|
Ramose (vizier)
The Ancient Egyptian noble, Ramose was Vizier under both Amenhotep III and Akhenaten. He was in office in the last decade of Amenhotep's III reign and at the beginning of the reign of the latter king. Ramose appears on jar labels found in the palace of king Amenhotep III at Malkata. Here appears also the vizier Amenhotep-Huy. Both viziers are also shown side by side in the temple of Soleb. In the New Kingdom the office of the vizier was divided in a northern vizier and a southern one. It is not entirely clear whether Ramose was the southern or northern one. Ramose was born into an influential family. His father was the mayor of Memphis Heby, in office at the beginning of Amenhotep's III reign. The brother of Ramose was the high steward of Memphis Amenhotep (Huy). Tomb His tomb TT55 is located in the Sheikh Abd el-Qurna – part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor, and is notable for the high quality decorations in both the traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT55
Tomb TT55 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Vizier Ramose. It has a main room originally containing thirty-two columns and a corridor with eight columns. This tomb is notable for the high quality decorations in both the traditional and Amarna styles. The tomb, which was featured in the first episode of the 2005 BBC documentary series ''How Art Made the World'', has been open to the public, from 7.00am to 5.00pm, since 2007, as part of a 3 tomb group with TT56 Userhet and TT57 Khaemhet. Non-flash photography is permitted, with a fee of LE 300 for cameras and at no fee for mobile phones, again, on the 3 tomb group basis. Tomb decoration The main body of the tomb is entered from the east facing open court, into a large columned hall, with four rows of eight columns. On the east wall, there are 'traditional' unpainted reliefs, showing Ramose, Ramose's wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Steward (Ancient Egypt)
The high steward (also called chief steward or great overseer of the house; Egyptian: ''imi-r pr wr'') was an important official at the royal court in Ancient Egypt in the Middle Kingdom and in the New Kingdom. He was the main person in charge of the estates supplying the palace and the royal residence with food. The office appears in the 11th Dynasty. To the earliest title holders belong Henenu and Meketre. After the vizier and the treasurer this was the most important office at the royal court; important title holders of the 12th Dynasty were Siese and Khnumhotep III, both were later in their career appointed vizier. The title was still very important in the New Kingdom and was in this period often called high steward of the king. An important title holder of the New Kingdom was Senenmut under Hatshepsut, other include Wadjetrenput serving under the same queen. Chief steward of the God's Wife During the 25th and 26th dynasties, the role of God's Wife of Amun greatly ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Style
Amarna art, or the Amarna style, is a style adopted in the Amarna Period during and just after the reign of Akhenaten (r. 1351–1334 BC) in the late Eighteenth Dynasty, during the New Kingdom. Whereas Ancient Egyptian art was famously slow to change, the Amarna style was a significant and sudden break from its predecessors both in the style of depictions, especially of people, and the subject matter. The artistic shift appears to be related to the king's religious reforms centering on the monotheistic or monolatric worship of the Aten, the disc of the Sun, as giver of life. Like Akhenaten's religious reforms, his preferred art style was abandoned after the end of his reign. By the reign of Tutankhamun, both the pre-Amarna religion and art style had been restored. Background and history Shortly after taking the throne, Amenhotep IV adopted a policy of religious reform centering on the Aten. While it is not clear if he held that the Aten was the only god (monotheism), he clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptian art refers to art produced in ancient Egypt between the 6th millennium BC and the 4th century AD, spanning from Prehistoric Egypt until the Christianization of Roman Egypt. It includes paintings, sculptures, drawings on papyrus, faience, jewelry, ivories, architecture, and other art media. It is also very conservative: the art style changed very little over time. Much of the surviving art comes from tombs and monuments, giving more insight into the ancient Egyptian afterlife beliefs. The ancient Egyptian language had no word for "art". Artworks served an essentially functional purpose that was bound with religion and ideology. To render a subject in art was to give it permanence. Therefore, ancient Egyptian art portrayed an idealized, unrealistic view of the world. There was no significant tradition of individual artistic expression since art served a wider and cosmic purpose of maintaining order (Ma'at). Art of Pre-Dynastic Egypt (6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxor
Luxor ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palaces) is a modern city in Upper (southern) Egypt which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of ''Thebes''. Luxor has frequently been characterized as the "world's greatest open-air museum", as the ruins of the Egyptian temple complexes at Karnak and Luxor stand within the modern city. Immediately opposite, across the River Nile, lie the monuments, temples and tombs of the west bank Theban Necropolis, which includes the Valley of the Kings and Valley of the Queens. Thousands of tourists from all around the world arrive annually to visit Luxor's monuments, contributing greatly to the economy of the modern city. The population of Luxor is 422,407 (2021), with an area of approximately . It is the capital of Luxor Governorate. It is among the oldest inhabited cities in the world. Etymology The name ''Luxor'' ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palace, pronounced , , Upper Egyptian: ) derives from the Arabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the List of rivers by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Erit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
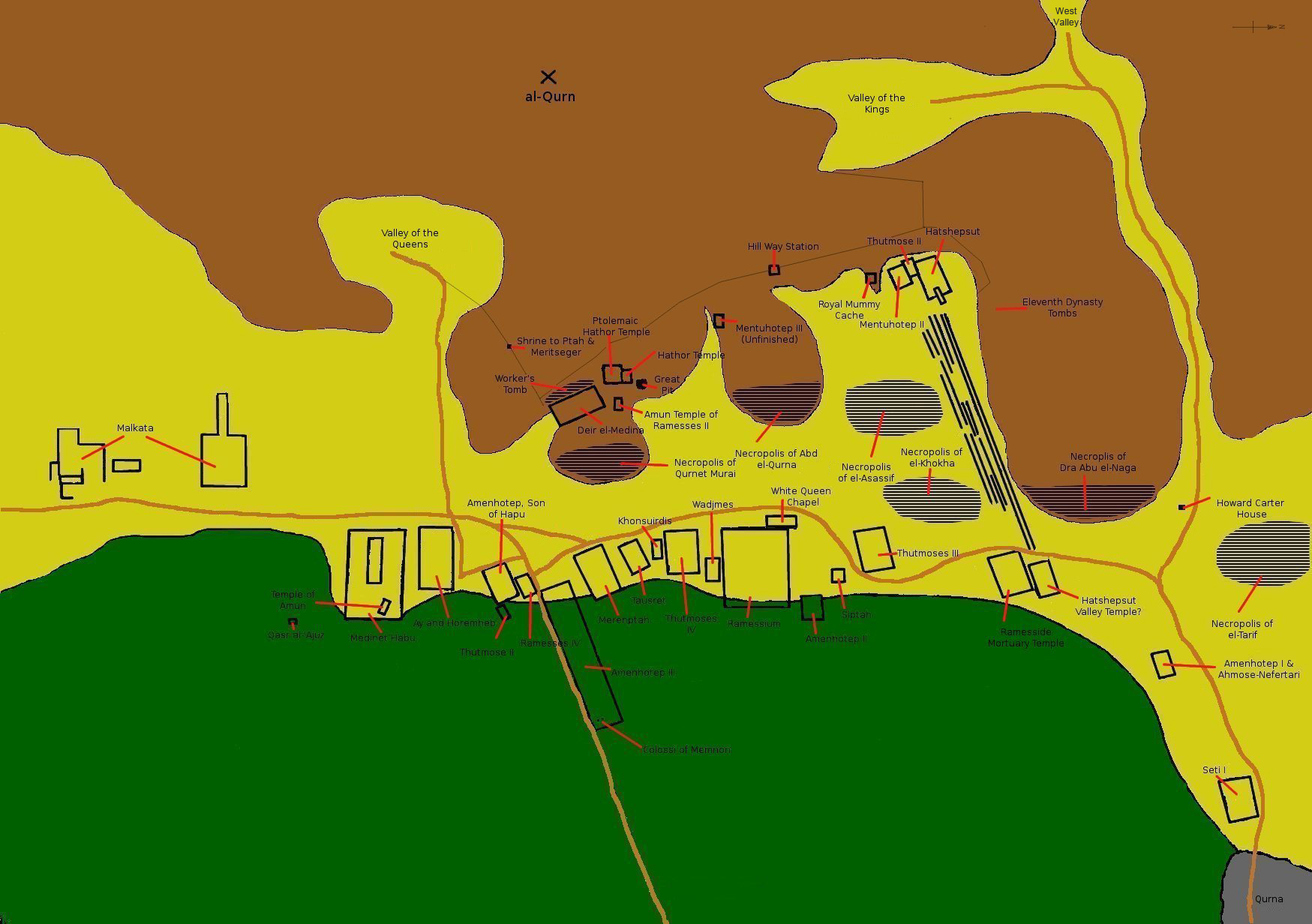
Theban Necropolis
The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom. Mortuary temples * Deir el-Bahri ** Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut ** Mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II ** Mortuary temple of Thutmose III * Medinet Habu ** Mortuary temple and palace of Ramesses III ** Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III ** Colossi of Memnon * Mortuary Temple of Merneptah * Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III * Mortuary Temple of Twosret * Temple of Nebwenenef * Qurna ** Mortuary Temple of Seti I * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep II * Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II) Royal Necropolis * Valley of the Kings (Modern: "''Wadi el-Muluk''") * Valley of the Queens (Modern: "''Biban el-Harim''") * Royal Cache * Bab el-Gasus Necropolis * Deir el-Medin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh Abd El-Qurna
The necropolis of Sheikh Abd el-Qurna ( ar, شيخ عبدالقرنة) is located on the West Bank at Thebes in Upper Egypt. It is part of the archaeological area of Deir el-Bahari, and named after the domed tomb of the local saint. This is the most frequently visited cemetery on the Theban west bank, with the largest concentration of private tombs. Tombs * TT21 User, Scribe, Steward of king Thutmose I * TT22 Wah, later usurped by Meryamun * TT23 – Tjay * TT30 Khonsmose, Amun treasury official, Ramesside * TT31 – Khonsu * TT38 Djeserkaraseneb, Scribe, Counter of grain in the granary of the divine offerings of Amun * TT41 Amenemopet called Ipy, Amun temple high steward * TT42 Amenmose, Captain of troops, Eyes of the King in the Two Lands of the Retenu * TT43 Neferrenpet, Overseer of the kitchen (stores?) of Pharaoh * TT44 Amenemhab, wab-priest in front of Amun * TT45 Djehuty, Steward of high priest of Amun Mery * TT46 Ramose, Steward of the Mansion of the At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep (Huy)
Amenhotep (Huy) was the '' high steward of Memphis'' under Amenhotep III in the Egyptian 18th Dynasty. With this title he was one of the highest officials at the royal court. Family Amenhotep, with the nickname Huy, was a member of an influential family. His father Heby was ''mayor of Memphis''. His brother Ramose was vizier under Amenhotep III.Dodson, Aidan, Amarna Sunrise: Egypt from Golden age to Age of Heresy, The American University in Cairo Press, 2014, p 48, p50, p 184 n35, p198 n84. His son Ipy was ''high steward'' under Akhenaten. Ipy likely succeeded his father sometime after the first Heb-Sed festival of Amenhotep III. He appears in the tomb of his uncle Ramose at the end of the reign of Amenhotep III when he has taken over his father's duties.O'Connor, David and Cline, Eric H. Amenhotep III: Perspectives on His Reign University of Michigan Press. 2001, pp 65, 203, 214; The family member's accomplishments are one of the rare cases where an influential family kep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
, alternate_name = , image = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the pillared hall of Ramesses IIat Mit Rahina , map_type = Egypt#Africa , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = , coordinates = , location = Mit Rahina, Giza Governorate, Egypt , region = Lower Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = Unknown, was already in existence during Iry-Hor's reignP. Tallet, D. Laisnay: ''Iry-Hor et Narmer au Sud-Sinaï (Ouadi 'Ameyra), un complément à la chronologie des expéditios minière égyptiene'', in: BIFAO 112 (2012), 381–395available online/ref> , material = , built = Earlier than 31st century BC , abandoned = 7th century AD , epochs = Early Dynastic Period to Early Middle Ages , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different authors, he ruled Egypt from June 1386 to 1349 BC, or from June 1388 BC to December 1351 BC/1350 BC, after his father Thutmose IV died. Amenhotep was Thutmose's son by a minor wife, Mutemwiya. His reign was a period of unprecedented prosperity and splendour, when Egypt reached the peak of its artistic and international power. When he died in the 38th or 39th year of his reign he was succeeded by his son Amenhotep IV, who later changed his name to Akhenaten. Family and early life Amenhotep was the son of Thutmose IV and his minor wife Mutemwiya. He was born probably around 1401 BC. Later in his life, Amenhotep commissioned the depiction of his divine birth to be displayed at Luxor Temple. Amenhotep claimed that his true father was the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 Songs * "New" (Daya song), 2017 * "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 *"new", by Loona from '' Yves'', 2017 *"The New", by Interpol from ''Turn On the Bright Lights'', 2002 Acronyms * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, a conservative university women's organization * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean film distribution company Identification codes * Nepal Bhasa language ISO 639 language code * New Century Financial Corporation (NYSE stock abbreviation) * Northeast Wrestling, a professional wrestling promotion in the northeastern United States Transport * New Orleans Lakefront Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)