|
Raman Spectroelectrochemistry
Raman spectroelectrochemistry (Raman-SEC) is a technique that studies the inelastic scattering or Raman scattering of monochromatic light related to chemical compounds involved in an electrode process. This technique provides information about vibrational energy transitions of molecules, using a monochromatic light source, usually from a laser that belongs to the UV, Vis or NIR region. Raman spectroelectrochemistry provides specific information about structural changes, composition and orientation of the molecules on the electrode surface involved in an electrochemical reaction, being the Raman spectra registered a real fingerprint of the compounds. When a monochromatic light beam samples the electrode/solution interface, most of the photons are scattered elastically, with the same energy than the incident light. However, a small fraction is scattered inelastically, being the energy of the laser photons shifted up or down. When the scattering is elastic, the phenomenon is denoted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroelectrochemistry
Spectroelectrochemistry (SEC) is a set of multi-response analytical techniques in which complementary chemical information ( electrochemical and spectroscopic) is obtained in a single experiment. Spectroelectrochemistry provides a whole vision of the phenomena that take place in the electrode process. The first spectroelectrochemical experiment was carried out by Theodore Kuwana, PhD, in 1964. The main objective of spectroelectrochemical experiments is to obtain simultaneous, time-resolved and in-situ electrochemical and spectroscopic information on reactions taking place on the electrode surface. The base of the technique consist in studying the interaction of a beam of electromagnetic radiation with the compounds involved in these reactions. The changes of the optical and electrical signal allow us to understand the evolution of the electrode process. The techniques on which the spectroelectrochemistry is based are: * Electrochemistry, which studies the interaction betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe. Examples of spectrometers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Electrode
The auxiliary electrode, often also called the counter electrode, is an electrode used in a three electrode electrochemical cell for voltammetric analysis or other reactions in which an electric current is expected to flow. The auxiliary electrode is distinct from the reference electrode, which establishes the electrical potential against which other potentials may be measured, and the working electrode, at which the cell reaction takes place. In a two-electrode system, either a known current or potential is applied between the working and auxiliary electrodes and the other variable may be measured. The auxiliary electrode functions as a cathode whenever the working electrode is operating as an anode and vice versa. The auxiliary electrode often has a surface area much larger than that of the working electrode to ensure that the half-reaction occurring at the auxiliary electrode can occur fast enough so as not to limit the process at the working electrode. When a three electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Electrode
A reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant (buffered or saturated) concentrations of each participant of the redox reaction. There are many ways reference electrodes are used. The simplest is when the reference electrode is used as a half-cell to build an electrochemical cell. This allows the reduction potential, potential of the other half cell to be determined. An accurate and practical method to measure an electrode's potential in isolation (absolute electrode potential) has yet to be developed. Aqueous reference electrodes Common reference electrodes and potential with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE): * Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) (E = 0.000 V) activity of H+ = 1 Molar * Normal hydrogen electrode (NHE) (E ≈ 0.000 V) concentration H+ = 1 Molar * Reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) (E = 0.000 V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Electrode
The working electrode is the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring. The working electrode is often used in conjunction with an auxiliary electrode, and a reference electrode in a three electrode system. Depending on whether the reaction on the electrode is a reduction or an oxidation, the working electrode is called cathodic or anodic, respectively. Common working electrodes can consist of materials ranging from inert metals such as gold, silver or platinum, to inert carbon such as glassy carbon, boron doped diamond or pyrolytic carbon, and mercury drop and film electrodes. Chemically modified electrodes are employed for the analysis of both organic and inorganic samples. Special types * Ultramicroelectrode (UME) * Rotating disk electrode (RDE) * Rotating ring-disk electrode (RRDE) * Hanging mercury drop electrode (HMDE) * Dropping mercury electrode (DME) See also * Auxiliary electrode * Electrochemical cell * Electrochemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanostat
A galvanostat (also known as amperostat) is a control and measuring device capable of keeping the current through an electrolytic cell in coulometric titrations constant, disregarding changes in the load itself. Its main feature is its ''nearly'' "''infinite''" (i.e. extremely high in respect to common loads) internal resistance. The designation "''galvanostat''" is mainly used in electrochemistry: this device differs from common constant current sources by its ability to supply ''and measure'' a wide range of currents (from picoamperes to amperes) of both polarities. The galvanostat responds to changes in the resistance of the cell by varying its output potential: as Ohm's law shows, : = the variable system resistance and the controlled voltage are directly proportional, i.e. : U_c = where *''I_o'' is the electric current that is kept constant *''U_c'' is the output control voltage of the amperostat *''R_v'' is the electrical resistance that varies; thus, an incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
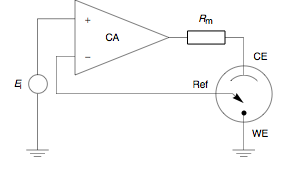
Potentiostat
A potentiostat is the electronic hardware required to control a three electrode cell and run most electroanalytical experiments. A ''Bipotentiostat'' and ''polypotentiostat'' are potentiostats capable of controlling two working electrodes and more than two working electrodes, respectively. The system functions by maintaining the potential of the working electrode at a constant level with respect to the reference electrode by adjusting the current at an auxiliary electrode. The heart of the different potentiostatic electronic circuits is an operational amplifier (op amp). It consists of an electric circuit which is usually described in terms of simple op amps. Primary use This equipment is fundamental to modern electrochemical studies using three electrode systems for investigations of reaction mechanisms related to redox chemistry and other chemical phenomena. The dimensions of the resulting data depend on the experiment. In voltammetry, electric current in amps is pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe. Examples of spectrometers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, Light, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All of these waves form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Classical electromagnetism, Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric field, electric and magnetic fields. Depending on the frequency of oscillation, different wavelengths of electromagnetic spectrum are produced. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, commonly denoted ''c''. In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. The position of an electromagnetic wave w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroelectrochemistry
Spectroelectrochemistry (SEC) is a set of multi-response analytical techniques in which complementary chemical information ( electrochemical and spectroscopic) is obtained in a single experiment. Spectroelectrochemistry provides a whole vision of the phenomena that take place in the electrode process. The first spectroelectrochemical experiment was carried out by Theodore Kuwana, PhD, in 1964. The main objective of spectroelectrochemical experiments is to obtain simultaneous, time-resolved and in-situ electrochemical and spectroscopic information on reactions taking place on the electrode surface. The base of the technique consist in studying the interaction of a beam of electromagnetic radiation with the compounds involved in these reactions. The changes of the optical and electrical signal allow us to understand the evolution of the electrode process. The techniques on which the spectroelectrochemistry is based are: * Electrochemistry, which studies the interaction betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Santiuste Cristina Moreno LydiaGarcía
Andrea is a given name which is common worldwide for both males and females, cognate to Andreas, Andrej and Andrew. Origin of the name The name derives from the Greek word ἀνήρ (''anēr''), genitive ἀνδρός (''andrós''), that refers to man as opposed to woman (whereas ''man'' in the sense of ''human being'' is ἄνθρωπος, ''ánthropos''). The original male Greek name, ''Andréas'', represents the hypocoristic, with endearment functions, of male Greek names composed with the ''andr-'' prefix, like Androgeos (''man of the earth''), Androcles (''man of glory''), Andronikos (''man of victory''). In the year 2006, it was the third most popular name in Italy with 3.1% of newborns. It is one of the Italian male names ending in ''a'', with others being Elia ( Elias), Enea ( Aeneas), Luca (Lucas), Mattia (Matthias), Nicola (Nicholas), Tobia ( Tobias). In recent and past times it has also been used on occasion as a female name in Italy and in Spain, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)