|
Raid On Dunkirk (1800)
The Raid on Dunkirk of 7 July 1800 was an attack by a British Royal Navy force on the well-defended French anchorage of Dunkirk in the English Channel during the French Revolutionary Wars. French naval forces had been blockaded in their harbours during the conflict, and often the only method of attacking them was through fireships or "cutting-out" expeditions, in which boats would carry boarding parties into the harbour at night, seize ships at anchor and bring them out. The attack on Dunkirk was a combination of both of these types of operation, aimed at a powerful French frigate squadron at anchor in Dunkirk harbour. The assault made use of a variety of experimental weaponry, some of which was tested in combat for the first time with mixed success. Although assault by the heavily armed sloop HMS ''Dart'' proved successful, the fireships achieved little and various other British craft involved in the operation had little effect on the eventual outcome. The French response was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Campaigns, Operations And Battles Of The French Revolutionary Wars
List of naval battles of the French Revolutionary Wars {, class="wikitable" , - ! Today's location of the battle, its name and date ! French leader ! Coalition leader , -style="vertical-align: top;" , Italy: French expedition to Sardinia1792-12-211793-05-25 , Defeat: French Republic: Truguet , Victory: KD Sardinia: Domenico Millelire KD Spain: Lángara , -style="vertical-align: top;" , France:Siege of Toulon1793-08-291793-12-19 , Victory: French Republic: Carteaux DugommierNapoleon PoypeCharlot , Defeat: French Royalists: d'Imbert French Federalists KD Great Britain:Hood O'HaraSmith Mulgrave KD Spain: Lángara Gravina KD Naples KD Sicily KD Sardinia , -style="vertical-align: top;" , Guernsey:Action of 23 April 17941794-04-23 , Defeat: French Republic: Desgareaux , Victory: KD Great Britain:Warren Strachan , -style="vertical-align: top;" , France:Atlantic campaign of May 17941794-05-021794-06-01 , Inconclusive: French Republic:Joyeuse Nielly , Inconclusive: KD Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
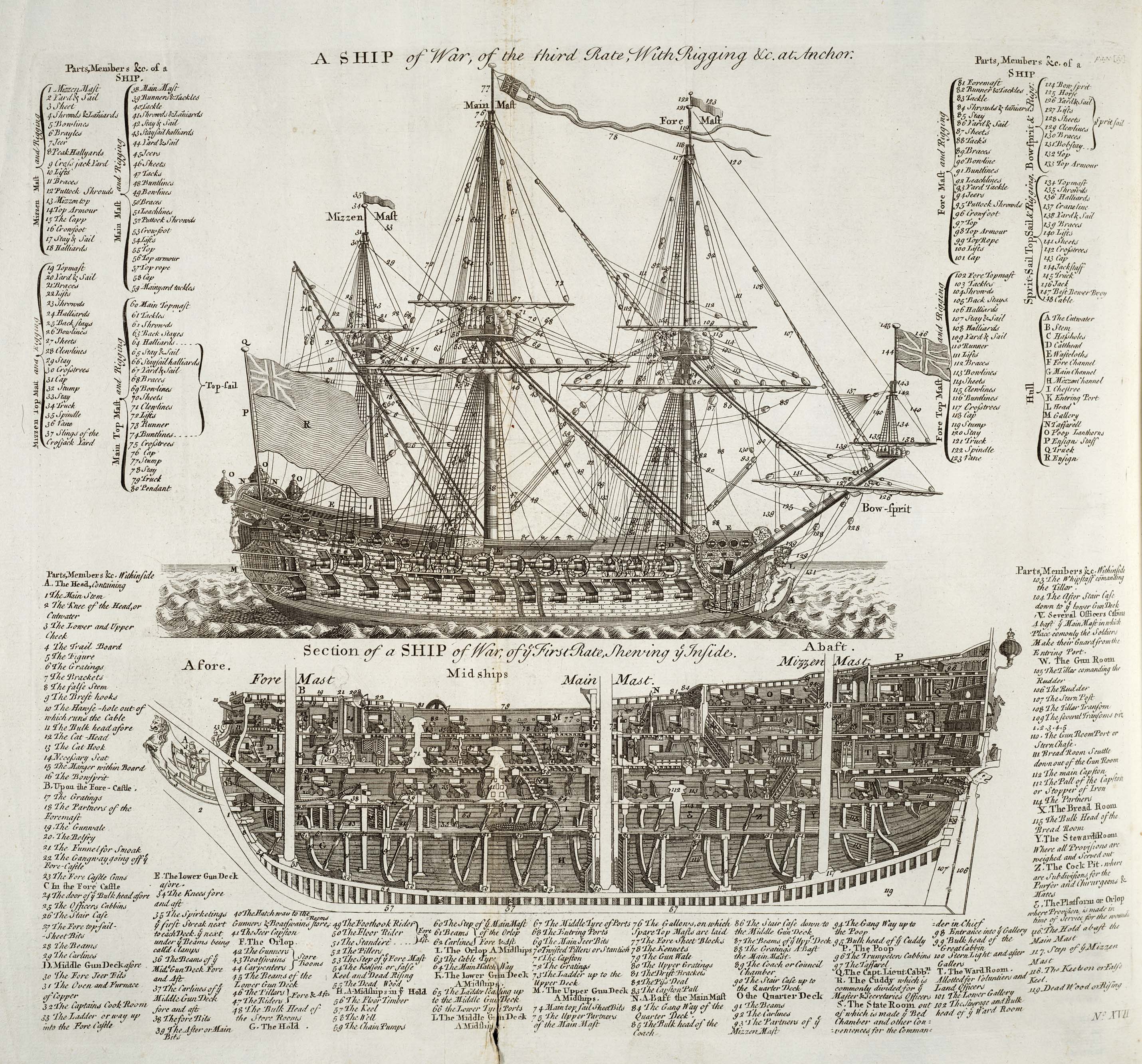
Ships Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carronades
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century. Its main function was to serve as a powerful, short-range, anti-ship and anti-crew weapon. The technology behind the carronade was greater dimensional precision, with the shot fitting more closely in the barrel thus transmitting more of the propellant charge's energy to the projectile, allowing a lighter gun using less gunpowder to be effective. Carronades were initially found to be very successful, but they eventually disappeared as naval artillery advanced, with the introduction of rifling and consequent change in the shape of the projectile, exploding shells replacing solid shot, and naval engagements being fought at longer ranges. History The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Artillery In The Age Of Sail
Naval artillery in the Age of Sail encompasses the period of roughly 1571–1862: when large, sail-powered wooden naval warships dominated the high seas, mounting a large variety of types and sizes of cannon as their main armament. By modern standards, these cannon were extremely inefficient, difficult to load, and short ranged. These characteristics, along with the handling and seamanship of the ships that mounted them, defined the environment in which the naval tactics in the Age of Sail developed. Firing Firing a naval cannon required a great amount of labour and manpower. The propellant was gunpowder, whose bulk had to be kept in the magazine, a special storage area below deck for safety. ''Powder boys'', typically 10–14 years old, were enlisted to run powder from the magazine up to the gun decks of a vessel as required. A typical firing procedure follows. A wet swab was used to mop out the interior of the barrel, extinguishing any embers from a previous firing whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating System Of The Royal Navy
The rating system of the Royal Navy and its predecessors was used by the Royal Navy between the beginning of the 17th century and the middle of the 19th century to categorise sailing warships, initially classing them according to their assigned complement of men, and later according to the number of their carriage-mounted guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy formally came to an end in the late 19th century by declaration of the Admiralty. The main cause behind this declaration focused on new types of gun, the introduction of steam propulsion and the use of iron and steel armour which made rating ships by the number of guns obsolete. Origins and description The first movement towards a rating system may be seen in the 15th century and the first half of the 16th century, when the largest carracks in the Navy (such as the ''Mary Rose'', the '' Peter Pomegranate'' and the ''Henri Grâce à Dieu'') were denoted "great ships". This was only on the basis of their roughly-esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Campbell (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral Sir Patrick Campbell, KCB (1773 – 13 October 1841) was a senior British Royal Navy officer of the early nineteenth century who was distinguished by his service in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. During his service in a number of ships in the Mediterranean and English Channel, Campbell saw several small ship actions and was successful in every one, even surviving a double shipwreck in 1805. Following the war, Campbell retired for ten years before returning to service, later commanding at the Cape of Good Hope. Naval career Campbell was born in 1773, the son of Colonel John and Colina Campbell of Melfort, Argyll. One of his younger brothers was to become the celebrated British Army general Sir Colin Campbell and another was General Frederick Campbell. Patrick Campbell went to sea at a young age and, following the outbreak of the French Revolutionary War, was promoted to lieutenant in 1794. In 1797, Campbell was again promoted, this time to comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square rig, square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part of the 19th century. In commercial use, they were gradually replaced by fore-and-aft rigged vessels such as schooners, as owners sought to reduce crew costs by having rigs that could be handled by fewer men. In Royal Navy use, brigs were retained for training use when the battle fleets consisted almost entirely of iron-hulled steamships. Brigs were prominent in the coasting coal trade of British waters. 4,395 voyages to London with coal were recorded in 1795. With an average of eight or nine trips per year for one vessel, that is a fleet of over 500 colliers trading to London alone. Other ports and coastal communities were also be served by colliers trading to Britain's coal ports. In the first half of the 19th century, the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Baker (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral Sir Thomas Baker KCB (1771 – 26 January 1845) was an officer of the Royal Navy, who saw service during the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He had obtained his own command during the French Revolutionary Wars and was to play a part in bringing about three of the battles of the Napoleonic Wars, the Battle of Copenhagen, the Battle of Trafalgar, and the Battle of Cape Ortegal. He only directly participated in the third, but his actions there, and the capture of the French frigate beforehand brought him honours and rewards. While towing the ''Didon'' to a British port, he and another vessel were sighted by the combined Franco-Spanish fleet under Pierre-Charles Villeneuve, and mistaken as scouts for the Channel Fleet. He therefore turned south to Cadiz, leading to the abandonment of the planned invasion of England, and the destruction of the French fleet at Trafalgar by Horatio Nelson some months later. He rose throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Nemesis (1780)
HMS ''Nemesis'' was a 28-gun ''Enterprise''-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. The French captured her in 1795 at Smyrna, but in 1796 a squadron led by brought her out of the neutral port of Tunis. Throughout her career she served under a number of commanders who would go on to have distinguished careers. She was converted to a troopship in 1812 and was sold in 1814. British service ''Nemesis'' was first commissioned in January 1780 under the command of Captain Richard Rodney Bligh. ''Nemesis'' was in company with on 3 January 1781 when they captured the Dutch vessel ''Catherine''. Then she captured the French privateer ''Alliance'' on 5 June. She was paid off from wartime service in 1784. Lastly, ''Nemesis'' was among the vessels sharing in the proceeds of the capture on 30 March 1783 of the Dutch ship ''Arendt op Zee''. She was paid off in May 1784 after wartime service. Between December 1787 and November 1789 ''Nemesis'' was at Deptford undergoing a major repair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Andromeda (1784)
HMS ''Andromeda'' was a 32-gun ''Hermione''-class fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was laid down in 1781 and launched in 1784 . She was commissioned for the first time in 1788 when Captain Prince William Henry took command of her and sailed for the West Indies. Prince William Henry paid her off in 1789 and she was not commissioned again until 1790 in response to the Spanish Armament. In 1792 ''Andromeda'' joined the Royal Navy's Evolution Squadron in the English Channel before sailing for the Leeward Islands where she stayed until the end of 1793 when Captain Lord Northesk brought her home. She was refitted for much of 1794 before in September joining the Downs Station. Captain William Taylor assumed command in 1795, briefly sailing her to Newfoundland before returning to the North Sea Fleet in 1796. She stayed here for 3 years, seizing the 36-gun Batavian frigate ''Zefir'' in the Firth of Forth in March 1798 and participating in the Raid on Dunkirk in July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboats
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to shore bombardment, bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for troopship, ferrying troops or auxiliary ship, supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannons, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Incorruptible (1795)
''Incorruptible'' was a 40-gun of the French Navy. On 15 July 1796, under captain Bescond, she fought against the 56-gun . In 1800, she was involved in the battle of Dunkirk. In January 1805, she was sent to observe British movements off Toulon, along with . On 4 February, they attacked a convoy, destroying 7 ships. Three days later, they encountered the convoy escorted by the 20-gun sloop and the 8-gun bomb vessel ; the frigates destroyed two Royal Navy vessels, and captured and burnt and two other merchant vessels of the convoy. In May 1807, ''Incorruptible'', ''Annibal'', , and the corvette A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the slo ... ''Victorieuse'' engaged off Cabrera in the Mediterranean. References * External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Incorruptible Age of Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)