|
Rattus Rattus
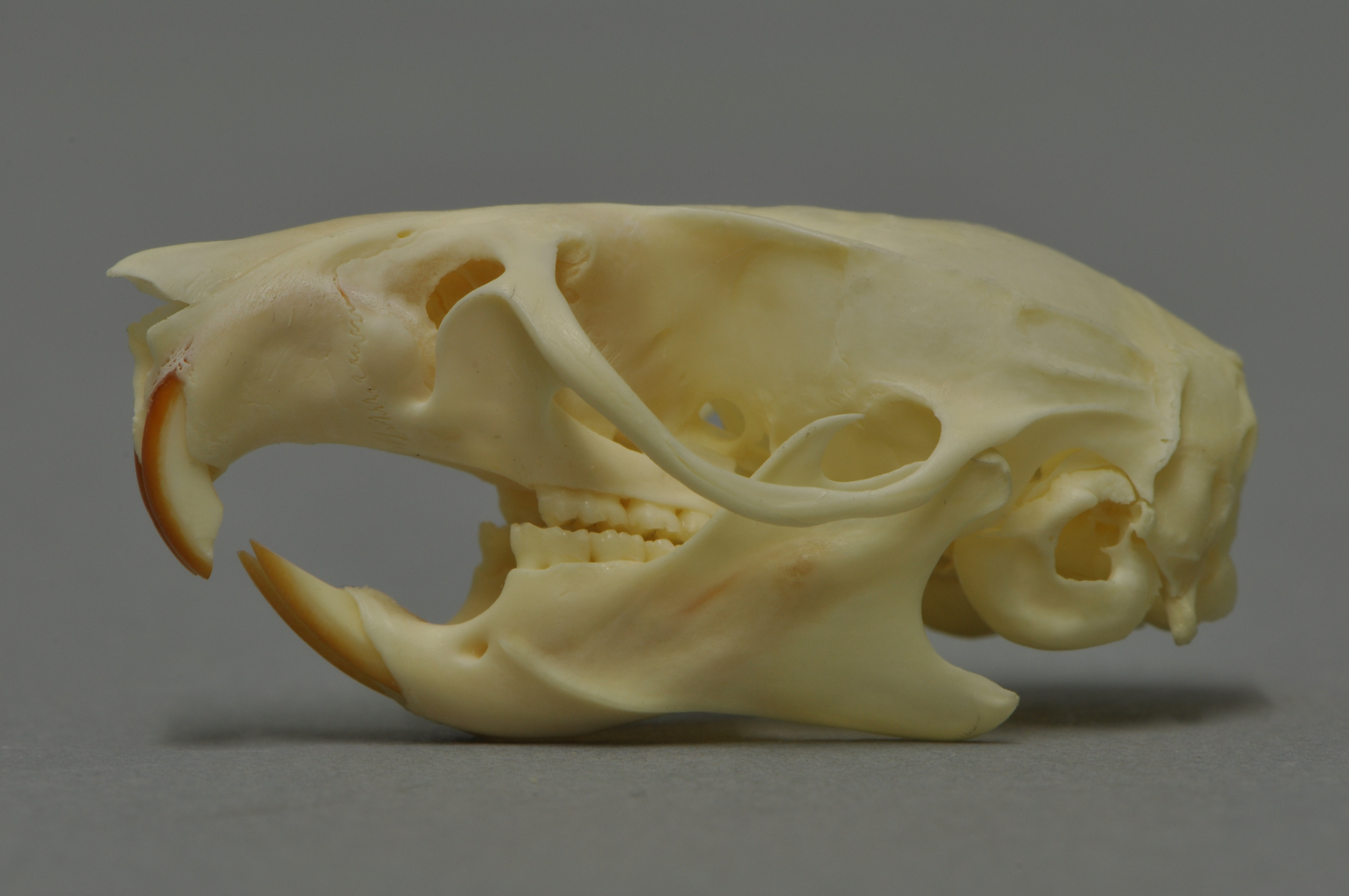
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus '' Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rat Skeleton
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government officials in much of Europe. It became the color worn by English romantic poets, businessme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague Of Justinian
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (541–549 AD) was the first recorded major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. The disease afflicted the entire Mediterranean Basin, Europe, and the Near East, severely affecting the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire and especially Constantinople. The plague is named for the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) who according to his court historian Procopius contracted the disease and recovered in 542, at the height of the epidemic which killed about a fifth of the population in the imperial capital. The contagion arrived in Roman Egypt in 541, spread around the Mediterranean Sea until 544, and persisted in Northern Europe and the Arabian Peninsula, until 549. In 2013, researchers confirmed earlier speculation that the cause of the plague of Justinian was ''Yersinia pestis'', the same bacterium responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yersinia Pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly '' Pasteurella pestis'') is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores that is related to both '' Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' and '' Yersinia enterocolitica''. It is a facultative anaerobic organism that can infect humans via the Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''). It causes the disease plague, which caused the first plague pandemic and the Black Death, the deadliest pandemic in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic. ''Yersinia pestis'' is a parasite of its host, the rat flea, which is also a parasite of rats, hence ''Y. pestis'' is a hyperparasite. ''Y. pestis'' was discovered in 1894 by Alexandre Yersin, a Swiss/French physician and bacteriologist from the Pasteur Institute, during an epidemic of the plague in Hong Kong. Yersin was a member of the Pasteur school of thought. Kitasato Shibasaburō, a Japanese bacteriologist who practised K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen to another living organism; agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as parasites or microbes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected a mosquito. Arthropods Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects feed on blood, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways. The '' Anopheles'' mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses (arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds on its host's blood. The parasites the mosquito carries are usually located in its saliv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaign History Of The Roman Military
From its origin as a city-state on the peninsula of Italy in the 8th century BC, to its rise as an empire covering much of Southern Europe, Western Europe, Near East and North Africa to its fall in the 5th century AD, the political history of Ancient Rome was closely entwined with its military history. The core of the campaign history of the Roman military is an aggregate of different accounts of the Roman military's land battles, from its initial defense against and subsequent conquest of the city's hilltop neighbors on the Italian peninsula, to the ultimate struggle of the Western Roman Empire for its existence against invading Huns, Vandals and Germanic tribes. These accounts were written by various authors throughout and after the history of the Empire. Following the First Punic War, naval battles were less significant than land battles to the military history of Rome due to its encompassment of lands of the periphery and its unchallenged dominance of the Mediterranean Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia (continent), Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of atolls of Maldives, 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is completely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the only parts that are south of the Equator. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postglacial
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria (region), Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Republic of Venice, Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Period
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror. William's claim to the English throne derived from his familial relationship with the childless Anglo-Saxon king Edward the Confessor, who may have encouraged William's hopes for the throne. Edward died in January 1066 and was succeeded by his brother-in-law Harold Godwinson. The Norwegian king Harald Hardrada invaded northern England in September 1066 and was victorious at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September, but Godwinson's army defeated and killed Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge on 25 September. Three days later on 28 September, William's invasion force of thousands of men and hundreds of ships landed at Pevensey in Sussex in southern England. Harold marched south to oppose him, leaving a significant portion of his a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Rat
The brown rat (''Rattus norvegicus''), also known as the common rat, street rat, sewer rat, wharf rat, Hanover rat, Norway rat, Norwegian rat and Parisian rat, is a widespread species of common rat. One of the largest muroids, it is a brown or grey rodent with a head and body length of up to long, and a tail slightly shorter than that. It weighs between . Thought to have originated in northern China and neighbouring areas, this rodent has now spread to all continents except Antarctica, and is the dominant rat in Europe and much of North America. With rare exceptions, the brown rat lives wherever humans live, particularly in urban areas. Selective breeding of the brown rat has produced the fancy rat (rats kept as pets), as well as the laboratory rat (rats used as model organisms in biological research). Both fancy rats and laboratory rats are of the domesticated subspecies ''Rattus norvegicus domestica''. Studies of wild rats in New York City have shown that populations liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 70,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing" division. Routledge is headquartered in the main T&F office in Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxfordshir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)
