|
Recoil Starter
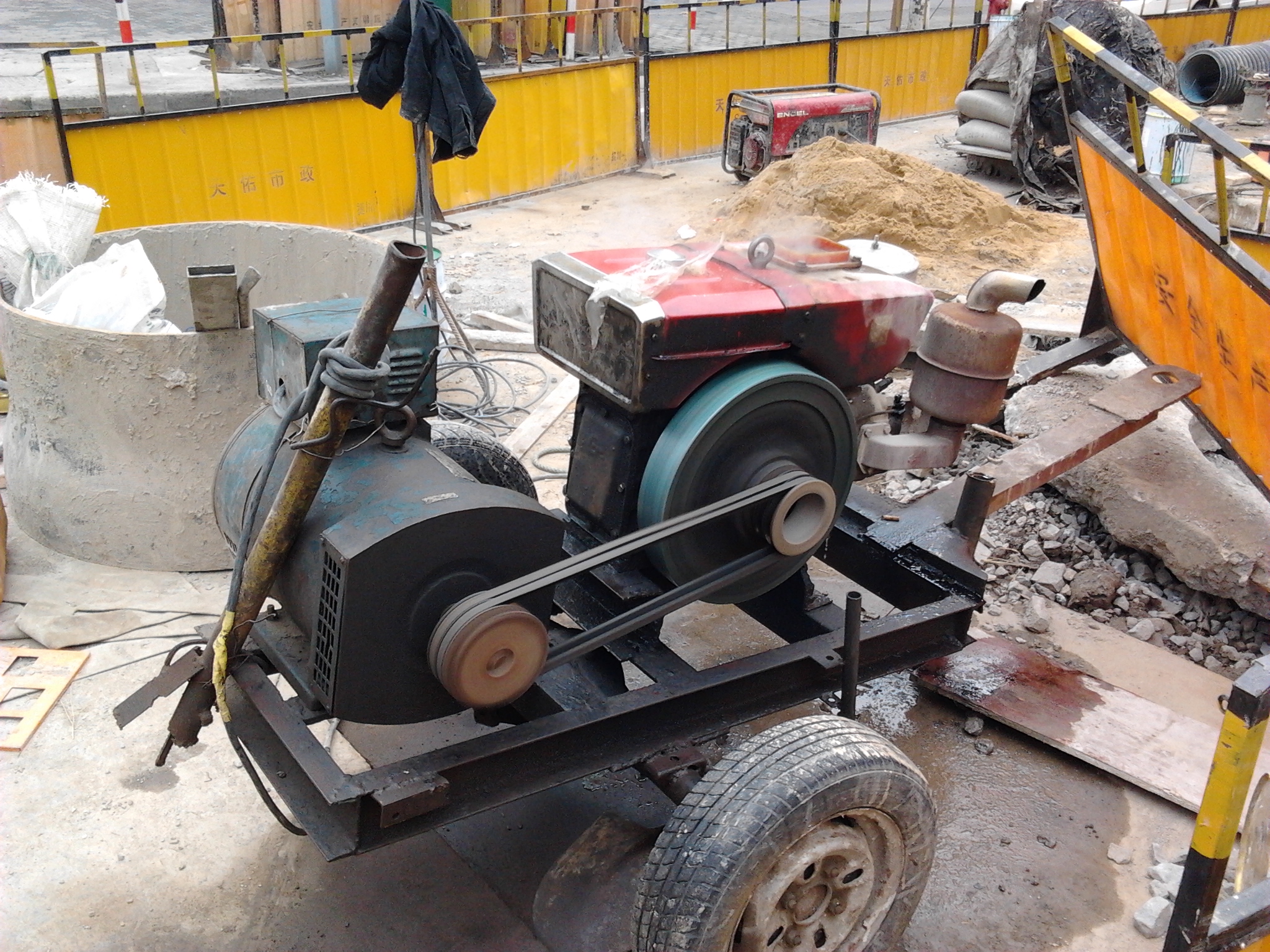
Rope start (also called pull start or ''rewind start'') is a method of starting an internal combustion engine, usually on small machines, such as lawn mowers, chainsaws, ultralight aircraft, small outboard motors and portable engine-generators. Also used on some small vehicles such as small go-karts, minibikes, and small ATVs. Recoil start This starter mechanism comprises a rope, with a grip at the end, moulded rope reels and a spring. The rope is coiled within a reel which is held under spring tension within an outer reel. This reel assembly is in contact with one end of the crankshaft through a ratcheting mechanism (specifically, a ''freewheel clutch''). When the rope's grip is pulled, the rope uncoils, tensions the spring, engages the clutch and turns the crankshaft, spinning it to crank or start the engine before the end of the pull stroke. The running of the engine then disengages the clutch. When the user releases the grip, the spring operated reel retracts the rope, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons ( piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle ( jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion engine, known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawn Mower
A lawn mower (also known as a mower, grass cutter or lawnmower) is a device utilizing one or more revolving blades (or a reel) to cut a grass surface to an even height. The height of the cut grass may be fixed by the design of the mower, but generally is adjustable by the operator, typically by a single master lever, or by a lever or nut and bolt on each of the machine's wheels. The blades may be powered by manual force, with wheels mechanically connected to the cutting blades so that when the mower is pushed forward, the blades spin or the machine may have a battery-powered or plug-in electric motor. The most common self-contained power source for lawn mowers is a small (typically one cylinder) internal combustion engine. Smaller mowers often lack any form of propulsion, requiring human power to move over a surface; "walk-behind" mowers are self-propelled, requiring a human only to walk behind and guide them. Larger lawn mowers are usually either self-propelled "walk-behind" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chainsaw
A chainsaw (or chain saw) is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pruning, cutting firebreaks in wildland fire suppression, and harvesting of firewood. Chainsaws with specially designed bar-and-chain combinations have been developed as tools for use in chainsaw art and chainsaw mills. Specialized chainsaws are used for cutting concrete during construction developments. Chainsaws are sometimes used for cutting ice; for example, ice sculpture and winter swimming in Finland. History In surgery The origin of chain saws in surgery is debated. A "flexible saw", consisting of a fine serrated link chain held between two wooden handles, was pioneered in the late 18th century (c. 1783–1785) by two Scottish doctors, John Aitken and James Jeffray, for symphysiotomy and excision of diseased bone, respectively. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultralight Aircraft
Ultralight aviation (called microlight aviation in some countries) is the flying of lightweight, 1- or 2-seat fixed-wing aircraft. Some countries differentiate between weight-shift control and conventional three-axis control aircraft with ailerons, elevator and rudder, calling the former "microlight" and the latter "ultralight". During the late 1970s and early 1980s, mostly stimulated by the hang gliding movement, many people sought affordable powered flight. As a result, many aviation authorities set up definitions of lightweight, slow-flying aeroplanes that could be subject to minimum regulations. The resulting aeroplanes are commonly called "ultralight aircraft" or "microlights", although the weight and speed limits differ from country to country. In Europe, the sporting (FAI) definition limits the maximum stalling speed to and the maximum take-off weight to , or if a ballistic parachute is installed. The definition means that the aircraft has a slow landing speed and short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outboard Motors
An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes engine, gearbox and propeller or jet drive, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom. They are the most common motorised method of propelling small watercraft. As well as providing propulsion, outboards provide steering control, as they are designed to pivot over their mountings and thus control the direction of thrust. The skeg also acts as a rudder when the engine is not running. Unlike inboard motors, outboard motors can be easily removed for storage or repairs. In order to eliminate the chances of hitting bottom with an outboard motor, the motor can be tilted up to an elevated position either electronically or manually. This helps when traveling through shallow waters where there may be debris that could potentially damage the motor as well as the propeller. If the electric motor required to move the pistons which raise or lower the engine is malfunctioning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine-generator
An engine–generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engine (prime mover) mounted together to form a single piece of equipment. This combination is also called an ''engine–generator set'' or a ''gen-set''. In many contexts, the engine is taken for granted and the combined unit is simply called a ''generator''. An engine–generator may be a fixed installation, part of a vehicle, or made small enough to be portable. Components In addition to the engine and generator, engine–generators generally include a fuel supply, a constant engine speed regulator (governor) and a generator voltage regulator, cooling and exhaust systems, and lubrication system. Units larger than about 1 kW rating often have a battery and electric starter motor; very large units may start with compressed air either to an air driven starter motor or introduced directly to the engine cylinders to initiate engine rotation. Standby power generating units often include an automatic start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Go-kart
A go-kart, also written as go-cart (often referred to as simply a kart), is a type of sports car, close wheeled car, open-wheel car or quadracycle. Go-karts come in all shapes and forms, from non-motorised models to high-performance Kart racing, racing karts. Karting is a type of racing in which a compact four-wheel unit called a go-kart is used. In the beginning, Art Ingels invented the first go-kart in Los Angeles in 1956. Etymology The exact origin of the term is unclear. One of the first appearances of the term is an 1885 painting by the Scottish artist Hugh Cameron (artist), Hugh Cameron RSA: "The Go-Cart". It is also unclear why the "C" was later changed to a "K". Non-motorised Gravity racers, in North America usually referred to as Soap Box Derby carts, are the simplest type of go-karts. They are propelled by gravity. Go-karts without motors (quadracycles) may also be propelled by bicycle pedals. Motorised Engines Traditionally, small Two-stroke engine, two-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minibikes
A minibike is a two-wheeled, motorized, off-highway recreational vehicle popularized in the 1960s and 1970s, but available continuously from a wide variety of manufacturers since 1959. Their off-highway nature and (in many countries) typically entirely off-road legal status differentiate minibikes from motorcycles and mopeds, and their miniature size differentiates them from dirt bikes. Traditionally, minibikes have a four-stroke, horizontal crankshaft engine, single- or two-speed centrifugal clutch transmissions with chain final-drive, 4" or 6" wheels and a low frame/seat height with elevated handlebars. Commercially available minibikes are usually equipped with small engines commonly found elsewhere on utilitarian equipment such as garden tillers History While the minibike had precursors in machines such as the Doodle Bug and Cushman Scooters, which share smaller wheels, tubular-steel frames, and air-cooled, single-cylinder engines, those vehicles had larger seat heights a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-terrain Vehicle
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV), also known as a light utility vehicle (LUV), a quad bike, or simply a quad, as defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI); is a vehicle that travels on low-pressure tires, with a seat that is straddled by the operator, along with handlebars for steering control. As the name implies, it is designed to handle a wider variety of terrain than most other vehicles. Although it is a street-legal vehicle in some countries, it is not street-legal within most states, territories and provinces of Australia, the United States or Canada. By the current ANSI definition, ATVs are intended for use by a single operator, although some companies have developed ATVs intended for use by the operator and one passenger. These ATVs are referred to as tandem ATVs. The rider sits on and operates these vehicles like a motorcycle, but the extra wheels give more stability at slower speeds. Although most are equipped with three or four wheels, six-wheel mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft located within the engine block, held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormous stresses, in some cases more than per cylinder. Crankshafts for single-cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratchet (device)
A ratchet (occasionally spelled rachet) is a mechanical device that allows continuous linear or rotary motion in only one direction while preventing motion in the opposite direction. Ratchets are widely used in machinery and tools. The word ''ratchet'' is also used informally to refer to a ratcheting socket wrench. __TOC__ Theory of operation A ratchet consists of a round gear or a linear rack with teeth, and a pivoting, spring-loaded finger called a '' pawl'' (or ''click'', in clocks and watches) that engages the teeth. The teeth are uniform but are usually asymmetrical, with each tooth having a moderate slope on one edge and a much steeper slope on the other edge. When the teeth are moving in the unrestricted (i.e. forward) direction, the pawl easily slides up and over the gently sloped edges of the teeth, with a spring forcing it (often with an audible 'click') into the depression between the teeth as it passes the tip of each tooth. When the teeth move in the opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)