|
Real Fábrica Del Buen Retiro
Real Fábrica del Buen Retiro (popularly called ''La China''; "Buen Retiro Porcelain Factory"; alternatively, Real Fábrica de Porcelana del Buen Retiro) was a porcelain manufacturing factory in Spain. It was located in Madrid's Parque del Buen Retiro, Madrid on a site near the ''Fuente del Ángel Caído''. The factory began by moving the Capodimonte porcelain factory from Naples in 1760, after its founder there had inherited the Spanish throne as Carlos III of Spain. He took the equipment and about 40 key workers, including Giuseppe Gricci (c. 1700–1770), the main modeller, and nearly five tons of porcelain paste. Since the paste, the main artists, and the fleur-de-lys factory mark, were all used by both factories, distinguishing between their products from the years around the move can be very difficult. The factory continued to make soft paste porcelain until 1803, when it switched to hard-paste porcelain; some pieces made were in fact creamware, an English style of fine ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
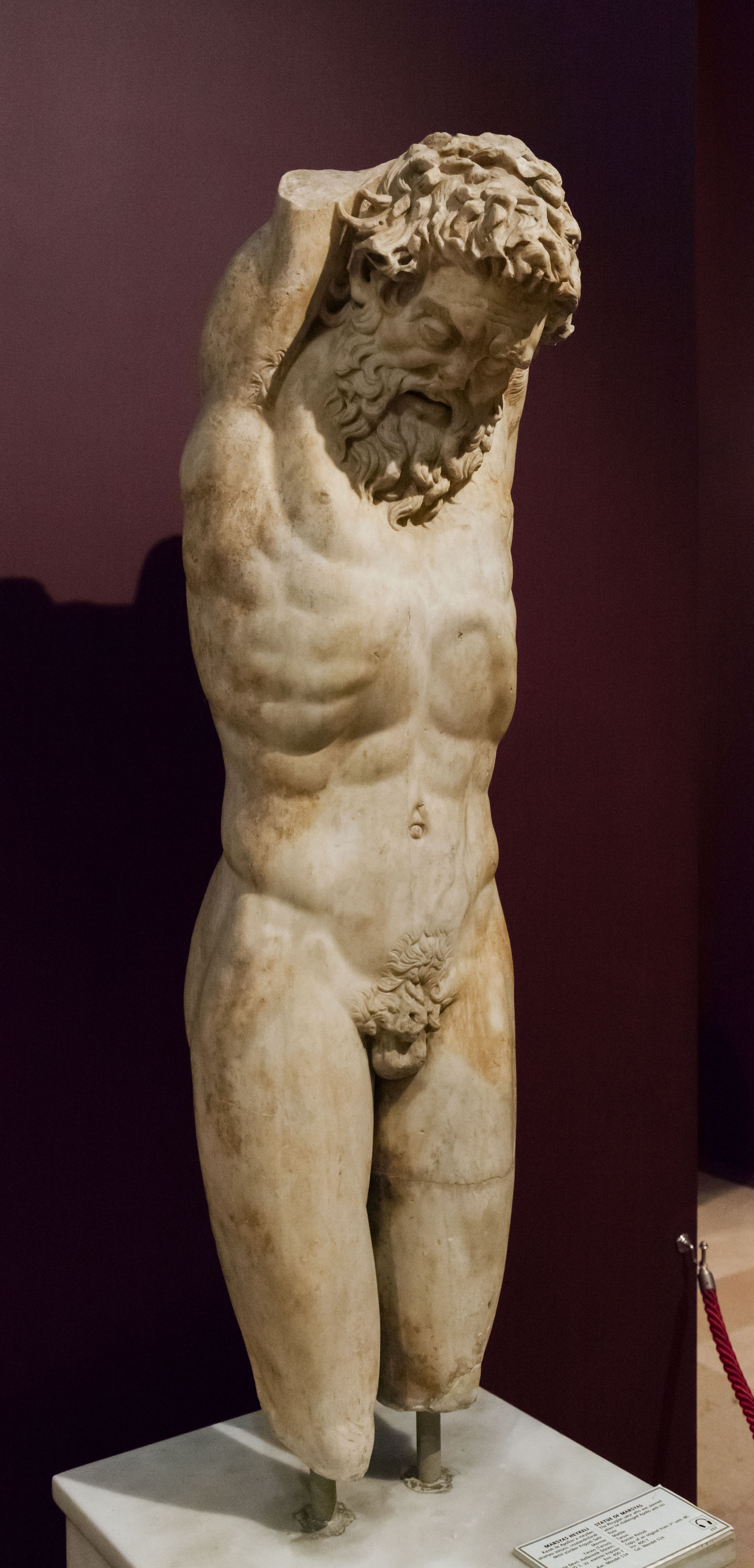
Marsyas And Apollo, Apparently But Unidentified - Museo Nacional De Artes Decorativas - Madrid, Spain - DSC08404
In Greek mythology, the satyr Marsyas (; grc-gre, Μαρσύας) is a central figure in two stories involving music: in one, he picked up the double oboe (''aulos'') that had been abandoned by Athena and played it; in the other, he challenged Apollo to a contest of music and lost his hide and life. In antiquity, literary sources often emphasize the ''hubris'' of Marsyas and the justice of his punishment. In one strand of modern comparative mythography, the domination of Marsyas by Apollo is regarded as an example of myth that recapitulates a supposed supplanting by the Olympian pantheon of an earlier "Pelasgian" religion of chthonic heroic ancestors and nature spirits. Marsyas was a devoté of the ancient Mother Goddess Rhea/Cybele, and his episodes are situated by the mythographers in Celaenae (or Kelainai), in Phrygia, at the main source of the Meander (the river Menderes in Turkey). Family When a genealogy was applied to him, Marsyas was the son of the "divine" Hyagni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Factory Of La Moncloa
Royal Factory of La Moncloa (Spanish: ''Real Fábrica de La Moncloa''; variations: Moncloa Porcelain Factory, or Royal Porcelain Factory and Thin Earthenware of the Moncloa, or Real Fábrica de Loza de la Moncloa) ( es, Real Fábrica de La Moncloa) was a Spanish manufacturing plant for porcelain and ceramics which was in operation in the 19th century. The Royal Factory of La Moncloa was located in Moncloa-Aravaca, Madrid, in a place called the Granjilla of Jeronimos in Cementerio de La Florida. History When the British attacked French positions in Madrid in 1812, during the Peninsular War they damaged the Real Fábrica del Buen Retiro, a porcelain factory on a site in the Buen Retiro Park. Later that year General Hill took his troops from Madrid to join the main army under Wellington near Alba de Tormes. Before leaving the Spanish capital, the British burned what remained of the factory. Although the building had been fortified as part of French defensive positions in the par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
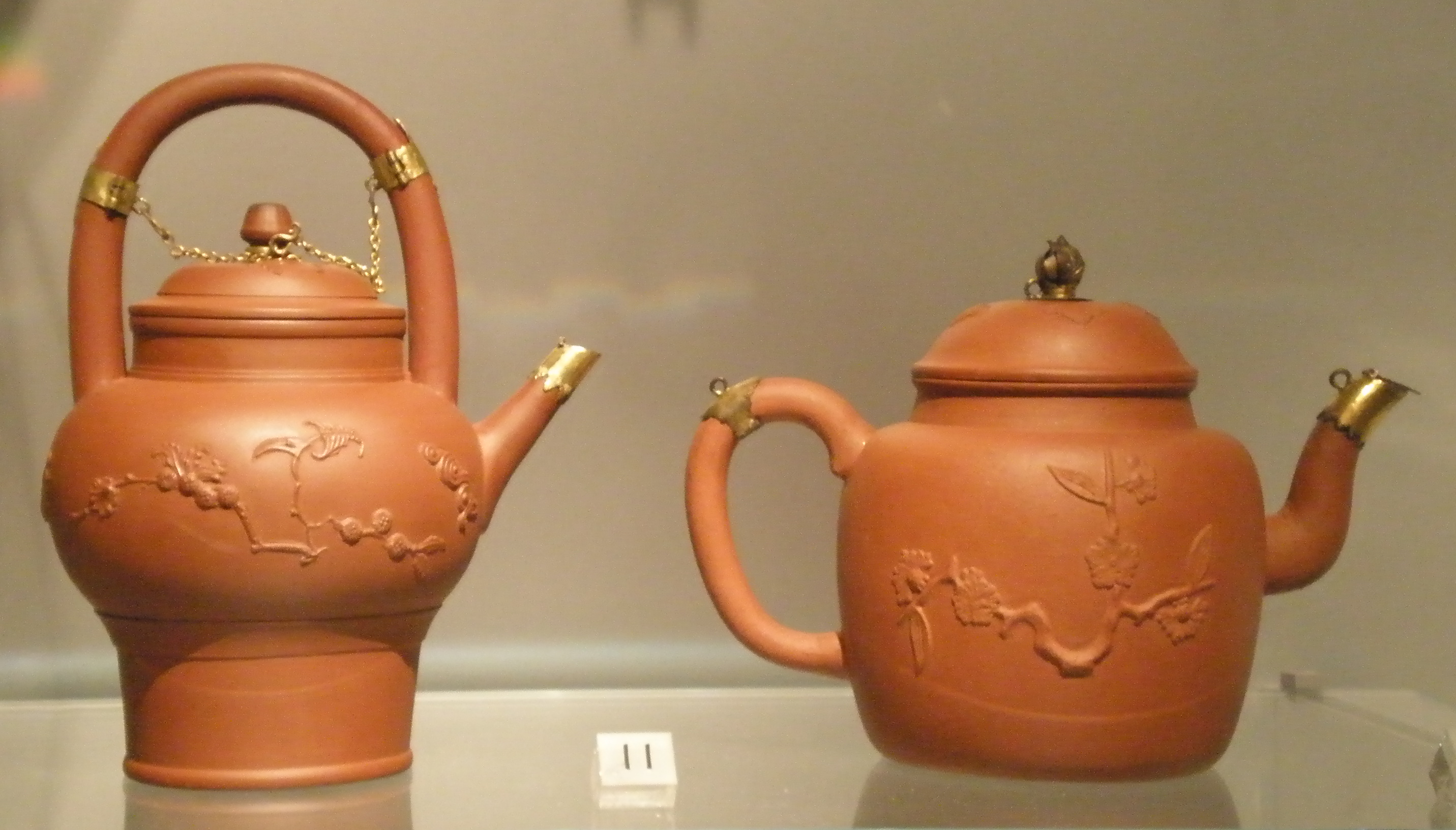
Sprigging (pottery)
Sprigging or sprigged decoration is a technique for decorating pottery with low relief shapes made separately from the main body and applied to it before firing. Usually thin press moulded shapes are applied to Pottery#Production stages, greenware or bisque (pottery), bisque. The resulting pottery is termed sprigged ware, and the added piece is a "sprig". The technique may also be described by terms such as "applied relief decoration", especially in non-European pottery. The alternative way to achieve similar effects without sprigging is to Molding (process), mould the whole body, which is also common. Pâte-sur-pâte is a very labour-intensive, and so expensive, method of producing similar, but more refined, effects in contrasting colors, invented in China and then in France in the mid-19th century. Technique The clay body for the sprig is pushed into the mould, the back scraped flat, then released on a damp cloth pad. The greenware is wetted lightly with a brush, and the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biscuit Porcelain
Biscuit porcelain, bisque porcelain or bisque is unglazed, white porcelain treated as a final product, with a matte appearance and texture to the touch. It has been widely used in European pottery, mainly for sculptural and decorative objects that are not tableware and so do not need a glaze for protection. The term "biscuit" refers to any type of fired but unglazed pottery in the course of manufacture, but only in porcelain is bisque a term for a final product. Unglazed earthenware as a final product is often called terracotta, and in stoneware equivalent unglazed wares (such as jasperware) are often called "dry-bodied". Many types of pottery, including most porcelain wares, have a glaze applied, either before a single firing, or at the biscuit stage, with a further firing. Small figurines and other decorative pieces have often been made in biscuit, as well as larger portrait busts and other sculptures; the appearance of biscuit is very similar to that of carved and smoothed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
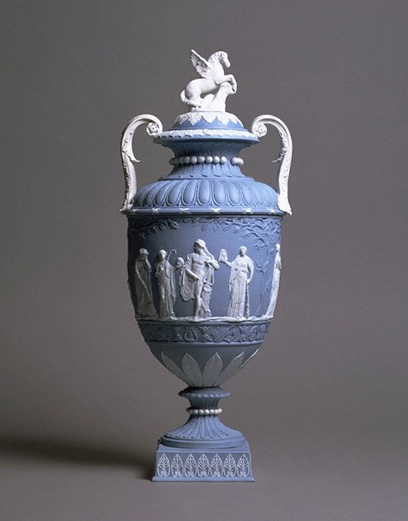
Jasperware
Jasperware, or jasper ware, is a type of pottery first developed by Josiah Wedgwood in the 1770s. Usually described as stoneware, it has an unglazed matte "biscuit" finish and is produced in a number of different colours, of which the most common and best known is a pale blue that has become known as Wedgwood Blue. Relief decorations in contrasting colours (typically in white but also in other colours) are characteristic of jasperware, giving a cameo effect. The reliefs are produced in moulds and applied to the ware as sprigs. After several years of experiments, Wedgwood began to sell jasperware in the late 1770s, at first as small objects, but from the 1780s adding large vases. It was extremely popular, and after a few years many other potters devised their own versions. Wedgwood continued to make it into the 21st century. The decoration was initially in the fashionable Neoclassical style, which was often used in the following centuries, but it could be made to suit oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedgwood
Wedgwood is an English fine china, porcelain and luxury accessories manufacturer that was founded on 1 May 1759 by the potter and entrepreneur Josiah Wedgwood and was first incorporated in 1895 as Josiah Wedgwood and Sons Ltd. It was rapidly successful and was soon one of the largest manufacturers of Staffordshire pottery, "a firm that has done more to spread the knowledge and enhance the reputation of British ceramic art than any other manufacturer", exporting across Europe as far as Russia, and to the Americas. It was especially successful at producing fine earthenware and stoneware that were accepted as equivalent in quality to porcelain (which Wedgwood only made later) but were considerably cheaper. Wedgwood is especially associated with the "dry-bodied" (unglazed) stoneware Jasperware in contrasting colours, and in particular that in "Wedgwood blue" and white, always much the most popular colours, though there are several others. Jasperware has been made continuously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casita Del Príncipe (El Escorial)
The Casita del Príncipe () is an eighteenth-century building located in San Lorenzo de El Escorial, Spain. It was designed by the neoclassical architect Juan de Villanueva for the private use of the heir to the Spanish throne Charles, Prince of Asturias, and his wife Maria Luisa. It was constructed in the 1770s and extended in the 1780s. The word ''casita'' is the diminutive of the Spanish word for "house". The building was designed without bedrooms, as its owners slept in the palace which had been built two centuries earlier for Philip II. Such buildings gave their royal occupants the opportunity to escape some of the formalities of court life. The Petit Trianon at Versailles offers a French example of the phenomenon. Setting The building is set in a formal garden. The garden is in turn set in a walled park. The garden, which is on several levels, is delineated by box hedges in 18th century style. It also features some exotic conifers, such as ''Sequoiadendron giganteum'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
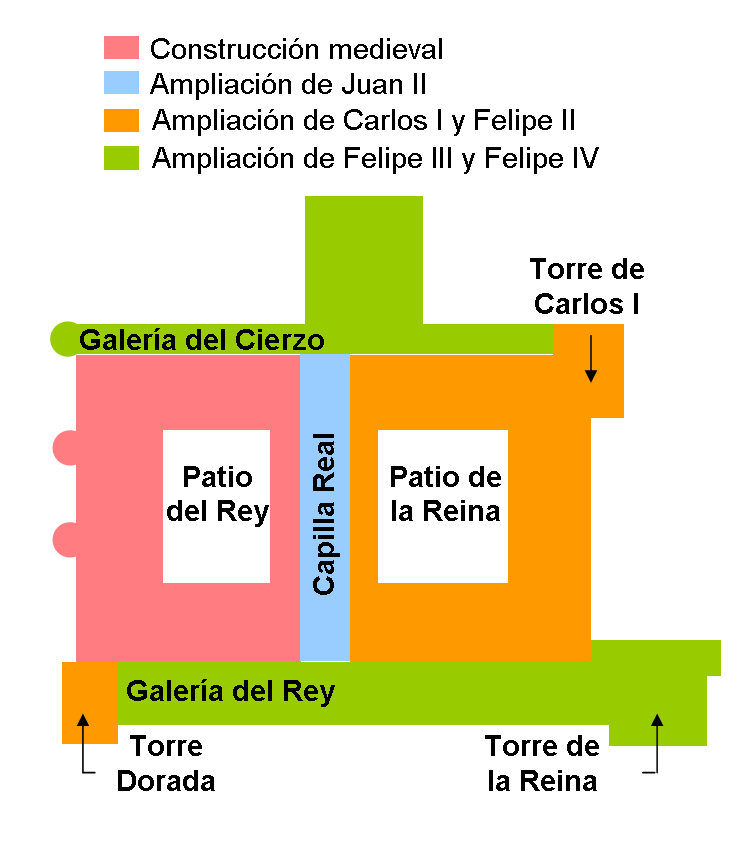
Palacio Real, Madrid
The Royal Palace of Madrid ( es, Palacio Real de Madrid) is the official residence of the Spanish royal family at the city of Madrid, although now used only for state ceremonies. The palace has of floor space and contains 3,418 rooms. It is the largest royal palace in Europe. The palace is now open to the public, except during state functions, although it is so large that only a selection of rooms are on the visitor route at any one time, the route being changed every few months. An admission fee of €13 is charged; however, at some times it is free. The palace is owned by the Spanish state and administered by the Patrimonio Nacional, a public agency of the Ministry of the Presidency. The palace is on Calle de Bailén ("Bailén Street") in the western part of downtown Madrid, east of the Manzanares River, and is accessible from the Ópera metro station. Felipe VI and the royal family do not reside in the palace, choosing instead the Palace of Zarzuela in El Pardo. The palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Aranjuez
The Royal Palace of Aranjuez ( es, Palacio Real de Aranjuez) is one of the official residences of the Spanish royal family. It is located in the town of Aranjuez (Madrid), Spain. Established in the 16th century as a royal hunting lodge, the palace was built by order of Philip II. Under his reign it became one of four seasonal seats of the court along Rascafría, El Escorial and the Royal Alcázar of Madrid. The royal estate comprises a set of landscaped and ornate gardens and woodlands that house an extensive botanical collection. Several international treaties were signed there and several members of the royal family died in the palace, including: Elisabeth of Valois in 1568, Barbara of Portugal in 1758, Elisabeth Farnese in 1766, Maria Antonia of Naples in 1806, Maria Isabel of Braganza in 1818 and Maria Josepha Amalia of Saxony in 1828. In 1931, during the Second Spanish Republic, the royal estate was declared an Artistic Historical Monument and opened to the public. Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Capodimonte
The Royal Palace of Capodimonte ( it, Reggia di Capodimonte) is a large palazzo in Naples, Italy. It was formerly the summer residence and hunting lodge of the Bourbon kings of the Two Sicilies, one of the two royal palaces in Naples. Today, it comprises the National Museum of Capodimonte and the Royal Forest ( it, Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte). The palace was constructed on its somewhat cooler hilltop location (''Capodimonte'' means "top of the hill") just outside the city, with urban Naples ultimately expanding around it. History In 1738, King Charles VII of Naples and Sicily (later Charles III, king of Spain) decided to build a hunting lodge on the Capodimonte hill. He then decided that he would instead build a grand palace (a Royal Palace, as in Italian ''Reggia'' means Royal), partly because his existing residence, the Palace of Portici, was too small to accommodate his court, and partly because he needed somewhere to house the fabulous Farnese art collection which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Portici
The Royal Palace of Portici (''Reggia di Portici'' or ''Palazzo Reale di Portici''; nap, Reggia ‘e Puortece) is a former royal palace in Portici, Southeast of Naples along the coast, in the region of Campania, Italy. Today it is the home of the ''Orto Botanico di Portici'', a botanical garden operated by the University of Naples Federico II. These gardens were once part of the large royal estate that included an English garden, a zoo and formal parterres. It is located just a few metres from the Roman ruins of Herculaneum and is home to the Accademia Ercolanese, the deposit for all found objects of archaeological site. This is in effect the Museum of Herculaneum, opened in 1758 by King Charles. History On 3 July 1735 at the age of 18, Infante Charles of Spain was crowned the King of Naples and Sicily. He had taken control of the two kingdoms by military force opposing the powerful Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor. In 1738, Charles and his consort Princess Maria Amalia of Saxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
