|
Rani Phool Bai Rathore
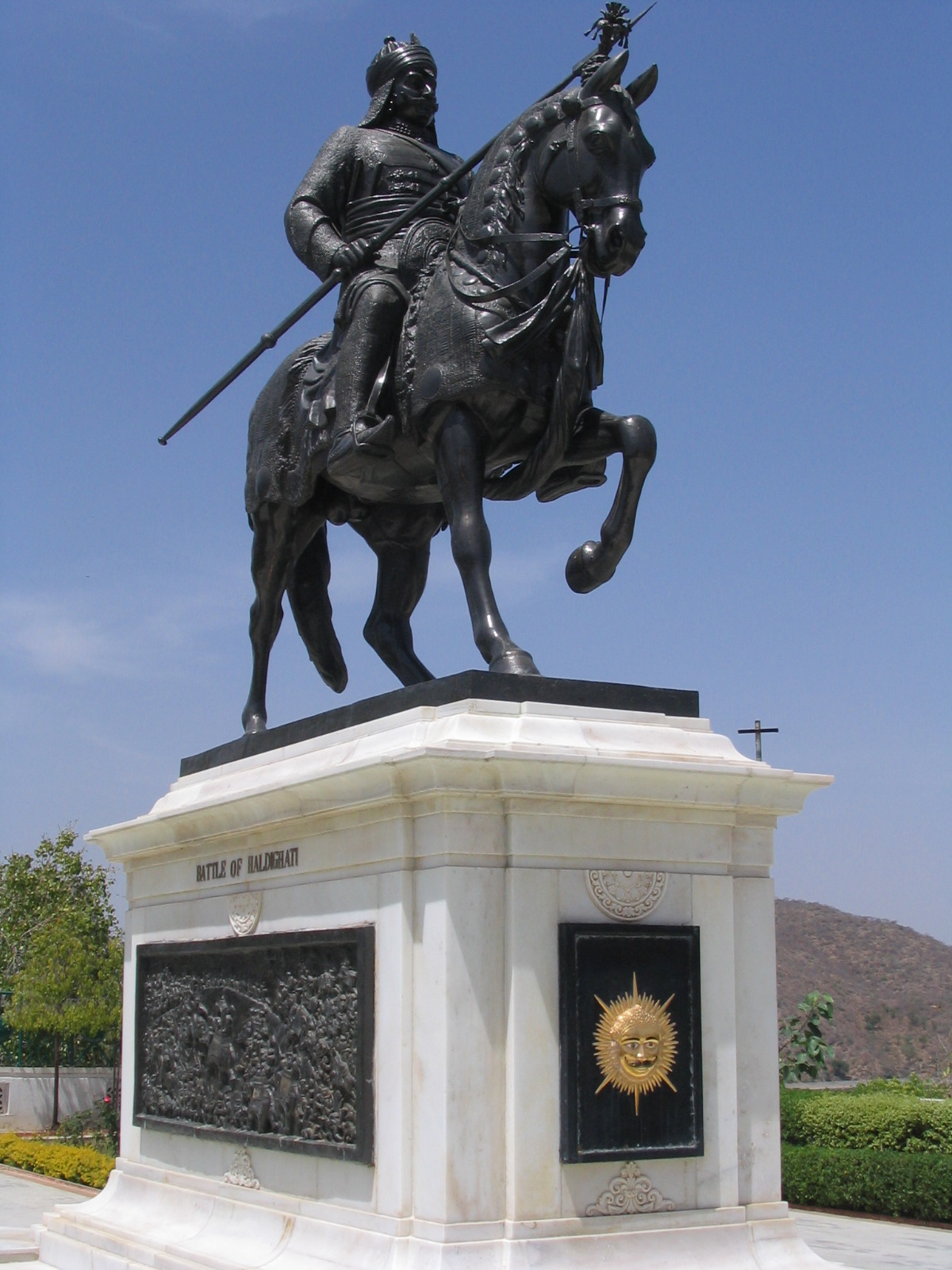
Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap (c. 9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), was a king of Mewar from the Sisodias of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty. Pratap became a folk hero for his military resistance against the expansionism of the Mughal Empire under Akbar through guerrilla warfare which proved inspirational for later rebels against Mughal Empire, Mughals including Shivaji. Early life and accession Maharana Pratap was born to Udai Singh II of Udaipur State, Mewar and Jaiwanta Bai. His younger brothers were Shakti Singh (16th century Indian noble), Shakti Singh, Vikram Singh and Jagmal Singh. Pratap also had 2 stepsisters: Chand Kanwar and Man Kanwar. He was married to Ajabde Punwar of Bijolia and he had married 10 other women and was survived by 17 sons and 5 daughters including Amar Singh I. He belonged to the Royal Family of Mewar. After the death of Udai Singh in 1572, Rani Dheer Bai wanted her son Jagmal Singh, Jagmal to succeed him but senior courtiers preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharana
Maharana is a variation on the Indian royal title Rana. Maharana denotes ' king of kings', similar to the word "Maharaja". Ruler title in British India Salute states (all in present India) The gun salutes enjoyed by the states that acceded to the Dominion of India on 14 August 1947, included the following Maharanas: *Hereditary salute of 19-guns (21-guns local): the Maharana of Udaipur State (Mewar) *Hereditary salute of 13-guns the Maharana of Rajpipla *Hereditary salute of 11-guns: the Maharana of Barwani Hereditary salutes of 9-guns: *The Maharana of Danta *The Maharana of Wadhwan *The Maharana of Sant Some of the rulers were granted increased gun salutes after the independence, e.g. the above-listed Maharana of Mewar (Hindu; at Udaipur, Maharajpramukh in Rajasthan) was raised to first place in the Order of Precedence, displacing the Nizam of Hyderabad and Berar (Muslim), and all 9-gun states were permitted the use of the style of Highness. Non-salute states ruled by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in India. A strong personality and a successful general, Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent. His power and influence, however, extended over the entire subcontinent because of Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration throughout his empire and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his non-Muslim subjects. Eschewing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
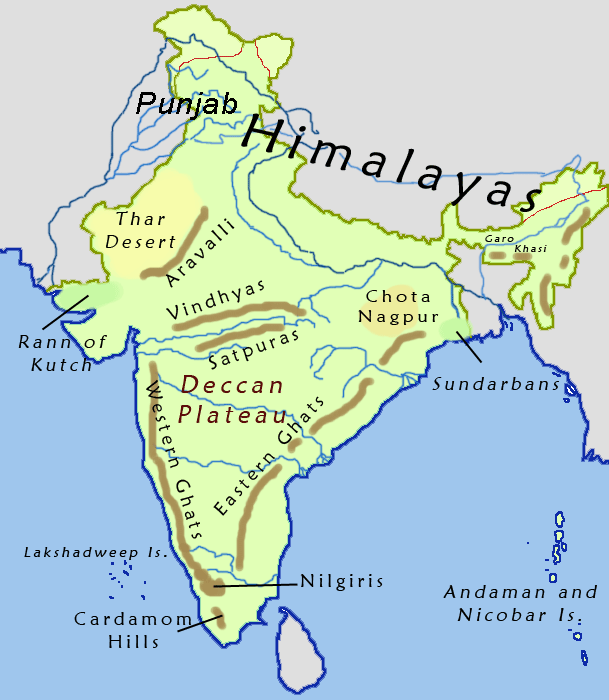
Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in Northern-Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu at . The Aravalli Range is arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth, having its origin in the Proterozoic era. The Aravalli Range is rich in natural resources and serves as check to the growth of the western desert. Etymology Aravalli, a composite Sanskrit word from the roots ''"ara"'' and ''"vali"'', literally means the ''"line of peaks"''. Natural history Geology The Aravalli Range, an eroded stub of ancient mountains, is believed to be the oldest range of fold mountains in India.Roy, A. B. (1990). Evolution of the Precambrian crust of the Aravalli Range. Developments in Precambrian Geology, 8, 327–347. The natural history of the Aravalli Range dates back to times when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Chittorgarh (1567–1568)
Siege of Chittorgarh (23 October 1567 – 23 February 1568) was a part of military expedition of Mughal Empire under Akbar against the Mewar kingdom that began in 1567 in which the Mughals successfully captured the fort of Chittorgarh after a hard-pressed siege that lasted for several months. Akbar, as part of his expansionist policy, besieged the politically important Sisodia capital of Chittor in October 1567 and gave a religious colour to the struggle by declaring it as a Jihād against the infidels. On Akbar's advance, Sisodia ruler Rana Udai Singh fled to the mountainous principality of his kingdom (on advice of his war councils) and placed the fort under the command of Jaimal Rathore. After over four months of seesaw action in which the Mughal forces suffered heavy casualties, the battle eventually break the deadloack when Jaimal succumbed to a musket shoot of Akbar on 22 February 1568. The fort was captured the next morning on the day of Holi after a gallant resistance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, starting in the early 13th century, wherein the powers to govern and collect tax from an estate was granted to an appointee of the state.Jāgīrdār system: INDIAN TAX SYSTEM Encyclopædia Britannica (2009) The tenants were considered to be in the servitude of the jagirdar. There were two forms of jagir, one being conditional and the other unconditional. The conditional jagir required the governing family to maintain troops and provide their service to the state when asked. The land grant w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahazpur
Jahazpur is a city and a municipality in Bhilwara district in the Indian state of Rajasthan.It is also the tehsil headquarters of the Jahazpur tehsil. It is commonly popular for a temple called Jain temple swastidham and built around a fort. History According to legend, the fort of Jahazpur was originally built by Samprati, grandson of the great Mauryan emperor Ashoka, who was a follower of Jainism. This fort used to protect the terrain of Hadoti Bundi and Mewar like a giridwar. In the tenth century, Rana Kumbha rebuilt the fort of Jahazpur. Jahazpur is an ancient town in Rajasthan near Bundi and Shahpura, towns of Bhilwara (polar coordinates: 25 ° 37'7 "N 75 ° 16'32" E), and the town of Deoli in Tonk district, . The ruins of several ancient Jain temples have been found at Jahazpur. It is also a municipal and assembly constituency. This area is full of mineral wealth. Geography Jahazpur is located at . It has an average elevation of . There is a Jain Mandir in the shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajmer
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as "''Ajayameru''" (translated as "Invincible Hills") by a Chahamana ruler, either Ajayaraja I or Ajayaraja II, and served as their capital until the 12th century CE. Home to the dargah of Moinuddin Chishti, Ajmer is one of the most important destinations of Islamic pilgrimage in South Asia. Ajmer is surrounded by the Aravalli Mountains. Ajmer had been a municipality since 1869. Ajmer has been selected as one of the heritage cities for the HRIDAY and Smart City Mission schemes of the Government of India. History Ajmer was originally known as ''Ajayameru''. The city was founded by an 11th-century Chahamana king Ajaydeva. Historian Dasharatha Sharma notes that the earliest mention of the city's name occurs in Palha's ''Pattavali'', which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sisodia
The Sisodia is an Indian Rajput dynasty belonging to the clan that ruled over the kingdom of Mewar in Rajasthan. The name of the clan is also transliterated as ''Sesodia'', ''Shishodia'', ''Sishodia'', ''Shishodya'', ''Sisodya'', ''Sisodiya'', ''Sisodia''. Origins The Sisodia dynasty traced its ancestry to Rahapa, a son of the 12th century Guhila King Ranasimha. He founded the village of Shisoda, in modern day Rajsamand district, as his capital, after which his descendants were called Sisodias. The main branch of the Guhila dynasty ended with their defeat against the Khalji dynasty at the Siege of Chittorgarh (1303). In 1326, Rana Hammir, who belonged to Sisodiya branch, reclaimed control of the region, re-established the dynasty, and also became the founder of the Sisodia dynasty clan, a branch of the Guhila dynasty, to which every succeeding Maharana of Mewar belonged, and the Sisodias regained control of Chittor, the former Guhila capital.''The Rajputs of Rajputana: a gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative. In most contexts, it means the inheritance of the firstborn son (agnatic primogeniture); it can also mean by the firstborn daughter (matrilineal primogeniture). Description The common definition given is also known as male-line primogeniture, the classical form popular in European jurisdictions among others until into the 20th century. In the absence of male-line offspring, variations were expounded to entitle a daughter or a brother or, in the absence of either, to another collateral relative, in a specified order (e.g. male-preference primogeniture, Salic primogeniture, semi-Salic primogeniture). Variations have tempered the traditional, sole-beneficiary, right (such as French appanage) or, in the West since World War II, eliminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth" , former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821) , budget = $10.3 billion (2021) , endowment = $17 billion (2021)As of October 25, 2021. , president = Santa Ono , provost = Laurie McCauley , established = , type = Public research university , academic_affiliations = , students = 48,090 (2021) , undergrad = 31,329 (2021) , postgrad = 16,578 (2021) , administrative_staff = 18,986 (2014) , faculty = 6,771 (2014) , city = Ann Arbor , state = Michigan , country = United States , coor = , campus = Midsize City, Total: , including arboretum , colors = Maize & Blue , nickname = Wolverines , sporti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagmal Singh
Jagmal Singh was a sixteenth century Indian prince and court figure. He was the son of Maharana Udai Singh II and Rani Dheerbai Bhatiyani. Biography After the death of Udai Singh II his favorite wife, Dheerbai Bhatiyani, wanted Jagmal to succeed Maharana Udai Singh after his death even though he was not the eldest son. On his deathbed, Udai Singh II named Jagmal Singh as the next Maharana. Jagmal was to be crowned as Maharana of Udaipur in 1572; however, the nobles of the court instead crowned Maharana Pratap.Tod, James (1829, reprint 2002). ''Annals & Antiquities of Rajas'than'', Vol.I, Rupa, New Delhi, , p.252-64 Jagmal left Mewar and went into the service of the Mughal Subedar in Ajmer, who gave him shelter. Later he met Akbar and was given the jagir of Jahazpur as a gift. Sometime before 1581, he married the daughter of Maharao Man Singh II of Sirohi and became the co-ruler of Sirohi in 1581. His brother-in-law Rao Surtran became his enemy after this. He was killed by Rao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakti Singh (16th Century Indian Noble)
Shakti Singh Sisodia, also referred to as Shakta, Sakta or Sagat, was the son of Maharana Udai Singh II Sisodia and Sajja Bai Solanki. He was a Kshatriya Rajput and was brother of famous Maharana Pratap, He started the Shaktawat clan of Sisodia Rajputs. Shakti Singh was fierce warrior. It is a very famous belief that at some point during his lifetime, due to hostile relations with his father, he was expelled from Mewar and spent some time at Dungarpur royal palace where he got angry on a cunning brahmin and killed him. However this is a folk lore and historical evidences are not clear in this regard. Early Life He was the 2nd son of Udai Singh II of Mewar born from his second wife Sajjabai Solanki. He was born just months later after his elder brother Maharana Pratap. He had hostile relations with his father. Some sources say he was expelled from Mewar by his father. Meeting with Akbar When Mughal Emperor Akbar was marching towards Chittor to capture it, he invited Shakti Singh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |