which was disbanded and partitioned by the French and the Austrians. The congress failed to achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaigns Of 1797 In The French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars continued from 1796, with France fighting the First Coalition. On 14 February, British admiral Jervis met and defeated a Spanish fleet off Portugal at the Battle of Cape St. Vincent. This prevented the Spanish fleet from rendezvousing with the French, removing a threat of invasion to Britain. However, the British fleet was weakened over the rest of the year by the Spithead and Nore mutinies, which kept many ships in port through the summer. On 22 February, a French invasion force consisting of 1,400 troops from the ''Légion Noire'' (The Black Legion) under the command of Irish American Colonel William Tate landed near Fishguard (Wales). They were met by a quickly assembled group of around 500 British reservists, militia and sailors under the command of John Campbell, 1st Baron Cawdor. After brief clashes with the local civilian population and Lord Cawdor's forces on 23 February, Tate was forced into an unconditional surrender by 24 February. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




