|
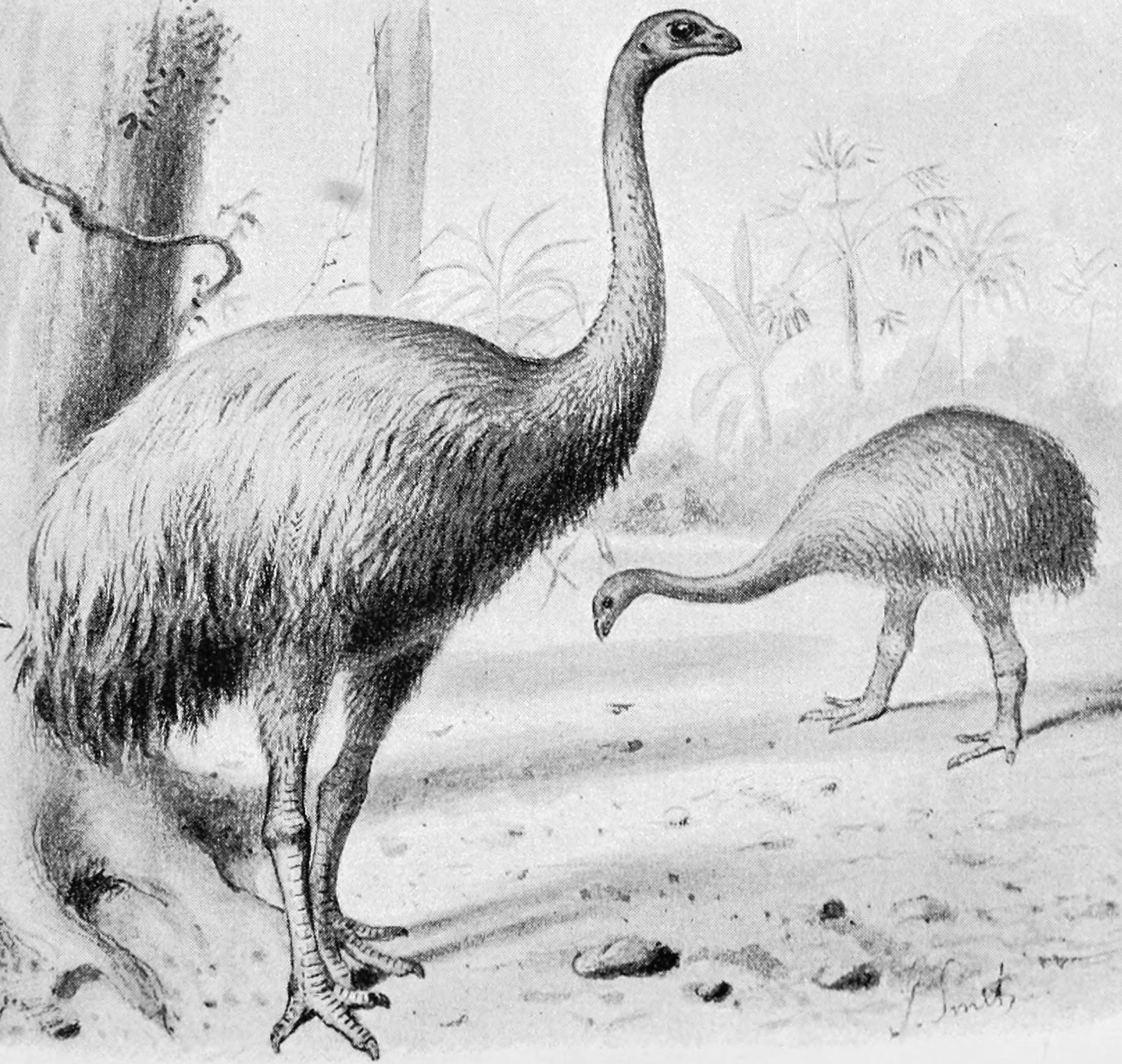
Ratite
Ratites () are a polyphyletic group consisting of all birds within the infraclass Palaeognathae that lack keels and cannot fly. They are mostly large, long-necked, and long-legged, the exception being the kiwi, which is also the only nocturnal extant ratite. The understanding of relationships within the paleognath clade has been in flux. Previously, all the flightless members had been assigned to the order Struthioniformes, which is more recently regarded as containing only the ostrich. The modern bird superorder Palaeognathae consists of ratites and the flighted Neotropic tinamous (compare to Neognathae). Unlike other flightless birds, the ratites have no keel on their sternum—hence the name, from the Latin ('raft', a vessel which has no keel—in contradistinction to extant flighted birds with a keel). Without this to anchor their wing muscles, they could not have flown even if they had developed suitable wings. Ratites are a polyphyletic group; tinamous fall within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeognathae
Palaeognathae (; ) is an infraclass of birds, called paleognaths or palaeognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant taxon, extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant order (biology), orders consisting of four flightless bird, flightless lineages (plus two that are extinct), termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of Kiwi (bird), kiwis (''Apteryx''), three of cassowary, cassowaries (''Casuarius''), one of emus (''Dromaius'') (another became extinct in historic times), two of Rhea (bird), rheas (''Rhea'') and two of ostriches (''Struthio'').Clements, J. C. ''et al''. (2010) Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite radiation, meaning flightlessness arose indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flightless Bird
Flightless birds are birds that cannot Bird flight, fly, as they have, through evolution, lost the ability to. There are over 60 extant species, including the well-known ratites (ostriches, emus, cassowary, cassowaries, Rhea (bird), rheas, and Kiwi (bird), kiwis) and penguins. The smallest flightless bird is the Inaccessible Island rail (length 12.5 cm, weight 34.7 g). The largest (both heaviest and tallest) flightless bird, which is also the largest living bird in general, is the common ostrich (2.7 m, 156 kg). Many domesticated birds, such as the domestic chicken and domestic duck, have lost the ability to fly for extended periods, although their ancestral species, the red junglefowl and mallard, respectively, are capable of extended flight. A few particularly bred birds, such as the Broad Breasted White turkey, have become totally flightless as a result of selective breeding; the birds were bred to grow massive breast meat that weighs too much for the bird's wings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinamiformes
Tinamous () are members of the order Tinamiformes (), and family Tinamidae (), divided into two distinct subfamily, subfamilies, containing 46 species found in Mexico, Central America, and South America. The word "tinamou" comes from the Carib language, Galibi term for these birds, ''tinamu''. Tinamous are the only living group of Palaeognathae, palaeognaths able to fly, and were traditionally regarded as the sister group of the flightless ratites, but recent work places them well within the ratite radiation as most closely related to the extinct moa of New Zealand, implying flightlessness emerged among ratites multiple times. Tinamous first appear in the fossil record in the Miocene epoch. They are generally sedentary, ground-dwelling and, though not flightless, when possible avoid flight in favour of hiding or running away from danger. They are found in a variety of habitats, ranging from semi-arid climate, semi-arid alpine climate, alpine grasslands to tropical rainforests. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apterygiformes
Kiwi are flightless birds endemic to New Zealand of the order Apterygiformes. The five extant species fall into the family Apterygidae and genus ''Apteryx''. Approximately the size of a domestic chicken, kiwi are the smallest ratites (which also include ostriches, emus, rheas, cassowaries and the extinct elephant birds and moa). DNA sequence comparisons have yielded the conclusion that kiwi are much more closely related to the extinct Malagasy elephant birds than to the moa with which they shared New Zealand. There are five recognised species, four of which are currently listed as vulnerable, and one of which is near threatened. All species have been negatively affected by historic deforestation, but their remaining habitat is well protected in large forest reserves and national parks. At present, the greatest threat to their survival is predation by invasive mammalian predators. The vestigial wings are so small as to be invisible under their bristly, hair-like, two-bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casuariiformes
The Casuariiformes is an order of large flightless birds that has four surviving members: the three species of cassowary, and the only remaining species of emu. They are divided into either a single family, Casuariidae, or occasionally two, with the emu splitting off into its own family, Dromaiidae. The IOC World Bird List and Cornell Lab of Ornithology's Birds of the World both do not recognize Dromaiidae, placing the emu in the family Casuariidae. All four living members are native to Australia-New Guinea,Clements, J (2007) but some possible extinct taxa occurred in other landmasses. Systematics and evolution The emus form a distinct branch, characterized by legs adapted for running. The total number of cassowary species described, based on minor differences in casque shape and color variations, formerly reached nine. Now, however, only three species are recognized, and most authorities only acknowledge few subspecies or none at all. The fossil record of casuariforms is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Rhea
The greater rhea (''Rhea americana'') is a species of flightless bird native to eastern South America. Other names for the greater rhea include the grey, common, or American rhea; ema (Portuguese (language), Portuguese); or ñandú (Guaraní language, Guaraní and Spanish language, Spanish). One of two species in the genus ''Rhea (bird), Rhea'', in the Family (biology), family Rheidae, it inhabits a variety of open areas, such as grasslands, savanna or grassy wetlands. Weighing , the greater rhea is the largest native bird in the Americas. In the wild, the greater rhea has a life expectancy of 10.5 years. It is also notable for its reproductive habits, and for the fact that a population has established itself in Northern Germany in recent years. The species is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN. Taxonomy The greater rhea was Species description, formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of his ''Syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
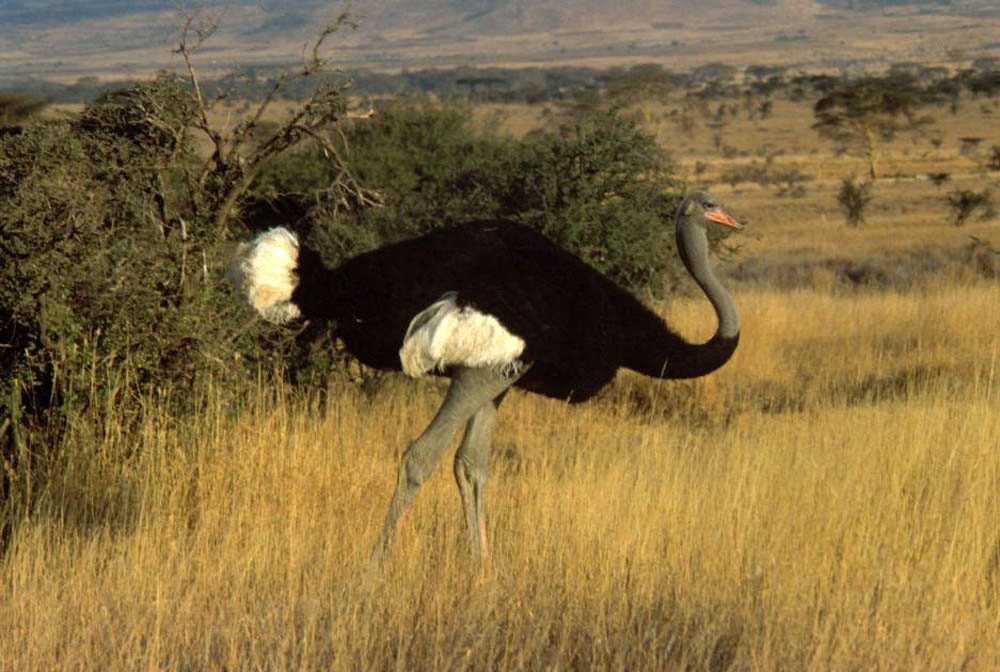
Ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds. Two living species are recognised, the common ostrich, native to large parts of sub-Saharan Africa, and the Somali ostrich, native to the Horn of Africa. They are the heaviest and largest living birds, with adult common ostriches weighing anywhere between 63.5 and 145 kilograms and laying the largest eggs of any living land animal.Del Hoyo, Josep, et al. Handbook of the birds of the world. Vol. 1. No. 8. Barcelona: Lynx edicions, 1992. With the ability to run at 70 km/h (43.5 mph), they are the fastest birds on land. They are farmed worldwide, with significant industries in the Philippines and in Namibia. South Africa produces about 70% of global ostrich products, with the industry largely centered around the town of Oudtshoorn. Ostrich leather is a lucrative commodity, and the large feathers are used as plumes for the decoration of ceremonial headgear. Ostrich eggs and meat have been used by humans for millennia. Ostrich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheiformes
Rheiformes is an order that contains the family Rheidae (rheas). It is in the infraclass Paleognathae, which contains all ratites. Extant members are found in South America. While the IOC World Bird List and the Clements Checklist categorise Rheiformes as its own order, the BirdLife Data Zone includes rheas, along with ostriches, tinamous, cassowaries, emu, and kiwis, in the order Struthioniformes. Of the two extant species of rheas recognized by the IUCN Red List, , '' Rhea americana'' is listed as near threatened, while '' Rhea pennata'' is listed as least concern. From 2014 to 2022, the IUCN The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ... recognised ''Rhea tarapacensis'' as a separate species, and listed it as near threatened in its last assessment in 2020; in 2022, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Cassowary
The southern cassowary (''Casuarius casuarius''), also known as double-wattled cassowary, Australian cassowary, or two-wattled cassowary, is a large Flightless bird, flightless black bird, found in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and northeastern Australia. It is one of the three living species of cassowary, alongside the dwarf cassowary and the northern cassowary. It is a ratite and therefore related to the emu, ostrich, Rhea (bird), rhea and Kiwi (bird), kiwi. The Australian population is listed as Endangered species, Endangered under federal and Queensland state legislation. Taxonomy Presently, most authorities consider the southern cassowary monotypic, but several subspecies have been described. It has proven very difficult to confirm the validity of these due to individual variations, age-related variations, the relatively few available Zoological specimen, specimens (and the bright skin of the head and neck – the basis upon which several subspecies have been described � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel (bird Anatomy)
A ''keel'' or ''carina'' (: carinae) in bird anatomy is an extension of the sternum (breastbone) which runs axially along the midline of the sternum and extends outward, perpendicular to the plane of the ribs. The keel provides an anchor to which a bird's wing muscles attach, thereby providing adequate leverage for flight. Not all birds have keels; in particular, some flightless birds lack a keel structure. Some flightless birds have a keel, such as the penguin; but in the penguin's case, its wings are too small for its body, so flight would require flapping its wings too fast to be practical. Historically, the presence or absence of a pronounced keel structure was used as a broad classification of birds into two orders: Carinatae (from ''carina'', "keel"), having a pronounced keel; and ratites (from ''ratis'', "raft"referring to the flatness of the sternum), having a subtle keel structure or lacking one entirely. However, this classification has become disused as evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenraad Jacob Temminck
Coenraad Jacob Temminck (; 31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch people, Dutch patrician, Zoology, zoologist and museum director. Biography Coenraad Jacob Temminck was born on 31 March 1778 in Amsterdam in the Dutch Republic. From his father, Jacob Temminck, who was treasurer of the Dutch East India Company with links to numerous travellers and collectors, he inherited a large collection of bird specimens. His father was a good friend of Francois Levaillant who also guided Coenraad. Temminck's ''Manuel d'ornithologie, ou Tableau systématique des oiseaux qui se trouvent en Europe'' (1815) was the standard work on European birds for many years. He was also the author of ''Histoire naturelle générale des Pigeons et des Gallinacées'' (1813–1817), illustrated by Pauline Rifer de Courcelles, Pauline Knip. He wrote ''Nouveau Recueil de Planches coloriées d'Oiseaux'' (1820–1839), and contributed to the mammalian sections of Philipp Franz von Siebold's ''Fauna jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |