|
Reactive Carbonyl Species
Reactive carbonyl species (RCS) are molecules with highly reactive carbonyl groups, and often known for their damaging effects on proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. They are often generated as metabolic products. Important RCSs include 3-deoxyglucosone, glyoxal, and methylglyoxal. RCSs react with amines and thiol groups leading to advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs). AGE's are indicators of diabetes. Reactive aldehyde species (RASP), such as malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal, are a subset of RCS that are implicated in a variety of human diseases. See also * Reactive oxygen species * Reactive sulfur species * Reactive nitrogen species Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are a family of antimicrobial molecules derived from nitric oxide (•NO) and superoxide (O2•−) produced via the enzymatic activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 ( NOS2) and NADPH oxidase respectivel ... References Molecules Carbon compounds {{Biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyoxal
Glyoxal is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ... with the chemical formula OCHCHO. It is the smallest dialdehyde (a compound with two aldehyde groups). It is a crystalline solid, white at low temperatures and yellow near the melting point (15 °C). The liquid is yellow, and the vapor is green.O'Neil, M.J. (2001): ''The Merck Index'', 13th Edition, page 803. Pure glyoxal is not commonly encountered because glyoxal is usually handled as a 40% aqueous solution (density near 1.24 g/mL). It forms a series of hydrates, including oligomers. For many purposes, these hydrated oligomers behave equivalently to glyoxal. Glyoxal is produced industrially as a precursor to many products. Production Glyoxal was first prepared and named by the German-British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylglyoxal
Methylglyoxal (MGO) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CHO. It is a reduced derivative of pyruvic acid. It is a reactive compound that is implicated in the biology of diabetes. Methylglyoxal is produced industrially by degradation of carbohydrates using overexpressed methylglyoxal synthase. Chemical structure Gaseous methylglyoxal has two carbonyl groups, an aldehyde and a ketone. In the presence of water, it exists as hydrates and oligomers. The formation of these hydrates is indicative of the high reactivity of MGO, which is relevant to its biological behavior. Biochemistry Biosynthesis and biodegradation In organisms, methylglyoxal is formed as a side-product of several metabolic pathways. Methylglyoxal mainly arises as side products of glycolysis involving glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. It is also thought to arise via the degradation of acetone and threonine. Illustrative of the myriad pathways to MGO, aristolochic acid caused 12-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Glycation Endproduct
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are proteins or lipids that become glycated as a result of exposure to sugars. They are a bio-marker implicated in aging and the development, or worsening, of many degenerative diseases, such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, and Alzheimer's disease. Dietary sources Animal-derived foods that are high in fat and protein are generally AGE-rich and are prone to further AGE formation during cooking. However, only low molecular weight AGEs are absorbed through diet, and vegetarians have been found to have higher concentrations of overall AGEs compared to non-vegetarians. Therefore, it is unclear whether dietary AGEs contribute to disease and aging, or whether only endogenous AGEs (those produced in the body) matter. This does not free diet from potentially negatively influencing AGE, but potentially implies that dietary AGE may deserve less attention than other aspects of diet that lead to elevated blood sugar levels and form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Aldehyde Species
Reactive aldehyde species (RASP), also known as reactive aldehydes, refer to a class of electrophilic organic aldehyde molecules that are generally toxic or facilitate inflammation. RASP covalently react with amine groups (via Schiff base formation) and thiol groups (via Michael addition), particularly in proteins. Following threshold amounts of binding to the electrophile-responsive proteome, RASP modify protein function, as has been described with MAP kinase, protein kinase C, and other proteins that potentiate cytokine release and other aspects of inflammation. Binding of RASP to proteins can also lead to NF-kB activation, autoantibody formation, inflammasome activation, and activation of Scavenger Receptor A. RASP are formed via a variety of processes, including oxidation of alcohols, polyamine metabolism and lipid peroxidation. In addition to binding to proteins and other amine or thiol-containing molecules such as glutathione, RASP are metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malondialdehyde
Malondialdehyde (MDA) is the organic compound with the nominal formula CH2(CHO)2. A colorless liquid, malondialdehyde is a highly reactive compound that occurs as the enol. It occurs naturally and is a marker for oxidative stress. Structure and synthesis Malondialdehyde mainly exists as the enol:V. Nair, C. L. O'Neil, P. G. Wang "Malondialdehyde", ''Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis'', 2008, John Wiley & Sons, New York. Article Online Posting Date: March 14, 2008 :CH2(CHO)2 → HOC(H)=CH-CHO In organic solvents, the ''cis''-isomer is favored, whereas in water the ''trans''-isomer predominates. The equilibrium is rapid and is inconsequential for many purposes. In the laboratory it can be generated in situ by hydrolysis of its acetal 1,1,3,3-tetramethoxypropane, which is commercially available and shelf-stable, unlike malondialdehyde. Malondialdehyde is easily deprotonated to give the sodium salt of the enolate (m.p. 245 °C). Biosynthesis and reactivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
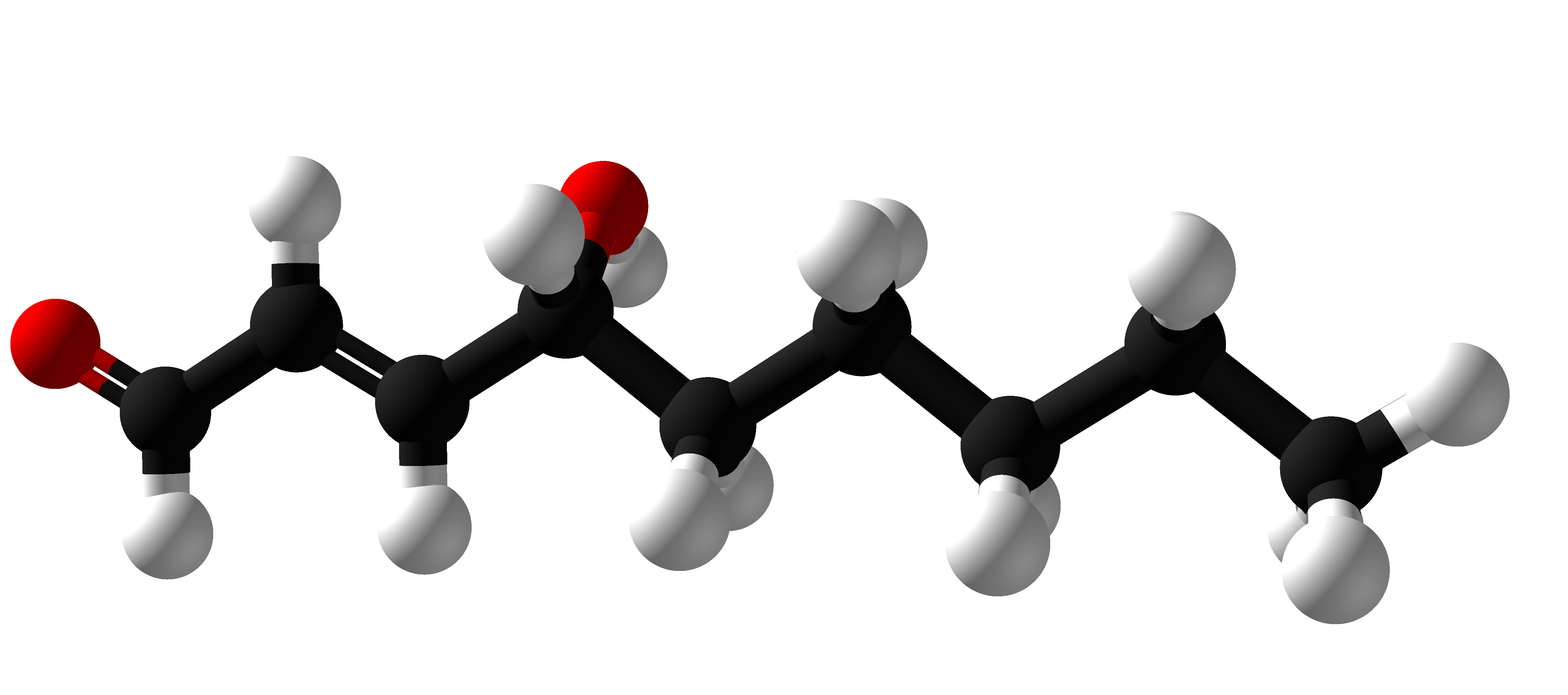
4-Hydroxynonenal
4-Hydroxynonenal, or 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal or 4-HNE or HNE, (), is an α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal that is produced by lipid peroxidation in cells. 4-HNE is the primary α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal formed in this process. It is a colorless oil. It is found throughout animal tissues, and in higher quantities during oxidative stress due to the increase in the lipid peroxidation chain reaction, due to the increase in stress events. 4-HNE has been hypothesized to play a key role in cell signal transduction, in a variety of pathways from cell cycle events to cellular adhesion. Early identification and characterization of 4-hydroxynonenal was reported by Esterbauer, et al., who also obtained the same compound synthetically. The topic has since been often reviewed. Synthesis 4-Hydroxynonenal is generated in the oxidation of lipids containing polyunsaturated Omega-6 fatty acid, omega-6 acyl groups, such as arachidonic or Linoleic acid, linoleic groups, and of the corresponding fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection and toleran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Sulfur Species
Reactive sulfur species (RSS) are a family of sulfur-based chemical compounds that can oxidize and inhibit thiol-proteins and enzymes. They are often formed by the oxidation of thiols and disulfides into higher oxidation states. Examples of RSS include persulfides, polysulfides and thiosulfate. See also * Reactive oxygen species * Reactive nitrogen species Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are a family of antimicrobial molecules derived from nitric oxide (•NO) and superoxide (O2•−) produced via the enzymatic activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 ( NOS2) and NADPH oxidase respectivel ... * Reactive carbonyl species References {{Reflist Molecules Sulfur compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Nitrogen Species
Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are a family of antimicrobial molecules derived from nitric oxide (•NO) and superoxide (O2•−) produced via the enzymatic activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 ( NOS2) and NADPH oxidase respectively. NOS2 is expressed primarily in macrophages after induction by cytokines and microbial products, notably interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Reactive nitrogen species act together with reactive oxygen species (ROS) to damage cells, causing nitrosative stress. Therefore, these two species are often collectively referred to as ROS/RNS. Reactive nitrogen species are also continuously produced in plants as by-products of aerobic metabolism or in response to stress. Types RNS are produced in animals starting with the reaction of nitric oxide (•NO) with superoxide (O2•−) to form peroxynitrite (ONOO−): * •NO (nitric oxide) + O2•− (superoxide) → ONOO− (peroxynitrite) Superoxide anion (O2� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |