|
Ramesh Raskar
Ramesh Raskar is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology Associate Professor and head of the MIT Media Lab's Camera Culture research group. Previously he worked as a Senior Research Scientist at Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) during 2002 to 2008. He holds 132 patents in computer vision, computational health, sensors and imaging. He received the $500K Lemelson–MIT Prize in 2016. The prize money will be used for launching REDX.io, a group platform for co-innovation in Artificial Intelligence. He is well known for inventing EyeNetra (mobile device to calculate eyeglasses prescription), EyeCatra (cataract screening) and EyeSelfie (retinal imaging), Femto-photography (trillion frames per second imaging) and his TED talk for cameras to see around corners. In February 2020, Raskar and his team launched Private Kit: SafePaths, a public health tool for contact tracing for COVID-19 pandemic. He is also the Founder and Chief Scientist of PathCheck. He is a co-founder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nashik
Nashik (, Marathi: aːʃik, also called as Nasik ) is a city in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Situated on the banks of river Godavari, Nashik is the third largest city in Maharashtra, after Mumbai and Pune. Nashik is well known for being one of the Hindu pilgrimage sites of the Kumbh Mela, which is held every 12 years. Nashik is located about 190 km north of state capital Mumbai. The city is called the "Wine Capital of India" as more than half of India's vineyards and wineries are located here. Around 90% of all Indian wine comes from the Nashik Valley. Nashik is one of the fastest-growing cities in India. It has been a major industrial center in automobile hub. The city houses companies like Exxelia, Atlas Copco, Robert Bosch GmbH, CEAT Limited, Crompton Greaves, Graphite India, ThyssenKrupp, Epcos, Everest Industries, Gabriel India, GlaxoSmithKline, Hindustan Coca-Cola, Hindustan Unilever Limited, Jindal Polyster, Jyoti Structures, Kirl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemelson–MIT Prize
The Lemelson-MIT Program awards several prizes yearly to inventors in the United States. The largest is the Lemelson–MIT Prize which was endowed in 1994 by Jerome H. Lemelson, funded by the Lemelson Foundation, and is administered through the School of Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The winner receives $500,000, making it the largest cash prize for invention in the U.S. The $100,000 Lemelson-MIT Award for Global Innovation (previously named the Award for Sustainability) was last awarded in 2013. The Award for Global Innovation replaced the $100,000 Lemelson-MIT Lifetime Achievement Award, which was awarded from 1995 to 2006. The Lifetime Achievement Award recognized outstanding individuals whose pioneering spirit and inventiveness throughout their careers improved society and inspired others. The Lemelson-MIT Program also awards invention prizes for college students, called the Lemelson-MIT Student Prize. List of winners Source: ;2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Review
''MIT Technology Review'' is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and editorially independent of the university. It was founded in 1899 as ''The Technology Review'', and was re-launched without "The" in its name on April 23, 1998 under then publisher R. Bruce Journey. In September 2005, it was changed, under its then editor-in-chief and publisher, Jason Pontin, to a form resembling the historical magazine. Before the 1998 re-launch, the editor stated that "nothing will be left of the old magazine except the name." It was therefore necessary to distinguish between the modern and the historical ''Technology Review''. The historical magazine had been published by the MIT Alumni Association, was more closely aligned with the interests of MIT alumni, and had a more intellectual tone and much smaller public circulation. The magazine, billed from 1998 to 2005 as "MIT's Magazine of Innovation," and from 2005 onwards as simply "published by MIT" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fondation Botnar
Fondation Botnar is a philanthropic foundation based in Basel, Switzerland. The foundation was founded in 2003 by Marcela Botnar, wife of businessman and philanthropist Octav Botnar. It is one of the largest foundations in Switzerland, holding CHF 3.8 billion in assets. Fondation Botnar champions the use of AI and digital technologies to improve the health and wellbeing of children and young people in growing urban environments. The foundation provides a range of funding opportunities to enable research and innovative projects that fit within its strategic focus. History In 2003, Fondation Botnar was founded by Marcela Botnar to continue the philanthropic work of herself and her husband Octav Botnar. Following the death of Marcela and Octav Botnar’s only child, Camelia Eugenia Botnar, who tragically died in 1972 at the age of 20 in a car accident, the couple focused on philanthropic work and funded several large projects in their daughter’s name. When Octav Botnar died, Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Field
The light field is a vector function that describes the amount of light flowing in every direction through every point in space. The space of all possible '' light rays'' is given by the five-dimensional plenoptic function, and the magnitude of each ray is given by its radiance. Michael Faraday was the first to propose that light should be interpreted as a field, much like the magnetic fields on which he had been working. The phrase ''light field'' was coined by Andrey Gershun in a classic 1936 paper on the radiometric properties of light in three-dimensional space. Modern approaches to light field display explore co-designs of optical elements and compressive computation to achieve higher resolutions, increased contrast, wider fields of view, and other benefits. The term “radiance field” may also be used to refer to similar concepts. The term is used in modern research such as neural radiance fields. The plenoptic function For geometric optics—i.e., to incoherent ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to aging but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. The underlying mechanism involves accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment in the lens that reduces transmission of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
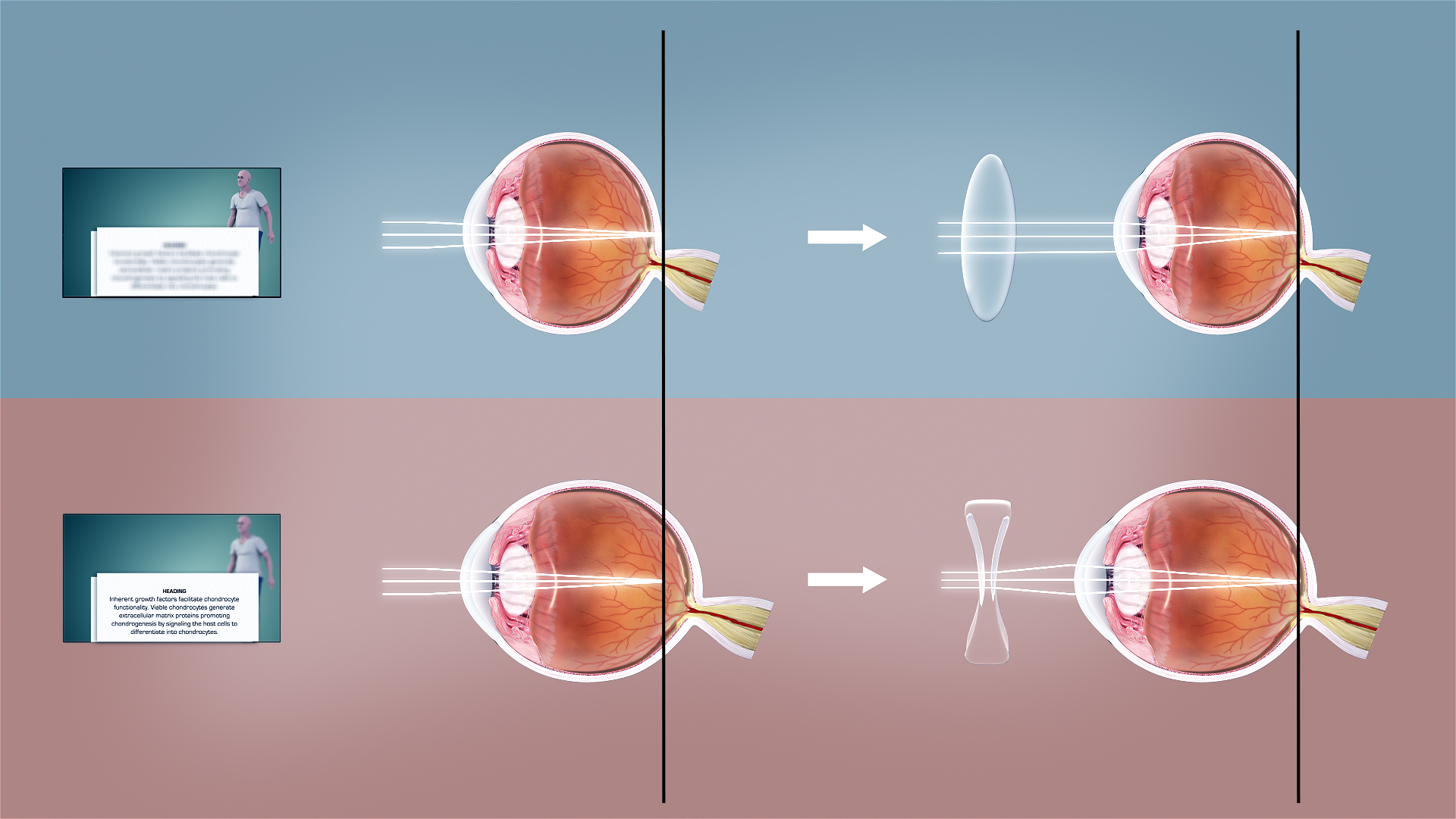
Refractive Error
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the human eye, eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurred vision, blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long, far-sightedness the eyeball too short, astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, and presbyopia aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PathCheck
PathCheck Foundation is a volunteer-led nonprofit organization founded in February 2020 at MIT that develops COVID-19 apps for digital contact tracing. The organization consists of over 1000 volunteers. In addition, various companies donate employee time to the foundation. The organization was previously known as COVID Safe Paths (and before MIT Safe Paths) but was renamed PathCheck Foundation on June 28, 2020. The original technology for the PathCheck app was based on the MIT Private Kit: Safe Paths app created by Ramesh Raskar with Sandy Pentland, Kent Larson, Steve Penrod, and Kevin Esvelt. The founding team included Abhishek Singh, Kristen Vilcans, Alina Clough, Francesco Maria Bendetti, Kaushal Jain, Khahlil Louisy, Sienna Leis, Greg Nadeau, Rachel Barbar, and John Werner. On July 8, 2020, Ramesh Raskar, chairman of PathCheck Foundation, addressed the United States House of Representatives Committee on Financial Services Task Force on Artificial Intelligence during their hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femto-photography
Femto-photography is a technique for recording the propagation of ultrashort pulses of light through a scene at a very high speed (up to 1013 frames per second). A femto-photograph is equivalent to an optical impulse response of a scene and has also been denoted by terms such as a light-in-flight recording or transient image. Femto-photography of macroscopic objects was first demonstrated using a holographic process in the 1970s by Nils Abramsson at the Royal Institute of Technology (Sweden). A research team at the MIT Media Lab led by Ramesh Raskar, together with contributors from the Graphics and Imaging Lab at the Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain, more recently achieved a significant increase in image quality using a streak camera synchronized to a pulsed laser and modified to obtain 2D images instead of just a single scanline. In their publications, Raskar's team claims to be able to capture exposures so short that light only traverses 0.6 mm (corresponding to 2 pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

_PHIL_4284_lores.jpg)