|
Reconnection
Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in highly conducting plasmas in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection occurs on timescales intermediate between slow resistive diffusion of the magnetic field and fast Alfvénic timescales. The concept of magnetic reconnection was first introduced in 1950 in the PhD thesis of James Dungey to explain the coupling of mass, energy and momentum from the solar wind into Earth's magnetosphere and was published for the first time on the open literature in his seminal paper in 1961. Fundamental principles Magnetic reconnection is a breakdown of "ideal-magnetohydrodynamics" and so of "Alfvén's theorem" (also called the "frozen-in flux theorem") which applies to large-scale regions of a highly-conducting magnetoplasma, for which the Magnetic Reynolds Number is very large: this makes the convective term in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnection
Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in highly conducting plasmas in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection occurs on timescales intermediate between slow resistive diffusion of the magnetic field and fast Alfvénic timescales. The concept of magnetic reconnection was first introduced in 1950 in the PhD thesis of James Dungey to explain the coupling of mass, energy and momentum from the solar wind into Earth's magnetosphere and was published for the first time on the open literature in his seminal paper in 1961. Fundamental principles Magnetic reconnection is a breakdown of "ideal-magnetohydrodynamics" and so of "Alfvén's theorem" (also called the "frozen-in flux theorem") which applies to large-scale regions of a highly-conducting magnetoplasma, for which the Magnetic Reynolds Number is very large: this makes the convective term in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dungey
James Wynne "Jim" Dungey (1923–2015) was a British space scientist who was pivotal in establishing the field of space weather and made significant contributions to the fundamental understanding of plasma physics. Early life and career Jim Dungey grew up in Stamford, Lincolnshire, the son of a schoolteacher. During World War II, he worked at British Thompson-Houston in Rugby, on developments for radar. After the end of the war, he gained a degree from Magdalene College, Cambridge in 1947, where he stayed to pursue a Ph.D. under the supervision of British polymath scientist Fred Hoyle. From 1950 to 1953 he worked at the University of Sydney with Ron Giovanelli, from 1953 to 1954 at Pennsylvania State University and from 1954 to 1957 back at Cambridge. From 1957 to 1959 he was a mathematics lecturer at King's College, Newcastle upon Tyne (now Newcastle University) and from 1959 to 1963 he worked at Aldermaston. In 1963 he moved to the Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College London, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Sheet
A current sheet is an electric current that is confined to a surface, rather than being spread through a volume of space. Current sheets feature in magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), the study of the behavior of electrically conductive fluids: if there is an electric current through part of the volume of such a fluid, magnetic forces tend to expel it from the fluid, compressing the current into thin layers that pass through the volume. The largest occurring current sheet in the Solar System is the so-called Heliospheric current sheet, which is about 10,000 km thick, and extends from the Sun and out beyond the orbit of Pluto. In astrophysical plasmas such as the solar corona, current sheets theoretically might have an aspect ratio (breadth divided by thickness) as high as 100,000:1. By contrast, the pages of most books have an aspect ratio close to 2000:1. Because current sheets are so thin in comparison to their size, they are often treated as if they have zero thickness; thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfvén's Theorem
In magnetohydrodynamics, Alfvén's theorem, or the frozen-in flux theorem, "states that in a fluid with infinite electric conductivity, the magnetic field is frozen into the fluid and has to move along with it." Hannes Alfvén put the idea forward for the first time in 1942. In his own words: "In view of the infinite conductivity, every motion (perpendicular to the field) of the liquid in relation to the lines of force is forbidden because it would give infinite eddy currents. Thus the matter of the liquid is “fastened” to the lines of force...." In later life, Alfvén changed his mind and advised against use of his own theorem. However, Alfvén's theorem is much used today because of a second mechanism, magnetic reconnection. This is a breakdown of Alfvén's theorem in thin current sheets and is important as it can untangle field lines that would become increasingly tangled by plasma velocity shears and vortices in regions of low plasma beta if Alfvén's theorem applied everywh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lundquist Number
In plasma physics, the Lundquist number (denoted by S) is a dimensionless ratio which compares the timescale of an Alfvén wave crossing to the timescale of resistive diffusion. It is a special case of the magnetic Reynolds number when the Alfvén velocity is the typical velocity scale of the system, and is given by :S = \frac , where L is the typical length scale of the system, \eta is the magnetic diffusivity and v_A is the Alfvén velocity of the plasma. High Lundquist numbers indicate highly conducting plasmas, while low Lundquist numbers indicate more resistive plasmas. Laboratory plasma experiments typically have Lundquist numbers between 10^2-10^8, while in astrophysical situations the Lundquist number can be greater than 10^. Considerations of Lundquist number are especially important in magnetic reconnection. See also * Magnetic Prandtl number * Péclet number In continuum mechanics, the Péclet number (, after Jean Claude Eugène Péclet) is a class of dimensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
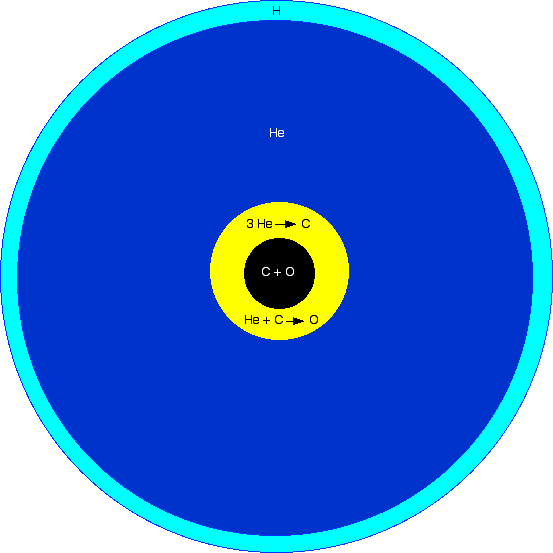
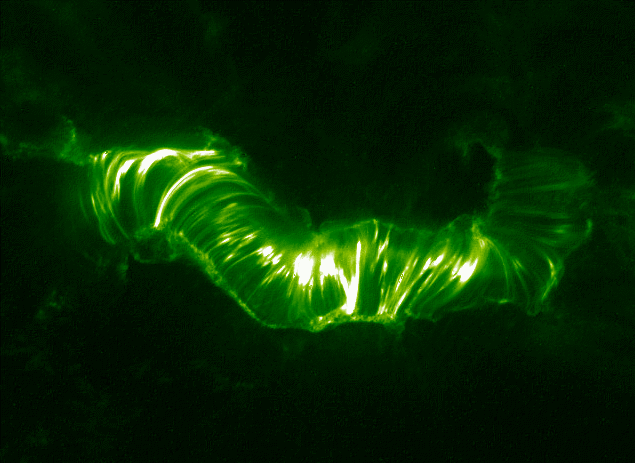
SDO Observes A Reconnection Event
A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type subdwarfs are much dimmer than regular O-type main-sequence stars, but with a brightness about 10 to 100 times that of the Sun, and have a mass approximately half that of the Sun. Their temperature ranges from 40,000 to 100,000 K. Ionized helium is prominent in their spectra. Gravity acceleration is expressed by log ''g'' between 4.0 and 6.5. Many sdO stars are moving at high velocity through the Milky Way and are found at high galactic latitudes. Structure The structure of a subdwarf O star is believed to be a carbon and oxygen core surrounded by a helium burning shell. The spectrum shows that the content is from 50 to 100% helium. History In the early 1970s Greenstein and Sargent measured temperatures and gravity strengths and were able to plot their correct position on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The Palomar-Green survey, Hamburg surveys, Sloan Digital Sky Survey and Supernova Ia Progenitor Survey (ESO-SPY ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. This increases the energy needed to pump fluid through a pipe. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Rey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ''stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Tension Force
In physics, magnetic tension is a restoring force with units of force density that acts to straighten bent magnetic field lines. In SI units, the force density \mathbf_T exerted perpendicular to a magnetic field \mathbf can be expressed as :\mathbf_T = \frac where \mu_0 is the vacuum permeability. Magnetic tension forces also rely on vector current densities and their interaction with the magnetic field. Plotting magnetic tension along adjacent field lines can give a picture as to their divergence and convergence with respect to each other as well as current densities. Magnetic tension is analogous to the restoring force of rubber bands. Mathematical statement In ideal magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) the magnetic tension force in an electrically conducting fluid with a bulk plasma velocity field \mathbf, current density \mathbf, mass density \rho, magnetic field \mathbf, and plasma pressure p can be derived from the Cauchy momentum equation: : \rho\left(\frac + \mathbf \cdot \nabla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field Lines
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Monopoles
In particle physics, a magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). A magnetic monopole would have a net north or south "magnetic charge". Modern interest in the concept stems from high-energy physics, particle theories, notably the grand unified theory, grand unified and superstring theory, superstring theories, which predict their existence. The known elementary particles that have electric charge are electric monopoles. Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets is not caused by magnetic monopoles, and indeed, there is no known experimental or observational evidence that magnetic monopoles exist. Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasiparticle, quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles. Historical background Early science and classical physics Many early scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |