|
Ram Sabnis
Zubbles is a commercial name for colored soap bubbles. Zubbles claim to fame is that they are the first colored soap bubbles that do not leave stains. Instead they fade away with exposure to air, pressure, and water. ''Popular Science'' named Zubbles the "Innovation of the Year" for 2005. ''Reader's Digest'' agreed, saying they were one of the "Best Innovations" of the year in 2006. Development Zubbles were invented by Tim Kehoe, a toy creator from St. Paul, Minnesota. After an unexplained breakthrough in his kitchen, he was able to produce blue bubbles, that, unsuitably for a toy, stained clothing. After an eight-year-long delay in developing the idea further, he recommenced his investigations after forming a new toy company. In the process of trying to rediscover the recipe, he changed the formula, making the coloring water-soluble. However, having to wash off the color from the bubbles rendered them unsuited to a mass-market toy. Kehoe hired the dye chemist Ram Sabnis, who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soap Bubble
A soap bubble is an extremely thin film of soap or detergent and water enclosing air that forms a hollow sphere with an iridescent surface. Soap bubbles usually last for only a few seconds before bursting, either on their own or on contact with another object. They are often used for children's enjoyment, but they are also used in artistic performances. Assembling many bubbles results in foam. When light shines onto a bubble it appears to change colour. Unlike those seen in a rainbow, which arise from differential refraction, the colours seen in a soap bubble arise from light wave interference, reflecting off the front and back surfaces of the thin soap film. Depending on the thickness of the film, different colours interfere constructively and destructively. Mathematics Soap bubbles are physical examples of the complex mathematical problem of minimal surface. They will assume the shape of least surface area possible containing a given volume. A true minimal surface is more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, including the American Society of Magazine Editors awards for its journalistic excellence in 2003 (for General Excellence), 2004 (for Best Magazine Section), and 2019 (for Single-Topic Issue). With roots beginning in 1872, ''Popular Science'' has been translated into over 30 languages and is distributed to at least 45 countries. Early history ''The Popular Science Monthly'', as the publication was originally called, was founded in May 1872 by Edward L. Youmans to disseminate scientific knowledge to the educated layman. Youmans had previously worked as an editor for the weekly ''Appleton's Journal'' and persuaded them to publish his new journal. Early issues were mostly reprints of English periodicals. The journal became an outlet for writings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reader's Digest
''Reader's Digest'' is an American general-interest family magazine, published ten times a year. Formerly based in Chappaqua, New York, it is now headquartered in midtown Manhattan. The magazine was founded in 1922 by DeWitt Wallace and his wife Lila Bell Wallace. For many years, ''Reader's Digest'' was the best-selling consumer magazine in the United States; it lost the distinction in 2009 to '' Better Homes and Gardens''. According to Mediamark Research (2006), ''Reader's Digest'' reached more readers with household incomes of over $100,000 than ''Fortune'', ''The Wall Street Journal'', '' Business Week'', and '' Inc.'' combined. Global editions of ''Reader's Digest'' reach an additional 40 million people in more than 70 countries, via 49 editions in 21 languages. The periodical has a global circulation of 10.5 million, making it the largest paid-circulation magazine in the world. It is also published in Braille, digital, audio, and a large type called "Reader's Digest Larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crayola
Crayola LLC, formerly the Binney & Smith Company, is an American manufacturing company specializing in art supplies. It is known for its brand ''Crayola'' and best known for its crayons. The company is headquartered in Forks Township, Pennsylvania in the Lehigh Valley region of the state. Since 1984, Crayola has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Hallmark Cards. Originally an industrial pigment supply company, Crayola soon shifted its focus to art products for home and school use, beginning with chalk, then crayons, followed later by colored pencils, markers, paints, modeling clay, and other related goods. All Crayola-branded products are marketed as nontoxic and safe for use by children. Most Crayola crayons are manufactured in the United States. Crayola also produces Silly Putty and a line of professional art products under the 'Portfolio Series brand', including acrylics, watercolor, tempera, and brushes. Crayola, LLC claims the Crayola brand has 99% name recognition in U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuco Dye
A leuco dye (from the Greek λευκός ''leukos'': white ) is a dye which can switch between two chemical forms; one of which is colorless. Reversible transformations can be caused by heat, light or pH; resulting in examples of thermochromism, photochromism and halochromism respectively. Irreversible transformations typically involve reduction or oxidation.Chemistry and Applications of Leuco Dyes. Ramaiah Muthyala. 302 pag. Springer; 1997 edition. The colorless form is sometimes referred to as the leuco form. Leuco dyes form the basis of thermal printer papers and certain pH indicators. Examples The most common example is in applying sulfur dyes and vat dyes; with indigo being a classic case. This is characteristically purple but is also completely insoluble in water, meaning that it cannot be applied to clothes directly. It is instead reduced to indigo white (sometimes Leucoindigo), which is water-soluble but colorless. When a submerged fabric is removed from a dyebath of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Violet Lactone
Crystal violet lactone (CVL) is a leuco dye, a lactone derivate of crystal violet 10B. In pure state it is a slightly yellowish crystalline powder, soluble in nonpolar or slightly polar organic solvents. The central carbon in the leuco form is in a tetrahedral configuration, with four covalent bonds. In an acidic environment, the lactone ring is broken, with the oxygen detaching from the central carbon. This now-trivalent position is a planar carbocation that is resonance stabilized, interconnecting the π systems of the aromatic rings and the amino functional groups. This single large conjugated system is a chromophore with strong absorption in visible spectrum, giving this compound its distinctive color. This chemical is usually drawn in the resonance structure with the cation on nitrogen. : It was the first dye used in carbonless copy papers, and it is still widely used in this application. It is also the leuco dye component in some thermochromic dyes, e.g. in the Hypercolor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfactants
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsion#Emulsifiers , emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants. The word "surfactant" is a Blend word, blend of ''surface-active agent'', coined . Agents that increase surface tension are "surface active" in the literal sense but are not called surfactants as their effect is opposite to the common meaning. A common example of surface tension increase is salting out: by adding an inorganic salt to an aqueous solution of a weakly polar substance, the substance will precipitate. The substance may itself be a surfactant – this is one of the reasons why many surfactants are ineffective in sea water. Composition and structure Surfactants are usually organic compounds that are amphiphilic, meaning each molecule contains both a hydrophilic "water-seeking" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
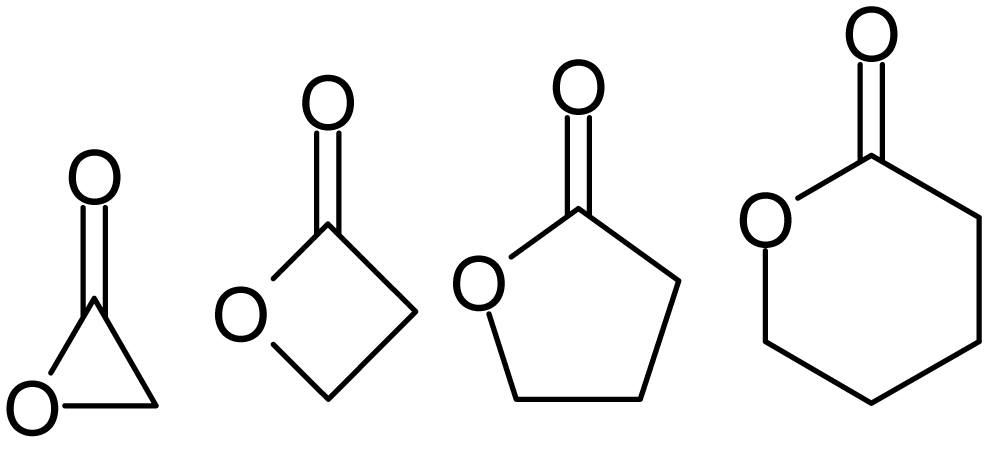
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |