|
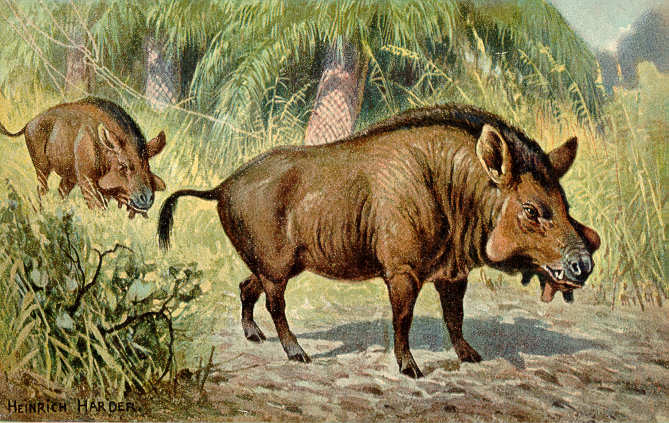
Raoellidae
The Raoellidae, previously grouped within Helohyidae, are an extinct family of semiaquatic digitigrade artiodactyls in the clade Whippomorpha. Fossils of raoellids are found in Eocene strata of South and Southeast Asia. An exceptionally complete skeleton of ''Indohyus'' from Kashmir suggests that raoellids are the " missing link" sister group to whales (Cetacea). All other Artiodactyla are relatives of these two groups. δO18 values and osteosclerotic bones indicate that the raccoon-like ''Indohyus'' was habitually aquatic. However, it is still unclear if ''Indohyus'' primarily fed on land or in water. It is hypothesized that Cetaceans evolved from ancestors similar to ''Indohyus'' and later fully adapted to aquatic life. Taxonomy *'' Raoella'' **''Raoella dograi'' *'' Haqueina'' **''Haqueina haquei'' *''Indohyus ''Indohyus'' is an extinct genus of digitigrade artiodactyls known from Eocene fossils in Asia. This small chevrotain-like animal found in the Himalayas is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whippomorpha
Whippomorpha or Cetancodonta is a group of animals that contains all living cetaceans (whales, dolphins, etc.) and hippopotamuses, as well as their extinct relatives, i.e. Entelodont, Entelodonts and Andrewsarchus. All Whippomorphs are descendants of the last common ancestor of ''Hippopotamus amphibius'' and ''Common bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncatus''. This makes it a crown group. Whippomorpha is a suborder within the order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates). The placement of Whippomorpha within Artiodactyla is a matter of some contention, as hippopotamuses were previously considered to be more closely related to Suidae (pigs) and Tayassuidae (peccaries). Most contemporary scientific Phylogenetics, phylogenetic and Morphology (biology), morphological research studies link hippopotamuses with cetaceans, and Genetic analysis, genetic evidence has overwhelmingly supported an Evolution, evolutionary relationship between Hippopotamidae and Cetacea. Modern Whippomorphs all share a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movement of their tail which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to maneuver. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number exclusively reside in brackish water or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species inhabit vast ranges where they migrate with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for their high intelligence and complex social behaviour as well as for the enormous size of some of the group's members, such as the blue whale which reaches a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 feet) and a weight of 173 tonnes (190 short to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indohyus
''Indohyus'' is an extinct genus of digitigrade artiodactyls known from Eocene fossils in Asia. This small chevrotain-like animal found in the Himalayas is one of the earliest known non-cetacean ancestors of whales. Discovery The fossils were discovered among rocks that had been collected more than 30 years ago in Kashmir by the Indian geologist A. Ranga Rao who found a few teeth and parts of a jawbone, but when he died many rocks had yet to be broken open. Ranga Rao's widow gave the rocks to Hans Thewissen, who was working on them when his technician accidentally broke one of the skulls they had found and Thewissen recognised the ear structure of the auditory bulla, formed from the ectotympanic bone in a shape which is highly distinctive, found only in the skulls of cetaceans both living and extinct, including ''Pakicetus''. Paleobiology About the size of a raccoon or domestic cat, this omnivorous pig-like creature shared some of the traits of whales, and showed signs of adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Fossil
A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors. In 1859, when Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as "the most obvious and gravest objection which can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Eocene
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age or lowest stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the lower Eocene. Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. Stratigraphic definition The Ypresian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1850. The Ypresian is named after the Flemish city of Ypres in Belgium (spelled ''Ieper'' in Dutch). The definitions of the original stage were totally different from the modern ones. The Ypresian shares its name with the Belgian Ieper Group (French: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
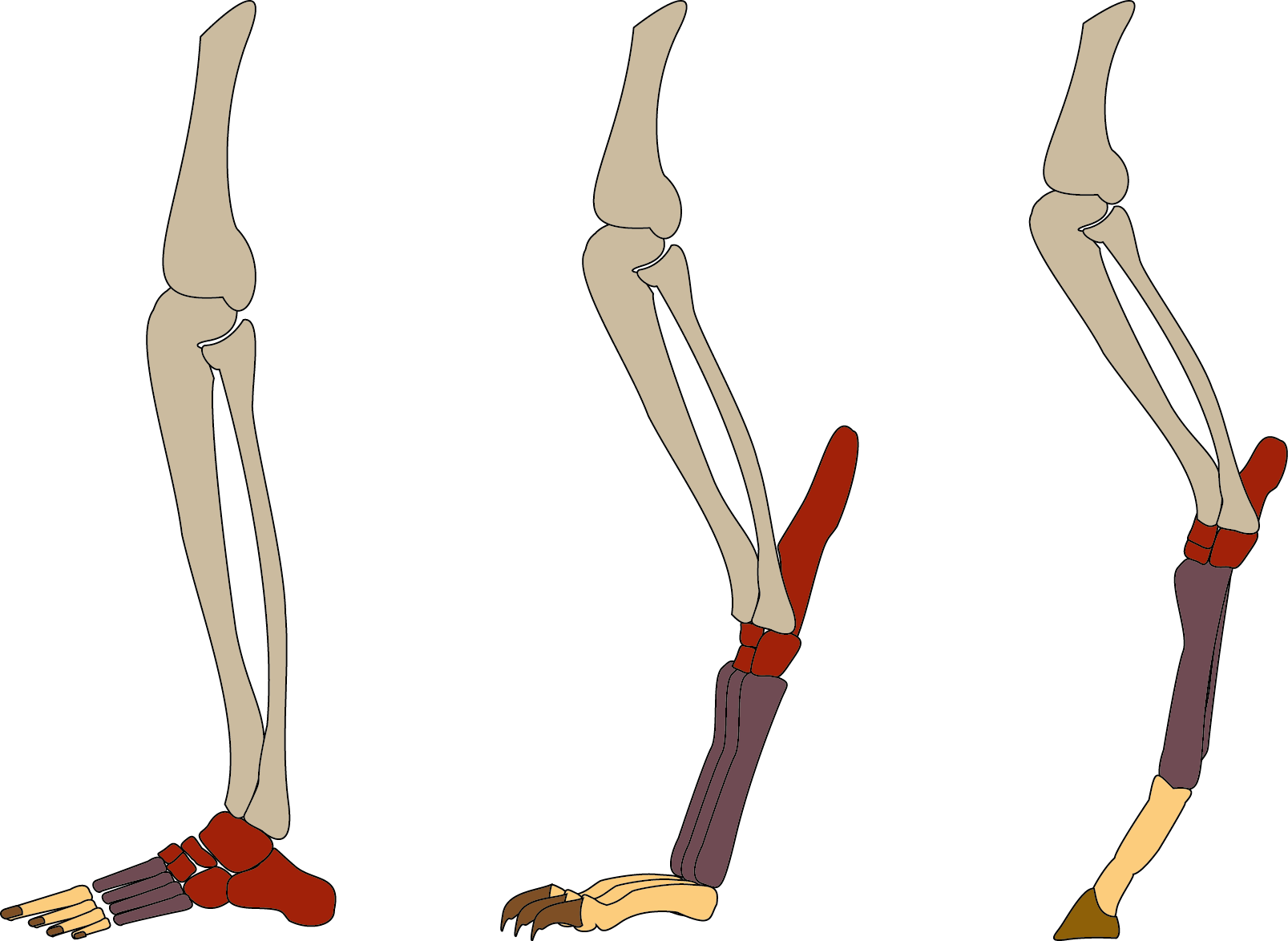
Digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the ground, and the rest of its foot lifted. Digitigrades include walking birds (what many assume to be bird knees are actually ankles), cats, dogs, and many other mammals, but not plantigrades or unguligrades. Digitigrades generally move more quickly and quietly than other animals. There are anatomical differences between the limbs of plantigrades, like humans, and both unguligrade and digitigrade limbs. Digitigrade and unguligrade animals have relatively long carpals and tarsals, and the bones which would correspond to the human ankle are thus set much higher in the limb than in a human. In a digitigrade animal, this effectively lengthens the foot, so much so that what are often thought of as a digitigrade animal's "hands" and "feet" correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene First Appearances
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the Stratum, strata that define the start and en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Mammals Of Asia
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of . Its grayish coat mostly consists of dense underfur, which insulates it against cold weather. Three of the raccoon's most distinctive features are its extremely dexterous front paws, its facial mask, and its ringed tail, which are themes in the mythologies of the indigenous peoples of the Americas relating to the animal. The raccoon is noted for its intelligence, as studies show that it is able to remember the solution to tasks for at least three years. It is usually nocturnal and omnivorous, eating about 40% invertebrates, 33% plants, and 27% vertebrates. The original habitats of the raccoon are deciduous and mixed forests, but due to their adaptability, they have extended their range to mountainous areas, coastal marshes, and urban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






_2.jpg)