|
Rauisuchid
Rauisuchidae is a group of large (up to or more) predatory Triassic archosaurs. There is some disagreement over which genera should be included in Rauisuchidae and which should be in the related Prestosuchidae and Poposauridae, and indeed whether these should even be thought of as separate valid Family (biology), families. Rauisuchids occurred throughout much of the Triassic, and may have first occurred in the Early Triassic if some archosaurian taxa such as ''Scythosuchus'' and ''Tsylmosuchus'' are considered to be within the family. An early cladistic analysis of crocodylotarsan (pseudosuchian) archosaurs included ''Lotosaurus'', ''Fasolasuchus'', ''Rauisuchus'', and "the Kupferzell rauisuchid" (later called ''Batrachotomus'') within Rauisuchidae.Parrish JM. 1993. Phylogeny of the Crocodylotarsi, with reference to archosaurian and crurotarsan monophyly. ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' 13: 287-308. However, a later study found that ''Batrachotomus'' was a more Basal (phyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivaron
''Vivaron'' is a genus of rauisuchid known from the Late Triassic (middle Norian) Chinle Formation in New Mexico. It is the second rauisuchid known from the southwestern United States, and it highlights the wide biogeographic range similar rauisuchid taxa occupied during the Late Triassic across Pangaea, despite the varied faunal assemblages at different latitudes. Discovery ''Vivaron'' was named in 2016 from material collected at the Hayden Quarry at Ghost Ranch, New Mexico in 2009. The locality is part of the Chinle Formation in the Petrified Forest Member, and dates to the middle Norian ~212 Ma, possibly representing one of the youngest known rauisuchids. Prior to its description, all Late Triassic rauisuchid material from Texas, Arizona and New Mexico had been referred to ''Postosuchus kirkpatricki''. However, the rauisuchid remains from Hayden Quarry could be clearly distinguished from ''Postosuchus'', and was erected as a new taxon ''Vivaron haydeni''. The generic epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
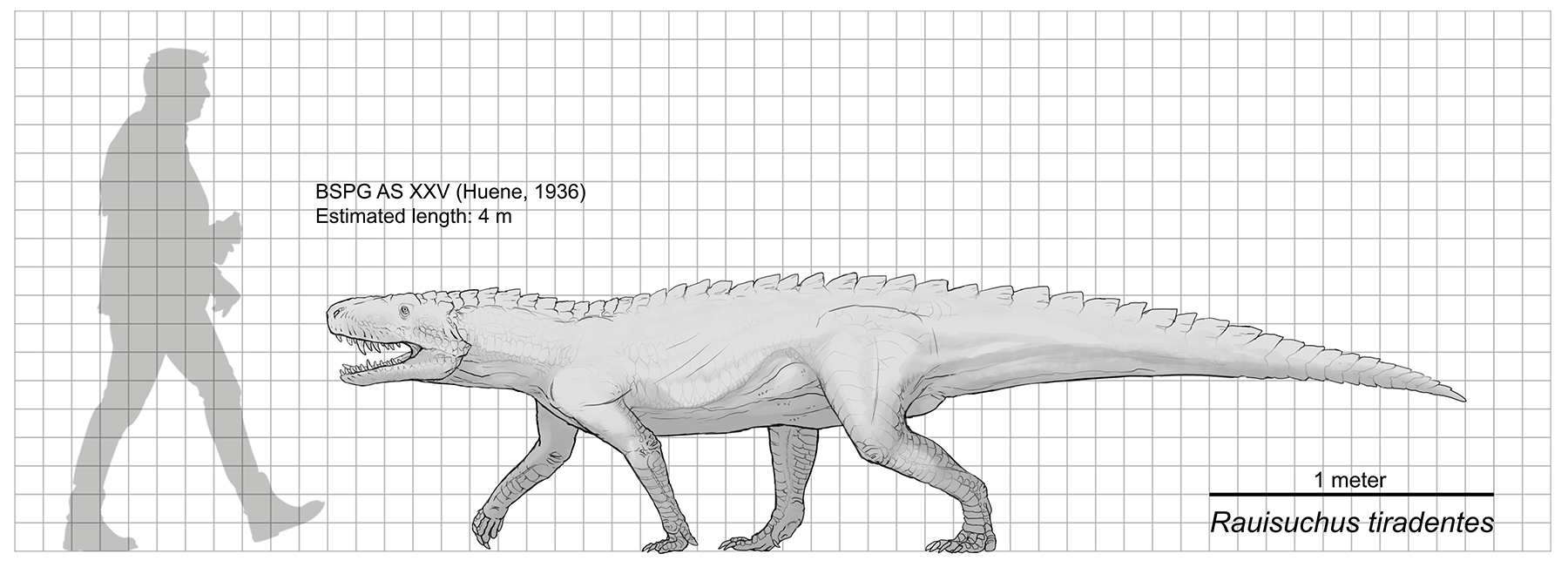
Rauisuchus
''Rauisuchus'' (meaning "Wilhelm Rau's crocodile") is a genus of extinct archosaurs which lived in what is now the Geopark of Paleorrota (Santa María Formation), Brazil, during the Late Triassic period (235–228 million years ago). It contains one species, ''R. tiradentes''.''Rauisuchus'' at Fossilworks.orgF. v. Huene. (1942) ''Die fossilen Reptilien des südamerikanischen Gondwanalandes. Ergebnisse der Sauriergrabung in Südbrasilien 1928/29.'' München: C.H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung Discovery and naming In 1928 or 1929, near the road from Sa ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Prior to 2011, the clade Pseudosuchia was often called Crurotarsi in reference to the crurotarsal ankle found in almost all members of the group, which traditionally included phytosaurs, ornithosuchids, and suchians. However, a major 2011 study of Triassic archosaur relations proposed that phytosaurs were not closely related to other traditional "crurotarsans", at least compared to "bird-line archosaurs" (Avemetatarsalians) such as pterosaurs and dinosaurs. As a result, the possession of a crurotarsal ankle was considered a plesiomorphic ("primitive") feature retained by pseudosuchians. Crurotarsi now refers to a broader group of reptiles including Pseudosuchia, Phytosauria, and Avemetatarsalia. Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestosuchidae
Prestosuchidae (in its widest usage) is a polyphyletic grouping of carnivorous archosaurs that lived during the Triassic. They were large active terrestrial apex predators, ranging from around in length. They succeeded the Erythrosuchidae as the largest archosaurs of their time. While resembling erythrosuchids in size and some features of the skull and skeleton, they were more advanced in their erect posture and crocodile-like ankle, indicating more efficient gait. "Prestosuchids" flourished throughout the whole of the middle, and the early part of the late Triassic, and fossils are so far known from Europe, India, Africa (Tanzania), Argentina, and Paleorrota in Brazil. However, for a long time experts disagree regarding the phylogenetic relationships of the group, what genera should be included, and whether indeed the "Prestosuchidae" constitute a distinct family. In 2011, Prestosuchidae in its broadest definition was determined to be a poorly-diagnosed and obsolete polyphyleti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batrachotomus
''Batrachotomus'' is a genus of prehistoric archosaur. Fossils of this animal have been found in southern Germany and dated from the Ladinian stage of the Middle Triassic period, around 242 to 237 million years ago. ''Batrachotomus'' was described by palaeontologist David J. Gower 22 years after its discovery. The locality where ''Batrachotomus'' lived was a swampy region and the name comes from the Greek ''batrachos/βάτραχος'' (frog) and ''tome/τομή'' (cutting, slicing), which refers to its preying on the large amphibian ''Mastodonsaurus''.Gower (1999), p. 6. In contrast with sprawling reptiles, like crocodiles, this large carnivore was very agile with locomotor superiority due to its erect stance. A remarkable feature seen on its back was a row of paired, flattened bony plates. ''Batrachotomus'' was possibly an early relative of ''Postosuchus'',Gower (1999), p. 1. which lived during the dawn of the dinosaurs. Description ''Batrachotomus'' was a heavily built, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postosuchus
''Postosuchus'', meaning "Crocodile from Post", is an extinct genus of rauisuchid reptiles comprising two species, ''P. kirkpatricki'' and ''P. alisonae'', that lived in what is now North America during the Late Triassic. ''Postosuchus'' is a member of the clade Pseudosuchia, the lineage of archosaurs that includes modern crocodilians (the other main group of archosaurs is Avemetatarsalia, the lineage that includes non-avian dinosaurs and their descendants, birds). Its name refers to Post Quarry, a place in Texas where many fossils of the type species, ''P. kirkpatricki'', were found. It was one of the apex predators of its area during the Triassic, larger than the small dinosaur predators of its time (such as ''Coelophysis''). It was a hunter which probably preyed on large bulky herbivores like dicynodonts and many other creatures smaller than itself (such as early dinosaurs). The skeleton of ''Postosuchus'' is large and robust with a deep skull and a long tail. It was a large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythosuchus
''Scythosuchus'' is an extinct genus of rauisuchid. Remains have been found from Olenekian-age Lower Triassic beds in Russia, hence the name meaning 'Scythian crocodile'. The type and only species is ''S. basileus'', described in 1999. ''Scythosuchus'' was between 2 and 3 metres long, and relatively heavily built. It is known from a partial skull, much of the spine, a fragment of the humerus and most of the hind leg and foot. It may have been the same animal as ''Tsylmosuchus''. Features Skull The skull material known is fragmentary, with a few parts of the cranium, the maxilla and some of the rostrum, and several examples of teeth. The maxilla is long, as is the preorbital fenestra just above it, and has a break indicating that there was probably a large medial process. The whole snout was slightly elongated but quite narrow. The blade-like teeth are laterally compressed and serrated, with a slight backwards curve, and would have been excellent for slicing through flesh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procerosuchus
''Procerosuchus'' is an extinct genus of loricatan archosaur. Fossils have been collected from the Late Triassic Santa Maria Formation in Geopark of Paleorrota, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, which is Carnian in age. The genus was first described by the German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1942. Classification Initially, ''Procerosuchus'' was regarded as a stagonolepidid along with the genera '' Rauisuchus'' and ''Prestosuchus''. Later, it was reassigned by Huene to the family Rauisuchidae. Alfred Sherwood Romer first considered ''Procerosuchus'' to be a possible ornithosuchid, but later assigned it to the family Prestosuchidae, which he constructed in 1966. In 1972, Romer assigned ''Procerosuchus'' as a possible member of the family Proterochampsidae. Krebs (1976) considered it to be a rauisuchid, as did Chatterjee (1985) and Carroll (1988). ''Procerosuchus'' has been suggested to be member of the subfamily Rauisuchinae and the tribe Rauisuchini. However, the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasolasuchus
''Fasolasuchus'' is an extinct genus of loricatan. Fossils have been found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina that date back to the Norian stage of the Late Triassic, making it one of the last rauisuchians to have existed before the order became extinct at the end of the Triassic. Description It is quite possibly the largest known member of Rauisuchia, with an estimated length of to , even bigger than the prestosuchid ''Saurosuchus'' at in length. This would make ''Fasolasuchus'' the largest terrestrial predator to have ever existed save for large theropods. Like ''Saurosuchus'', it had only a single row of caudal osteoderms, unusual among rauisuchians. It also had a hyposphene-hypantrum articulation that gave the vertebral column extra rigidity. This feature is also seen in several other rauisuchians such as ''Postosuchus'' as well as saurischian dinosaurs. Phylogeny Cladogram after the analysis of Nesbitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenhosuchus
''Fenhosuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform. The holotype, IVPP V 2697, and referred materials have been found in the Hsishihwa locality at Wuhsiang, China, from the Upper Ermaying Formation (also Ehrmaying). The locality dates back to the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic. The genus was named after the Fen River in Shanxi Province from which specimens were found. It may prove to be a chimera being composed of material from several different animals. Some material were believed to represent a rauisuchid. The calcaneum of ''Fenhosuchus'' seems to belong to an erythrosuchid or other basal archosauriform.Gower, D. J. (1996). The tarsus of erythrosuchid archosaurs, and implications for early diapsid phylogeny. ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 116:347–375. Much of the material of the tarsal bones seem to be similar to those of the genus '' Shansisuchus''. According to Nesbitt (2009) the assessment of Gower (2000) was correct, the holotype is a mix of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postosuchus Kirkpatricki
''Postosuchus'', meaning "Crocodile from Post, Texas, Post", is an extinct genus of rauisuchidae, rauisuchid reptiles comprising two species, ''P. kirkpatricki'' and ''P. alisonae'', that lived in what is now North America during the Late Triassic. ''Postosuchus'' is a member of the clade Pseudosuchia, the lineage of archosaurs that includes modern crocodilians (the other main group of archosaurs is Avemetatarsalia, the lineage that includes non-avian dinosaurs and their descendants, Aves, birds). Its name refers to Post Quarry, a place in Texas where many fossils of the type species, ''P. kirkpatricki'', were found. It was one of the apex predators of its area during the Triassic, larger than the small dinosaur predators of its time (such as ''Coelophysis''). It was a hunter which probably preyed on large bulky herbivores like dicynodonts and many other creatures smaller than itself (such as early dinosaurs). The skeleton of ''Postosuchus'' is large and robust with a deep skull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jushatyria
''Jushatyria'' is an extinct genus of archosaur. Fossils have been found in the Koltaevo III Locality, district of Kumertau near the Ural Mountains in European Russia from the Bukobay Gorizont. The locality dates back to the Ladinian stage of the Middle Triassic. Additional material has been described from a locality on the banks of the Berdyanka River that was previously assigned to a rauisuchid-like archosaur. However, this material differed from the original specimens because it lacked slit-like antorbital openings accompanying the antorbital fossa. Nesbitt (2009) and Gower and Sennikov (2000) suggested that all material currently referred to ''Jushatyria'' most likely does not represent a single taxon.Gower, D. J. and Sennikov, A. G. (2000). Early Archosaurs from Russia ''In:'' Benton, M. J., Kurochkin, E. N., Shishkin, M. A. and Unwin, D. M., eds., ''The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia''. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press; pp. 140–159. Thus, ''Jushatyria'' is kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |