|
RNA World
The RNA world is a hypothetical stage in the evolutionary history of life on Earth in which self-replicating RNA molecules proliferated before the evolution of DNA and proteins. The term also refers to the hypothesis that posits the existence of this stage. Alexander Rich first proposed the concept of the RNA world in 1962, and Walter Gilbert coined the term in 1986. Alternative chemical paths to life have been proposed, and RNA-based life may not have been the first life to exist. Even so, the RNA world hypothesis seems to be the most favored abiogenesis paradigm, but even proponents agree it still has not reached conclusive evidence to completely falsify other paradigms and hypotheses. The concurrent formation of all four RNA building blocks further strengthened the hypothesis. Regardless of its plausibility in a prebiotic scenario, the RNA world can serve as a model system for studying the origin of life. Like DNA, RNA can store and replicate genetic information. Like p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
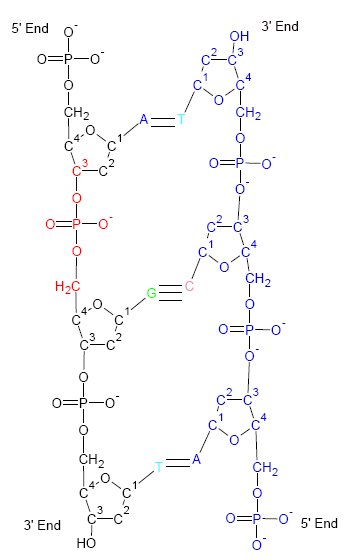
Difference DNA RNA-EN
Difference, The Difference, Differences or Differently may refer to: Music * ''Difference'' (album), by Dreamtale, 2005 * ''Differently'' (album), by Cassie Davis, 2009 ** "Differently" (song), by Cassie Davis, 2009 * ''The Difference'' (album), Pendleton, 2008 * "The Difference" (The Wallflowers song), 1997 * "The Difference", a song by Westlife from the 2009 album ''Where We Are'' * "The Difference", a song by Nick Jonas from the 2016 album ''Last Year Was Complicated'' * "The Difference", a song by Meek Mill featuring Quavo, from the 2016 mixtape '' DC4'' * "The Difference", a song by Matchbox Twenty from the 2002 album '' More Than You Think You Are'' * "The Difference", a 2020 song by Flume featuring Toro y Moi * "The Difference", a 2022 song by Ni/Co which represented Alabama in the ''American Song Contest'' * "Differences" (song), by Ginuwine, 2001 Science and mathematics * Difference (mathematics), the result of a subtraction * Difference equation, a type of recur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The cofactor is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction, also with H+, forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Orgel
Leslie Eleazer Orgel FRS (12 January 1927 – 27 October 2007) was a British chemist. He is known for his theories on the origin of life. Biography Leslie Orgel was born in London, England, on . He received his Bachelor of Arts degree in chemistry with first-class honours from the University of Oxford in 1948. In 1951 he was elected a Fellow of Magdalen College, Oxford and in 1953 was awarded his PhD in chemistry. Orgel started his career as a theoretical inorganic chemist and continued his studies in this field at Oxford, the California Institute of Technology and the University of Chicago. Together with Sydney Brenner, Jack Dunitz, Dorothy Hodgkin, and Beryl M. Oughton he was one of the first people in April 1953 to see the model of the structure of DNA, constructed by Francis Crick and James Watson, at the time he and the other scientists were working at Oxford University's Chemistry Department. According to the late Dr. Beryl Oughton, later Rimmer, they all travelled toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term " central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to proteins, it cannot flow back to nucleic acids. In other words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Szent-Györgyi
Albert Imre Szent-Györgyi de Nagyrápolt ( hu, nagyrápolti Szent-Györgyi Albert Imre; September 16, 1893 – October 22, 1986) was a Hungarian biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1937. He is credited with first isolating vitamin C and discovering the components and reactions of the citric acid cycle. He was also active in the Hungarian Resistance during World War II, and entered Hungarian politics after the war. Early life Szent-Györgyi was born in Budapest, Kingdom of Hungary in 1893. His father, Miklós Szent-Györgyi, was a landowner, born in Marosvásárhely, Transylvania (today Târgu Mureş, Romania), a Calvinist, and could trace his ancestry back to 1608 when Sámuel, a Calvinist predicant, was ennobled. At the time of Szent-Györgyi's birth, being of the nobility was considered important and created opportunities that otherwise were not available. (Miklós Szent-Györgyi's parents were Imre Szent-Györgyi and Mária Csiky). His mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abiogenesis
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single event, but an evolutionary process of increasing complexity that involved the formation of a habitable planet, the prebiotic synthesis of organic molecules, molecular self-replication, self-assembly, autocatalysis, and the emergence of cell membranes. Many proposals have been made for different stages of the process. The study of abiogenesis aims to determine how pre-life chemical reactions gave rise to life under conditions strikingly different from those on Earth today. It primarily uses tools from biology and chemistry, with more recent approaches attempting a synthesis of many sciences. Life functions through the specialized chemistry of carbon and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be divided into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Note that some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomers
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Monomers can be classified in many ways. They can be subdivided into two broad classes, depending on the kind of the polymer that they form. Monomers that participate in condensation polymerization have a different stoichiometry than monomers that participate in addition polymerization: : Other classifications include: *natural vs synthetic monomers, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively *polar vs nonpolar monomers, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively *cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two different monomers. In the case of condensation polymerizations, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biocatalysis
Biocatalysis refers to the use of living (biological) systems or their parts to speed up (catalyze) chemical reactions. In biocatalytic processes, natural catalysts, such as enzymes, perform chemical transformations on organic compounds. Both enzymes that have been more or less isolated and enzymes still residing inside living cells are employed for this task. Modern biotechnology, specifically directed evolution, has made the production of modified or non-natural enzymes possible. This has enabled the development of enzymes that can catalyze novel small molecule transformations that may be difficult or impossible using classical synthetic organic chemistry. Utilizing natural or modified enzymes to perform organic synthesis is termed chemoenzymatic synthesis; the reactions performed by the enzyme are classified as chemoenzymatic reactions. History Biocatalysis underpins some of the oldest chemical transformations known to humans, for brewing predates recorded history. The olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Storage
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, Phonograph record, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA and DNA are considered by some as data storage. Recording may be accomplished with virtually any form of energy. Electronic data storage requires electrical power to store and retrieve data. Data storage in a digital, machine-readable medium is sometimes called ''digital data''. Computer data storage is one of the core functions of a general-purpose computer. Electronic documents can be stored in much less space than paper documents. Barcodes and magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) are two ways of recording machine-readable data on paper. Recording media A recording medium is a physical material that holds information. Newly created information is distributed and can be stored in four storage media–print, film, magnetic, and opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNP World
The RNP world is a hypothesized intermediate period in the origin of life characterized by the existence of ribonucleoproteins. The period followed the hypothesized RNA world and ended with the formation of DNA and contemporary proteins. During this time, RNA molecules continued to perform many essential functions, but began to synthesize peptides, which eventually assumed most of the function of those RNA molecules (i.e. became ''proteins''), leading to life as we know it.{{Cite journal, last=Cech, first=Thomas R., date=2009-02-20, title=Crawling Out of the RNA World, journal=Cell, language=en, volume=136, issue=4, pages=599–602, doi=10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.002, pmid=19239881, s2cid=13933577, issn=0092-8674, doi-access=free Principle of concept Thomas Cech in 2009 proposed the existence of the RNP world after his observation of apparent differences in the composition of catalysts in the two most fundamental processes that maintain and express genetic systems. DNA replication a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins. Structures Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The tertiary structures and biological functions of many nucleoproteins are understood.Graeme K. Hunter G. K. (2000): Vital Forces. The discovery of the molecular basis of life. Academic Press, London 2000, . Important techniques for determining the structures of nucleoproteins include X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and cryo-electron microscopy. Viruses Virus genomes (either DNA or RNA) are extremely tightly packed into the viral capsid. Many viruses are therefore little more than an organised collection of nucleoproteins with their binding sites pointing inwards. Structurally characterised viral nucleoproteins include influenza, rabies, Ebola, Bunyamwera, Schma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |