|
Reciprocal Voice
A reciprocal construction (abbreviated ) is a grammatical pattern in which each of the participants occupies both the role of agent and patient with respect to the other. An example is the English sentence ''John and Mary criticized each other'': John criticized Mary, and Mary criticized John. Reciprocal constructions can be said to express mutual relationships. Many languages, such as Semitic languages, Altaic languages or Bantu languages, have special reciprocal affixes in verbs. Other languages, including English, use reciprocal pronouns such as ''"each other"'' to indicate a mutual relation. Latin uses the preposition ''inter'' and its reflexive pronoun ''inter se'' (between themselves) when the verb is third person. Most Indo-European languages do not have special reciprocal affixes on verbs, and mutual relations are expressed through reflexive constructions or other mechanisms. For example, Russian reciprocal constructions have the suffix -sja (-ся, 'self'), which al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glossing Abbreviations
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. These will generally be the glosses used on Wikipedia. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or common. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Pronoun
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers to another noun or pronoun (its antecedent) within the same sentence. In the English language specifically, a reflexive pronoun will end in ''-self'' or ''-selves'', and refer to a previously named noun or pronoun (''myself'', ''yourself'', ''ourselves'', ''themselves'', etc.). English intensive pronouns, used for emphasis, take the same form. In generative grammar, a reflexive pronoun is an anaphor that must be bound by its antecedent (see binding). In a general sense, it is a noun phrase that obligatorily gets its meaning from another noun phrase in the sentence. Different languages have different binding domains for reflexive pronouns, according to their structure. Origins and usage In Indo-European languages, the reflexive pronoun has its origins in Proto-Indo-European. In some languages, some distinction exists between normal object and reflexive pronouns, mainly in the third person: whether one says "I like me" or "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Haspelmath
Martin Haspelmath (; born 2 February 1963 in Hoya, Lower Saxony) is a German linguist working in the field of linguistic typology. He is a researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, where he worked from 1998 to 2015 and again since 2020. Between 2015 and 2020, he worked at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. He is also an honorary professor of linguistics at the University of Leipzig. Career Haspelmath is one of the editors of the World Atlas of Language Structures and the Glottolog online database, one of the founders of the open access publisher Language Science Press, and has worked on the Standard Average European sprachbund. Besides typology, his research interests include syntactic and morphological theory, language change and language contact. He is a member of the Academia Europaea. According to Google Scholar, his work has been cited over 32,000 times and he has an h-index The ''h''-index is an author-le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Verb
In grammar, a reflexive verb is, loosely, a verb whose direct object is the same as its subject; for example, "I wash myself". More generally, a reflexive verb has the same semantic agent and patient (typically represented syntactically by the subject and the direct object). For example, the English verb ''to perjure'' is reflexive, since one can only perjure ''oneself''. In a wider sense, the term refers to any verb form whose grammatical object is a reflexive pronoun, regardless of semantics; such verbs are also more broadly referred to as pronominal verbs, especially in grammars of the Romance languages. Other kinds of pronominal verbs are reciprocal (''they killed each other''), passive (''it is told''), subjective, idiomatic. The presence of the reflexive pronoun changes the meaning of a verb, e.g. Spanish ''abonar'' to pay, ''abonarse'' to subscribe. There are languages that have explicit morphology or syntax to transform a verb into a reflexive form. In many languages, ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
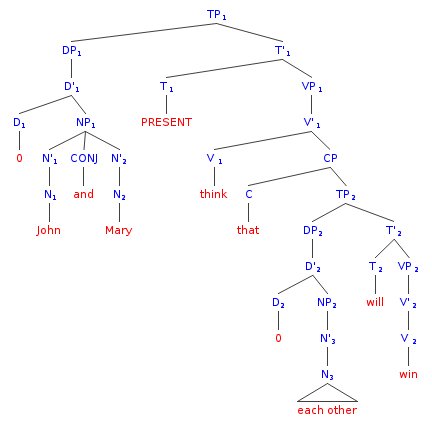
Reciprocal Pronoun
A reciprocal pronoun is a pronoun that indicates a reciprocal relationship. A reciprocal pronoun can be used for one of the participants of a reciprocal construction, i.e. a clause in which two participants are in a mutual relationship. The reciprocal pronouns of English are ''one another'' and ''each other'', and they form the category of anaphors along with reflexive pronouns (''myself'', ''yourselves'', ''themselves,'' etc.). Defining properties Semantics of reciprocal relation Reflexive pronouns are used similarly to reciprocal pronouns in the sense that they typically refer back to the subject of the sentence. (1) ''John and Mary like themselves.'' (2) ''John and Mary like each other.'' The main difference between reflexives, as in example (1), and reciprocal pronouns, as in example (2), is that reflexives are used when the subject acts upon itself, while reciprocals are used when members of a group perform the same action relative to one another. Reciprocal pronouns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Voice
A passive voice construction is a grammatical voice construction that is found in many languages. In a clause with passive voice, the grammatical subject expresses the ''theme'' or ''patient'' of the main verb – that is, the person or thing that undergoes the action or has its state changed. This contrasts with active voice, in which the subject has the agent role. For example, in the passive sentence "The tree was pulled down", the subject (''the tree'') denotes the patient rather than the agent of the action. In contrast, the sentences "Someone pulled down the tree" and "The tree is down" are active sentences. Typically, in passive clauses, what is usually expressed by the object (or sometimes another argument) of the verb is now expressed by the subject, while what is usually expressed by the subject is either omitted or is indicated by some adjunct of the clause. Thus, turning an active sense of a verb into a passive sense is a valence-decreasing process ("detransitivizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Verb
In grammar, a reflexive verb is, loosely, a verb whose direct object is the same as its subject; for example, "I wash myself". More generally, a reflexive verb has the same semantic agent and patient (typically represented syntactically by the subject and the direct object). For example, the English verb ''to perjure'' is reflexive, since one can only perjure ''oneself''. In a wider sense, the term refers to any verb form whose grammatical object is a reflexive pronoun, regardless of semantics; such verbs are also more broadly referred to as pronominal verbs, especially in grammars of the Romance languages. Other kinds of pronominal verbs are reciprocal (''they killed each other''), passive (''it is told''), subjective, idiomatic. The presence of the reflexive pronoun changes the meaning of a verb, e.g. Spanish ''abonar'' to pay, ''abonarse'' to subscribe. There are languages that have explicit morphology or syntax to transform a verb into a reflexive form. In many languages, ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocal Pronoun
A reciprocal pronoun is a pronoun that indicates a reciprocal relationship. A reciprocal pronoun can be used for one of the participants of a reciprocal construction, i.e. a clause in which two participants are in a mutual relationship. The reciprocal pronouns of English are ''one another'' and ''each other'', and they form the category of anaphors along with reflexive pronouns (''myself'', ''yourselves'', ''themselves,'' etc.). Defining properties Semantics of reciprocal relation Reflexive pronouns are used similarly to reciprocal pronouns in the sense that they typically refer back to the subject of the sentence. (1) ''John and Mary like themselves.'' (2) ''John and Mary like each other.'' The main difference between reflexives, as in example (1), and reciprocal pronouns, as in example (2), is that reflexives are used when the subject acts upon itself, while reciprocals are used when members of a group perform the same action relative to one another. Reciprocal pronouns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and Grammar#Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency, Fluent speakers of a variety (linguistics), language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's First language, native language(s) – are language acquisition, acquired not by conscious study or language teaching, instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affix
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. Affixes may be derivational, like English ''-ness'' and ''pre-'', or inflectional, like English plural ''-s'' and past tense ''-ed''. They are bound morphemes by definition; prefixes and suffixes may be separable affixes. Affixation is the linguistic process that speakers use to form different words by adding morphemes at the beginning (prefixation), the middle (infixation) or the end (suffixation) of words. Positional categories of affixes ''Prefix'' and ''suffix'' may be subsumed under the term ''adfix'', in contrast to ''infix.'' When marking text for interlinear glossing, as in the third column in the chart above, simple affixes such as prefixes and suffixes are separated from the stem with hyphens. Affixes which disrupt the stem, or which themselves are discontinuous, are often marked off with angle brackets. Reduplication is often shown with a tilde. Affixes which c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |