|
Random Column Packing
Random column packing is the practice of packing a distillation column with randomly fitting filtration material in order to optimize surface area over which reactants can interact while minimizing the complexity of construction of such columns. Random column packing is an alternative to structured column packing. Packed columns Packed columns utilizing filter media for chemical exchange are the most common devices used in the chemical industry for reactant contact optimization. Packed columns are used in a range of industries to allow intimate contact between two immiscible/partly immiscible fluids, which can be liquid/gas or liquid/liquid. The fluids are passed through a column in a countercurrent flow. In the column it is important to maintain an effective mass transfer, so its essential that a packing is selected which will support a large surface area for mass transfer. History Random packing was used as early as 1820. Originally the packing material consisted of glass s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distillation Column
A fractionating column or fractional column is an essential item used in the distillation of liquid mixtures to separate the mixture into its component parts, or fractions, based on the differences in volatilities. Fractionating columns are used in small scale laboratory distillations as well as large scale industrial distillations. Laboratory fractionating columns A laboratory fractionating column is a piece of glassware used to separate vaporized mixtures of liquid compounds with close volatility. Most commonly used is either a Vigreux column or a straight column packed with glass beads or metal pieces such as Raschig rings. Fractionating columns help to separate the mixture by allowing the mixed vapors to cool, condense, and vaporize again in accordance with Raoult's law. With each condensation-vaporization cycle, the vapors are enriched in a certain component. A larger surface area allows more cycles, improving separation. This is the rationale for a Vigreux column or a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Scrubber
A carbon dioxide scrubber is a piece of equipment that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). It is used to treat exhaust gases from industrial plants or from exhaled air in life support systems such as rebreathers or in spacecraft, submersible craft or airtight chambers. Carbon dioxide scrubbers are also used in controlled atmosphere (CA) storage. They have also been researched for carbon capture and storage as a means of combating climate change. Technologies Amine scrubbing The primary application for CO2 scrubbing is for removal of CO2 from the exhaust of coal- and gas-fired power plants. Virtually the only technology being seriously evaluated involves the use of various amines, e.g. monoethanolamine. Cold solutions of these organic compounds bind CO2, but the binding is reversed at higher temperatures: :CO2 + 2 ↔ + , this technology has only been lightly implemented because of capital costs of installing the facility and the operating costs of utilizing it. Minerals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a passive film that can protect the material and self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both aluminium and copper, having a biological cleanability comparable to glass. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dixon Rings
Dixon rings are a form of random packing used in chemical processing. They consist of a stainless steel mesh formed into a ring with a central divider, and are intended to be packed randomly into a packed column. Dixon rings provide a large surface area and low pressure drop while maintaining a high mass transfer rate, making them useful for distillations and many other applications. Background Packed columns Packed columns are used in a range of industries to allow intimate contact between two immiscible fluids which can be liquid/liquid or liquid/gas. The fluids are passed through in a countercurrent flow through a column. Random column packing Random column packing used to characterize the maximum volume fraction of a solid object obtained when they are packed randomly. This method of packing has been used since the early 1820s; the types of packing used were originally made out of glass spheres. However, in 1850 they were replaced by a more porous pumice stone and piec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Surface Area
Specific surface area (SSA) is a property of solids defined as the total surface area of a material per unit of mass, (with units of m2/kg or m2/g) or solid or bulk volume (units of m2/m3 or m−1). It is a physical value that can be used to determine the type and properties of a material (e.g. soil or snow). It has a particular importance for adsorption, heterogeneous catalysis, and reactions on surfaces. Measurement Values obtained for specific surface area depend on the method of measurement. In adsorption based methods, the size of the adsorbate molecule (the probe molecule), the exposed crystallographic planes at the surface and measurement temperature all affect the obtained specific surface area. For this reason, in addition to the most commonly used Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (N2-BET) adsorption method, several techniques have been developed to measure the specific surface area of particulate materials at ambient temperatures and at controllable scales, including me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, economic, cultural and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Old Town with Wawel Royal Castle was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the first 12 sites granted the status. The city has grown from a Stone Age settlement to Poland's second-most-important city. It began as a hamlet on Wawel Hill and was reported by Ibrahim Ibn Yakoub, a merchant from Cordoba, as a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. With the establishment of new universities and cultural venues at the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918 and throughout the 20th century, Kraków reaffirmed its role as a major national academic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bialecki Ring
Raschig rings are pieces of tube, approximately equal in length and diameter, used in large numbers as a packed bed within columns for distillations and other chemical engineering processes. They are usually ceramic, metal or glass and provide a large surface area within the volume of the column for interaction between liquid and gas vapours. Raschig rings are named after their inventor, German chemist Friedrich Raschig, who patented them in 1914. Use They form what is known as random packing, and enabled Raschig to perform distillations of much greater efficiency than his competitors using fractional distillation columns with trays. In a distillation column, the reflux or condensed vapour runs down the column, covering the surfaces of the rings, while vapour from the reboiler goes up the column. As the vapour and liquid pass each other countercurrently in a small space, they tend towards equilibrium. Thus, less volatile material tends to go downwards, and more volatile material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Reaction
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time. Reaction rates can vary dramatically. For example, the oxidative rusting of iron under Earth's atmosphere is a slow reaction that can take many years, but the combustion of cellulose in a fire is a reaction that takes place in fractions of a second. For most reactions, the rate decreases as the reaction proceeds. A reaction's rate can be determined by measuring the changes in concentration over time. Chemical kinetics is the part of physical chemistry that concerns how rates of chemical reactions are measured and predicted, and how reaction-rate data can be used to deduce probable reaction mechanisms. The concepts of chemical kinetics are applied in many disciplines, such as chemical engineering, enzymology and environmental engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Drop
Pressure drop is defined as the difference in total pressure between two points of a fluid carrying network. A pressure drop occurs when frictional forces, caused by the resistance to flow, act on a fluid as it flows through the tube. The main determinants of resistance to fluid flow are fluid velocity through the pipe and fluid viscosity The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the inte .... Pressure drop increases proportionally to the frictional shear forces within the piping network. A piping network containing a high relative roughness rating as well as many pipe fittings and joints, tube convergence, divergence, turns, surface roughness, and other physical properties will affect the pressure drop. High flow velocities and/or high fluid viscosities result in a larger pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mond Nickel Company
The Mond Nickel Company Limited was a United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom-based List of mining companies, mining company, formed on September 20, 1900, licensed in Canada to carry on business in the province of Ontario, from October 16, 1900. The firm was founded by Ludwig Mond (1839-1909) to process Canadian ore from mines near Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, which were then shipped to Mond's works in Britain for final purification via his patented carbonyl process. The first of Mond's Canadian mining properties located in Denison Township, was purchased from Rinaldo McConnell and associates in 1899. this site renamed the Victoria Mines, Ontario, Victoria Mine began development in 1900. About the same time, Mond's refinery at Clydach, Swansea, Clydach, near Swansea, Wales, was being erected. Around the same time, Mond purchased a second mining location from Rinaldo McConnell called the Garson Mine which was developed later on in Garson, Ontario, Garson Township. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raschig Ring
Raschig rings are pieces of tube, approximately equal in length and diameter, used in large numbers as a packed bed within columns for distillations and other chemical engineering processes. They are usually ceramic, metal or glass and provide a large surface area within the volume of the column for interaction between liquid and gas vapours. Raschig rings are named after their inventor, German chemist Friedrich Raschig, who patented them in 1914. Use They form what is known as random packing, and enabled Raschig to perform distillations of much greater efficiency than his competitors using fractional distillation columns with trays. In a distillation column, the reflux or condensed vapour runs down the column, covering the surfaces of the rings, while vapour from the reboiler goes up the column. As the vapour and liquid pass each other countercurrently in a small space, they tend towards equilibrium. Thus, less volatile material tends to go downwards, and more volatile material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
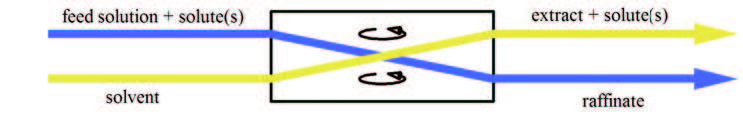
Liquid%E2%80%93liquid Extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE), also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes, based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water (polar) and an organic solvent (non-polar). There is a net transfer of one or more species from one liquid into another liquid phase, generally from aqueous to organic. The transfer is driven by chemical potential, i.e. once the transfer is complete, the overall system of chemical components that make up the solutes and the solvents are in a more stable configuration (lower free energy). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called the raffinate. LLE is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment called as mixer settlers. This type of process is commonly performed after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |